A method for improving the fermentative production of glucaric acid by Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strains
A technology of glucaric acid and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., and can solve problems such as easy loss, unstable expression of plasmids, and unsuitability for industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
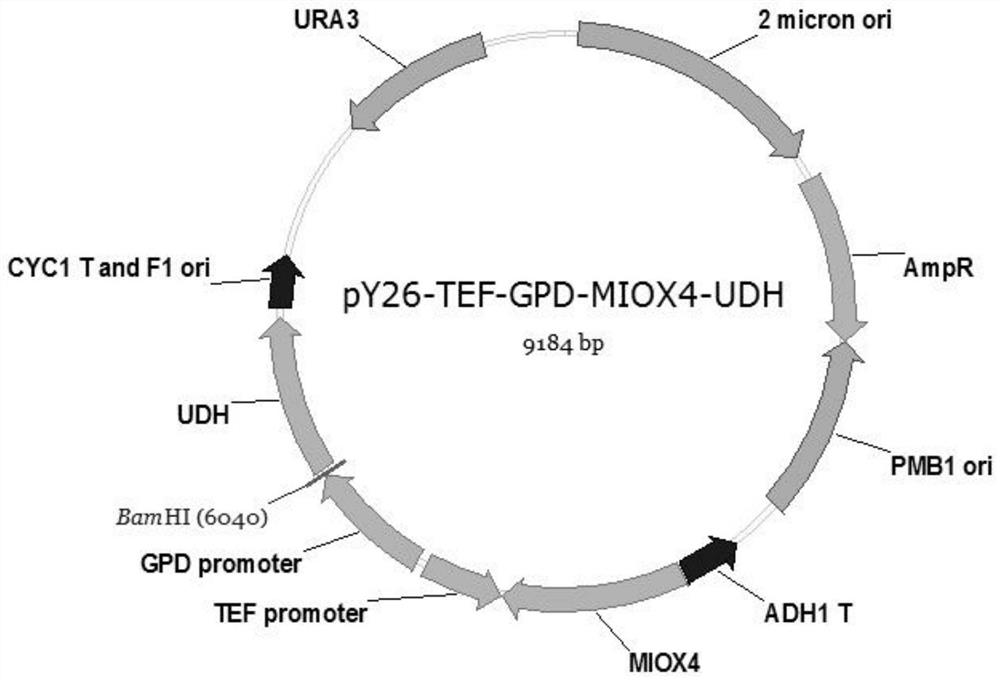
[0042] Example 1 Construction of plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4-UDH
[0043] Using PUC57-MIOX4-UDH as template, using pY26-MIOX4F / pY26-MIOX4R and pY26-UDHF / pY26-UDHR as primers to amplify MIOX4 and UDH genes. The MIOX4 recovered product and plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD were digested with BglII / NotI, respectively, to obtain pY26-MIOX4 plasmid, which was purified and recovered by T4 ligase overnight to construct plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4. The pY26-MIOX4-UDH will be constructed using Gibson Assembly assembly, and then the plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-UDH plasmid will be digested with EcoRI, and the pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4-UDH plasmid will be constructed using Gibson Assembly assembly, and the primers will be verified as veri- pYF and veri-pYR. After colony PCR verification, the plasmid construction was successful.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Obtaining integration fragments DMH-001 and DUH-001 fragments.
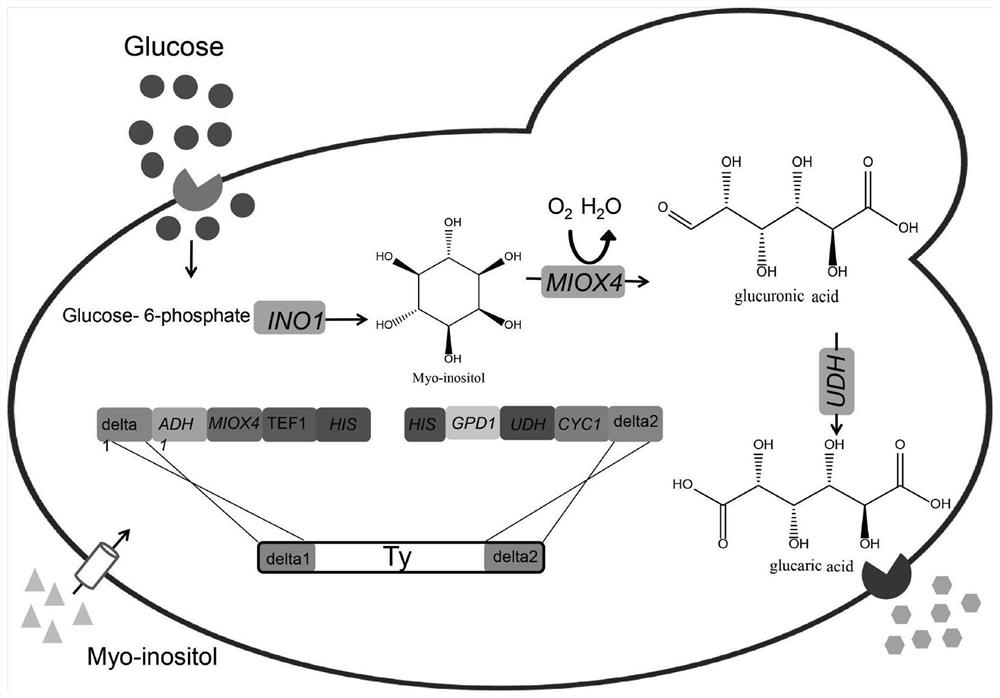
[0045] Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 genome as a template, Delta1F / Delta1R and Delta2F / Delta2R were used as primers to amplify the Delta1 and Delta2 fragments; the plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4-UDH (constructed by our laboratory, the nucleotide sequence is as SEQ ID NO.1) is the template, U-GPDF / U-GPDR and M-TEFF / M-TEFR are primers to amplify the fragment U-TEF (including promoter GPD, gene UDH, terminator CYC1) and M- TEF (including promoter TEF, gene MIOX4, terminator ADH1); using plasmid pRS313 (preserved in this experiment, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2) as a template, primers His1F / His1F and His2F / His2R were expanded Add fragments His1 and His2. The three fragments of Delta1, M-TEF, His1 were subjected to landing PCR, and the PCR product was used as a template, and Delta1F / His1R was used as primers to amplify DMH-001. Perform landing PCR on His2, U-GPD, and Delta2,...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Obtaining of high-yield gluconic acid integrated strain Bga-001
[0047] The two integrated fragments DMH-001 and DUH-001 were transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741ΔOPI (preserved by our laboratory) by the lithium acetate transformation method, coated with SD-His-deficient medium, and the transformants were picked after 2-3 days. In order to integrate the successful recombinant bacteria, the positive transformants were inserted into 10ml YPD liquid medium as seeds, cultured overnight, and transferred to 50ml YPD (60mM inositol added to the medium) liquid medium with 2% inoculum, 30℃, 250rpm shaking Bed culture for 7 days. Sampling was taken every 12h, centrifuged at 13000rpm for 5min to take the supernatant, filtered with 0.22μm filter membrane. The output of glucaric acid was detected by Hitachi High Performance Liquid Chromatograph, differential detector, column temperature 30°C, and injection volume 30ul. From this, a strain with high glucaric aci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com