Gene sequencing substrate, preparation method thereof and gene sequencing device
A gene sequencing and substrate technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, optomechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of high production costs, reduce production costs, fast detection response, and facilitate high-throughput testing Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
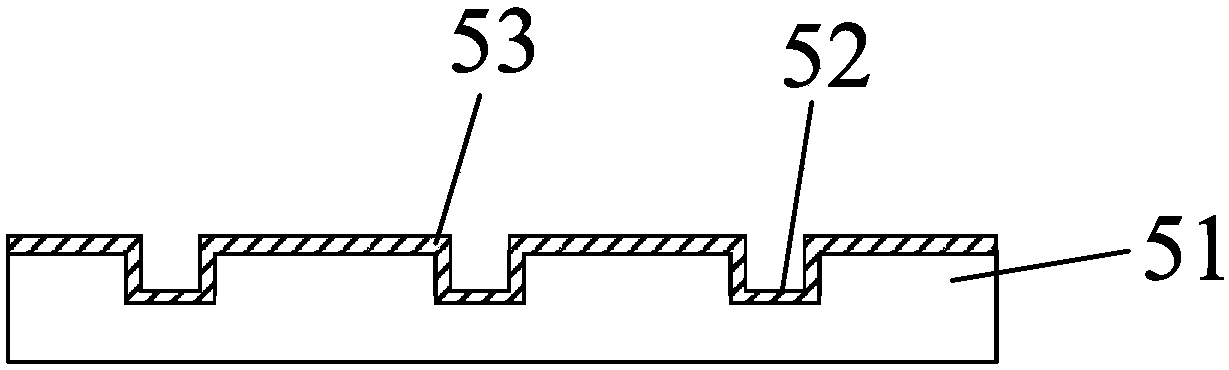
[0031] This embodiment provides a gene sequencing substrate, such as figure 2 As shown, a substrate 51 formed of plastic material is included, and a concave structure 52 is provided on one side of the substrate 51, and the concave structure 52 is a reaction pool for gene sequencing; on the inner wall of the concave structure 52 A first protective layer 53 is provided.
[0032] The gene sequencing substrate of this embodiment uses a plastic material as a substrate 51, and a concave structure 52 is formed on the plastic surface as a reaction pool (also called a nanowell). Among them, the plastic material refers to the material that is not destroyed even though it undergoes significant deformation under the action of external force. Since the substrate 51 has plasticity, a simple process can be used to form the concave structure 52, which reduces the production cost of the gene sequencing substrate. At the same time, the function of adding the first protective layer 53 on the ...
Embodiment 2
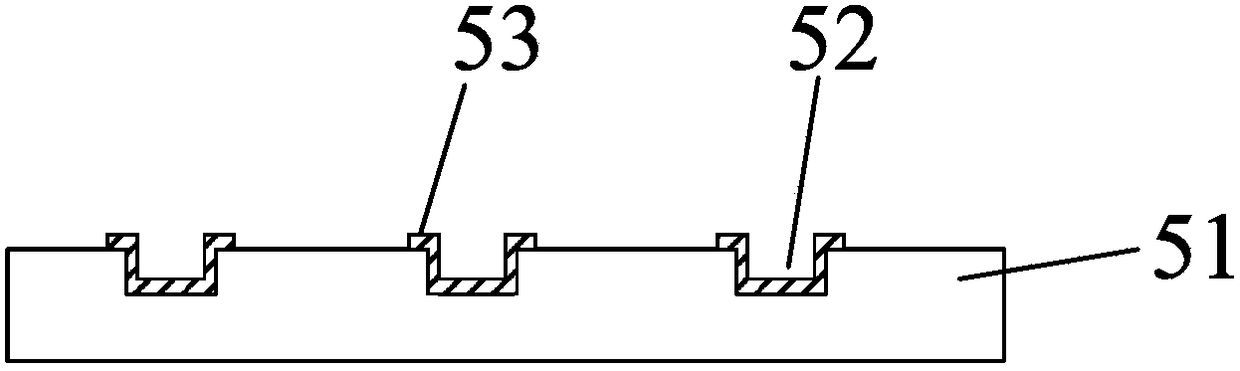
[0034] This embodiment provides a gene sequencing substrate, such as image 3 , Figure 4 As shown, a substrate 51 formed of plastic material is included, and a concave structure 52 is provided on one side of the substrate 51, and the concave structure 52 is a reaction pool for gene sequencing; on the inner wall of the concave structure 52 A first protective layer 53 is provided. Wherein, the first protective layer 53 can be as figure 2 Shown is the full protective layer, which can also be shown as image 3 As shown in the section of , it is only provided at the position for contacting with the reaction liquid to save material.
[0035] As an optional implementation in this embodiment, the plastic material includes polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET ) in any one or several.
[0036] That is to say, unlike the rigid glass substrate 51 in the prior art, a plastic polymer material is selected as the substrate 51 in t...
Embodiment 3
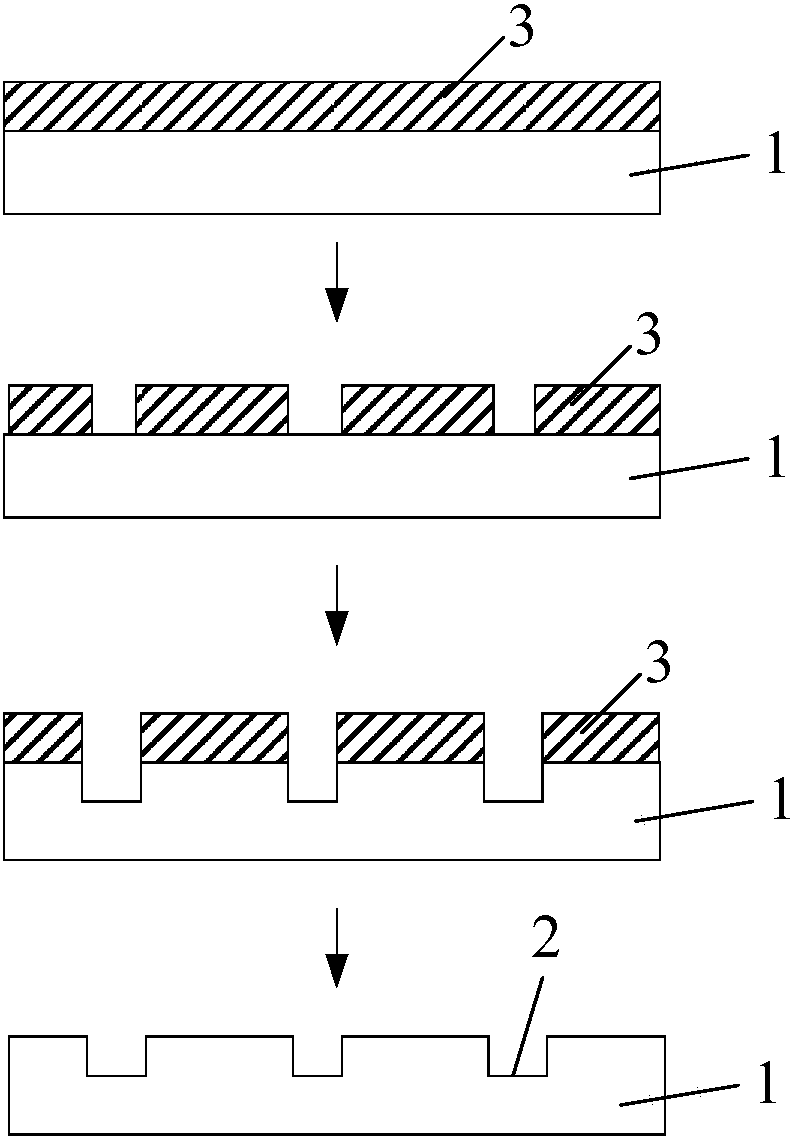
[0044] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a gene sequencing substrate, such as Figure 7 As shown, the following preparation steps are included:
[0045] S01, heating the plastic material to soften the plastic material; wherein, the actual heating temperature in this step can refer to the glass transition temperature of the material. The plastic material is selected from any one or more of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The effect of the heating in this step is to soften the plastic material so as to deform its surface to form the concave structure 52 . The specific heating temperature can be changed according to the selection of different materials.
[0046] S02, using a nanoimprint process to directly form a concave structure 52 on one side of the plastic material, and the concave structure 52 is a reaction pool for gene sequencing;
[0047]Nano-imprinting is to use a rigid stamper with nano-p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com