Transverse flux reluctance type low-speed large-torque direct drive synchronous motor
A transverse magnetic flux, synchronous motor technology, applied in synchronous machines, synchronous motors for single-phase current, magnetic circuit rotating parts, etc. Accurate spatial positioning and phase setting, simplified process flow, high mechanical strength effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
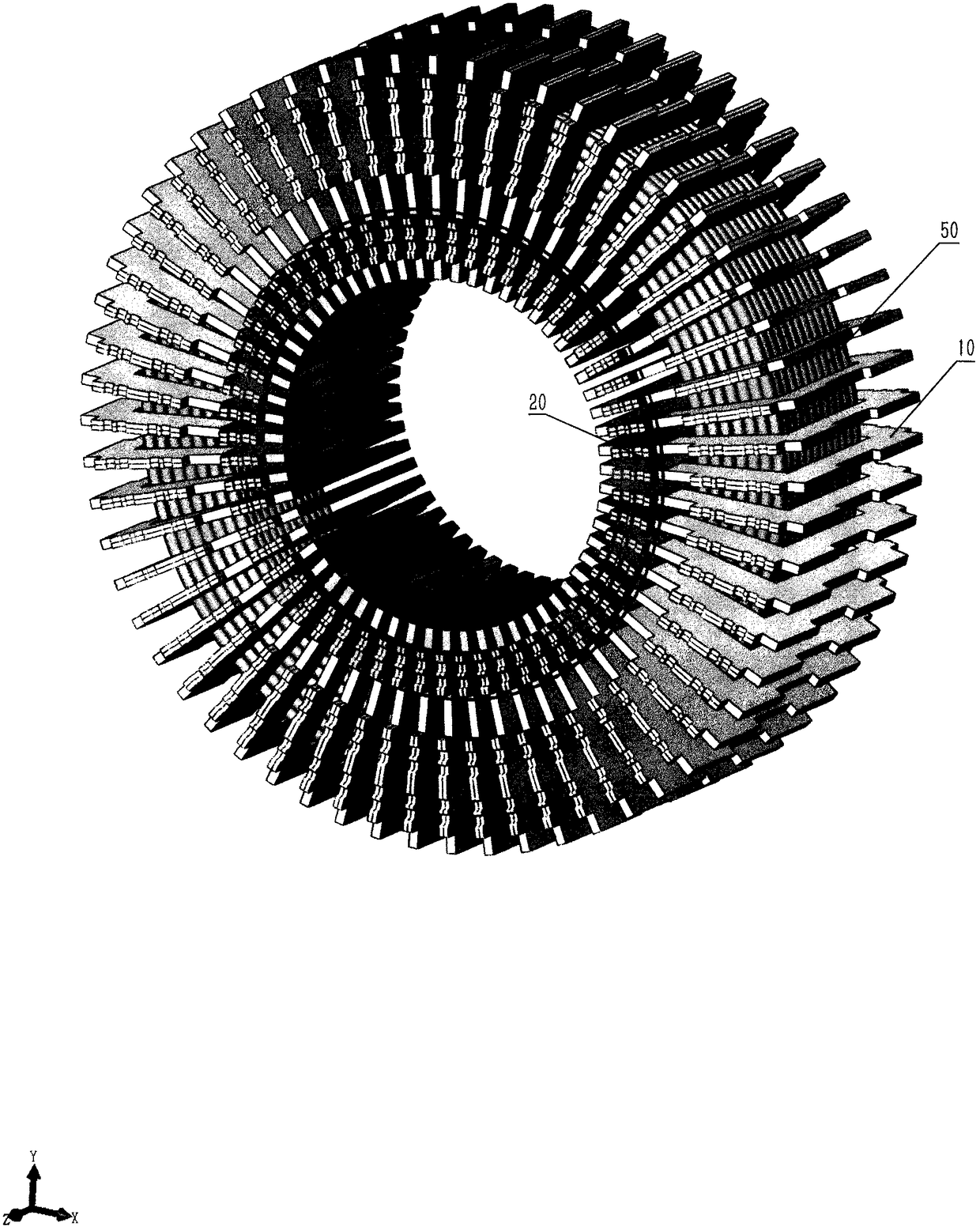
[0052] In the transverse flux reluctance type low-speed high-torque direct drive synchronous motor of the present invention, the main purpose of mechanical manufacturing and structure is to wind each phase winding on the stator base, and install the discrete phase stators and rotor cores on the stator and on the rotor base. Hereinafter, specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0053] The primary task of implementing the present invention is to manufacture the stator iron core and the rotor iron core, and the manufacturing steps are as follows:
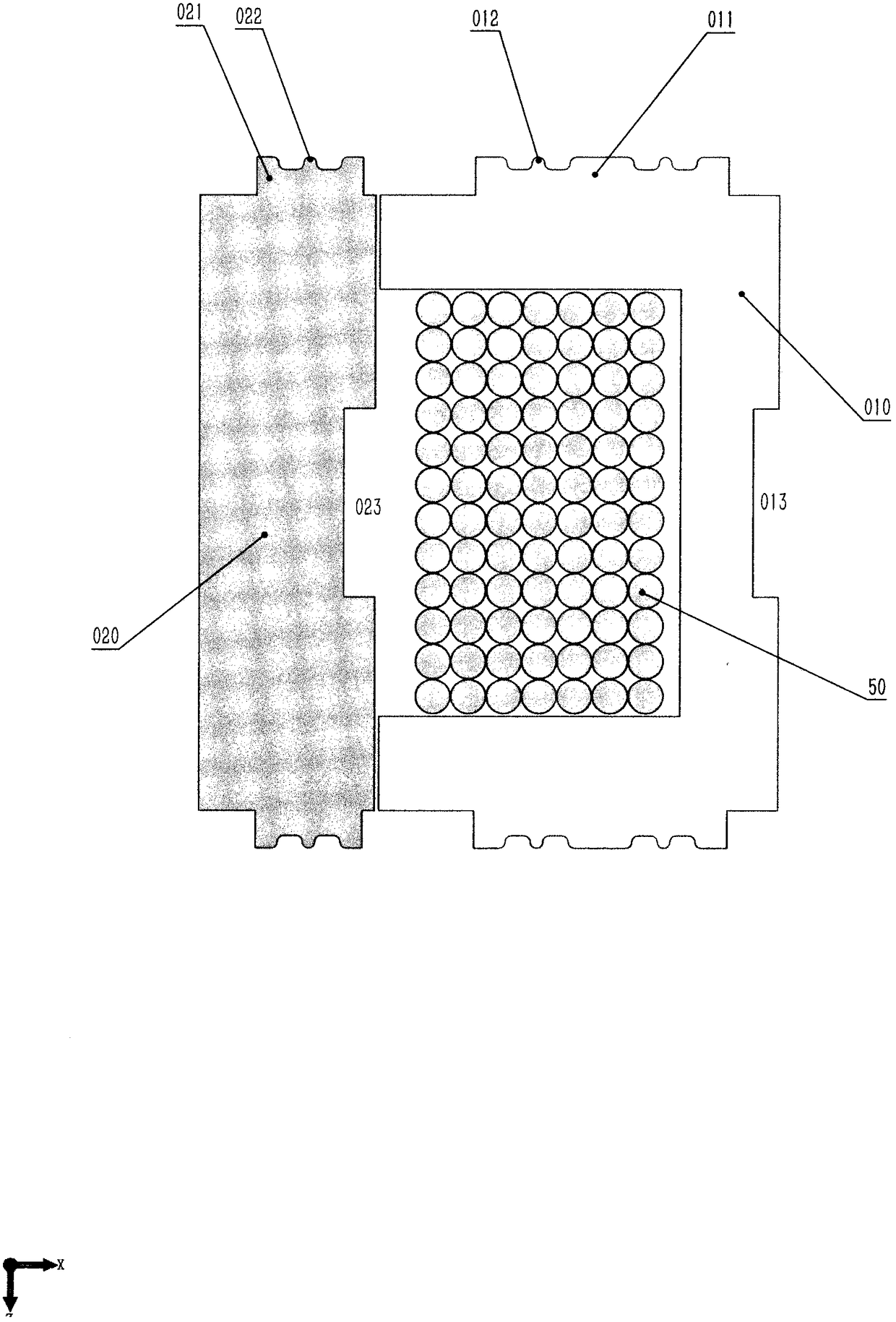
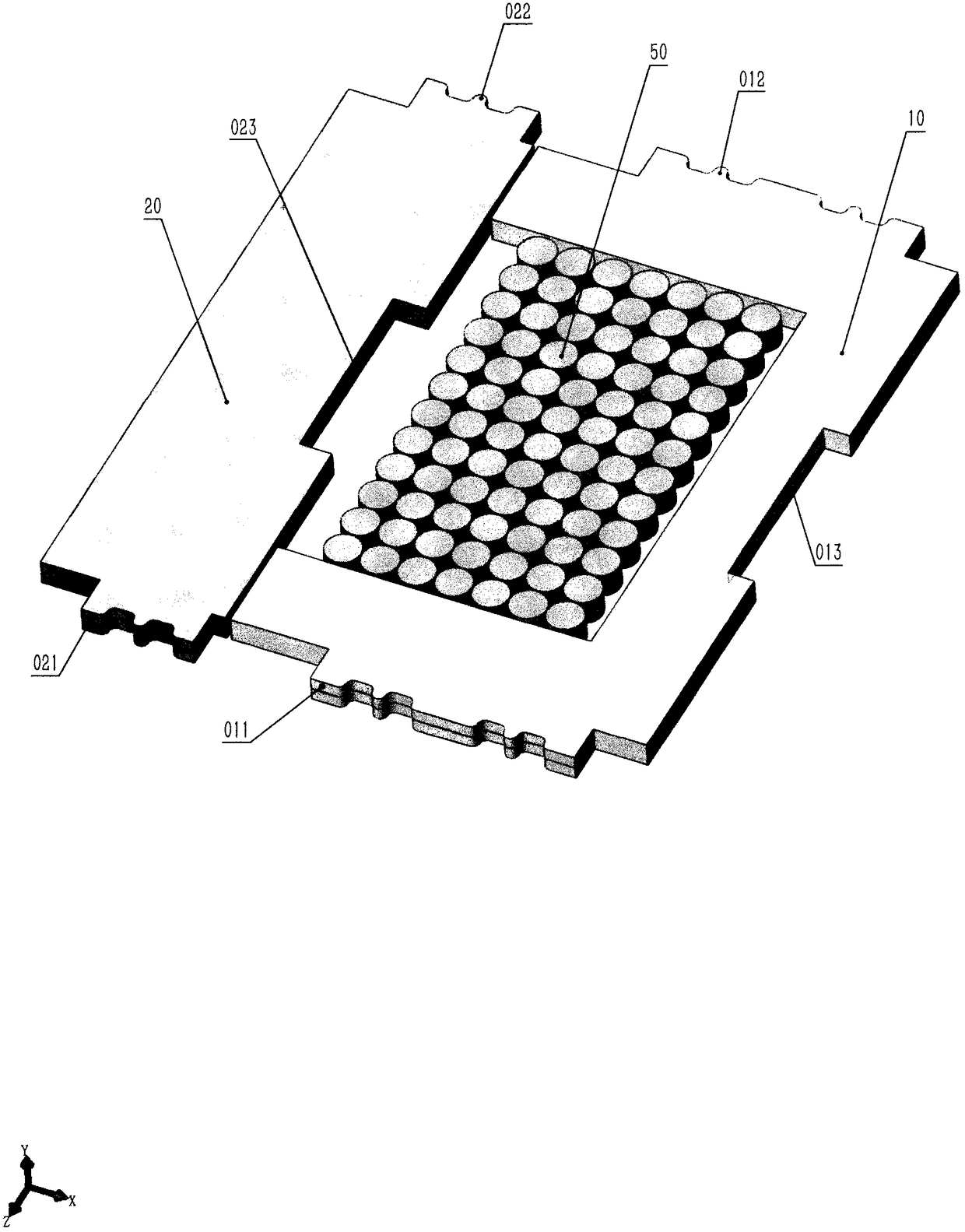
[0054] (1) Stator and rotor core punching sheets are made by punching silicon steel sheets. For the pattern of stator core punch 010 and rotor core punch 020, see figure 1 , the basic figure of the stator core punching sheet 010 is "U" shape, there are rectangular protrusions 011 on both sides of the stator core punching sheet 010, and its outer edge is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com