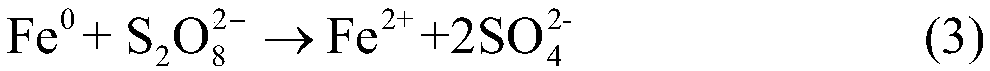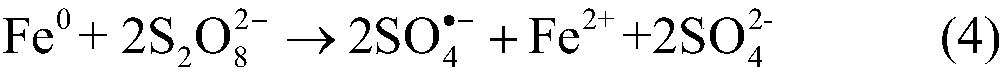Medicament for in-situ repair of high-concentration polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon polluted soil and application thereof
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, in-situ remediation technology, applied in the field of soil pollution remediation, can solve the problems of difficult to popularize results and large differences in reactivity, and achieve the effects of high utilization rate, environmental disturbance, and technical environmental friendliness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Under laboratory test conditions, the effect of the amount of micro-nano iron flakes on the degradation efficiency of PAHs in soil catalyzed by persulfate degradation was investigated.
[0028]Taking the soil of the actual PAHs polluted site as the research object, in the heterogeneous reaction of sodium persulfate (PS) catalytic activation using micro-nano iron sheets, a 250mL brown serum bottle with a polytetrafluoroethylene stopper was used as the reactor, and 100g was weighed The soil and 100mL of reaction solution were added, the initial concentration of persulfate was 30g / kg (126mM), and the initial dosage of micro-nano iron flakes were 0.35 (6.3mM), 0.70 (12.6mM), 1.4 (25.2mM) , 3.5 (63mM) and 7.0g / kg (126mM), the molar ratios of micro-nanometer iron flakes and sodium persulfate were 1:20, 1:10, 1:5, 1:2 and 1:1, PAHs in polluted soil The concentration of the solution is 201.1 mg / kg, the water-soil ratio is 1:1, and the reaction bottle is placed in a vibrating be...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Taking the actual PAHs-contaminated site soil as the research object, the effect of sodium persulfate dosage on the removal efficiency of PAHs was studied.
[0038] In the heterogeneous reaction of sodium persulfate (PS) catalyzed by micro-nano iron sheets, a 250mL brown serum bottle with a polytetrafluoroethylene plug was used as the reactor, and 100g of soil was weighed and 100mL of the reaction solution was added. The initial dosage of iron sheet is 3.5g / kg (63mM), the initial concentration of sodium persulfate is 7.5 (31.5), 15 (63mM), 30 (126mM), 60g / kg (252mM), sodium persulfate and micro The molar ratios of the nano-iron flakes are 1:2, 1:1, 2:1 and 4:1 respectively, the concentration of PAHs in the polluted soil is 201.1mg / kg, and the ratio of water to soil is 1:1. The rotational speed is 150 rpm and the temperature is 25°C.
[0039] In the experiment of adding 3.5g / kg micro-nano iron flakes alone, there is no need to add sodium persulfate, and other conditions...
Embodiment 3
[0046] On the basis of the optimal dosage of sodium persulfate and micro-nanometer iron flakes screened in the laboratory test (embodiment 1 and embodiment 2) are respectively 30 and 3.5g / kg (molar ratio is 2:1), carried out Pilot demonstration project.
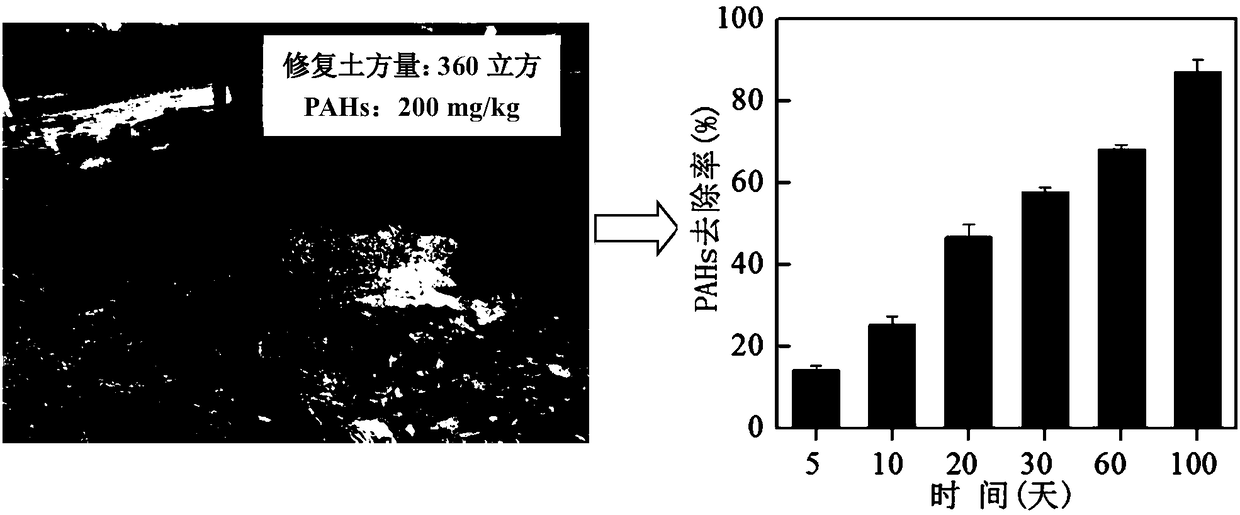
[0047] Select a PAHs-contaminated site, the concentration of total PAHs is 201.1mg / kg, the area of the pilot test is 90 square meters, the depth of pollution is 4 meters deep, and the total earth volume is 360 cubic meters. The specific site steps are as follows: on the basis of the previous land leveling, first build the in-situ reaction pool through earthwork construction work, then backfill the polluted soil, first add sodium persulfate agent and stir evenly, then add micro-nano iron flake suspension and stir Evenly, the sodium persulfate consumption is 54kg / cubic soil (30 * 1.8=54; 1 cubic soil = 1.8 tons of soil), and the consumption of micronano iron sheet is 6.3kg / cubic soil (3.5 * 1.8=6.3), naturally react under ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com