Polyurethane composite polyether, polyurethane rigid foam and preparation method of polyurethane rigid foam
A technology of combining polyether and rigid foam, applied in the field of polyurethane materials, can solve the problems of low smoke density, high compressive strength to density ratio, reduce foam mechanical properties, etc., achieve flame retardancy and smoke suppression performance improvement, high compressive strength Effect of Density Ratio, Specific Extinction Area Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] A preparation method of rigid polyurethane foam, comprising the steps of:
[0036] A. Preparation of polyurethane combination polyether: Add melamine polyol, phosphorus-containing polyester diol, smoke suppressing flame retardant, foam stabilizer, chemical foaming agent and catalyst into the reaction kettle, pre-stir, and then add physical foaming agent Foaming agent, after stirring again, polyurethane combination polyether is obtained;
[0037] B. Preparation of polyurethane rigid foam: Mix component B and polyurethane combined polyether uniformly, and form it to obtain polyurethane rigid foam.
[0038] Further, the pre-stirring temperature in step A is 20-25°C, the pre-stirring time is 10 minutes, and the re-stirring time is 0.5h-1h; the molding operation in step B uses a high-pressure foaming agent machine to mix and foam Double track continuous molding.
[0039] Concrete preparation method is as follows:
[0040] Proceed as follows:
[0041] (1) Mix 30-70 parts of...
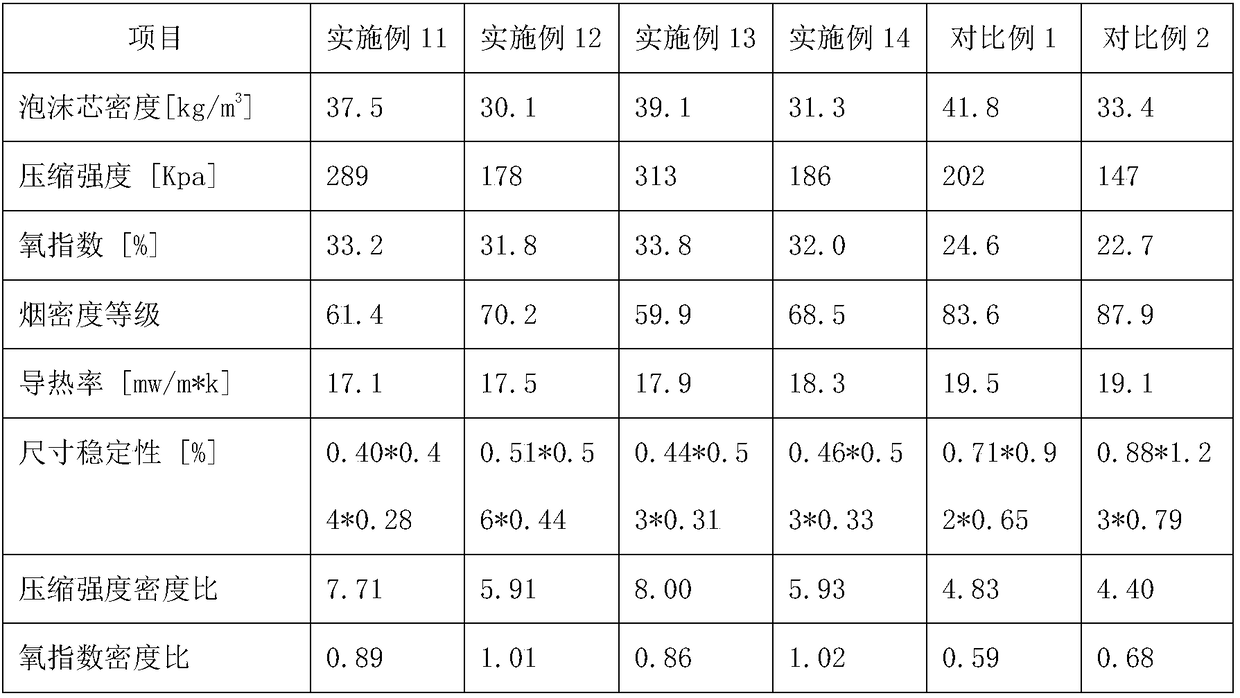
Embodiment 1
[0053] A polyurethane combined polyether, comprising component A; said component A comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30 parts of melamine polyol, 30 parts of phosphorus-containing polyester diol, 10 parts of smoke suppressing flame retardant , 10 parts of physical foaming agent, 1 part of foam stabilizer, 1 part of chemical foaming agent and 2 parts of catalyst;
[0054] Melamine polyol is a polyol similar to multi-melamine as the initiator, the hydroxyl value is 210±10mgKOH / g, the viscosity is 6000±1000mPa·s / 25℃, and the acid value is ≤1.0mgKOH / g;
[0055] The phosphorus-containing polyester diol is a phosphorus-containing aromatic diol, and the phosphorus-containing aromatic diol has a hydroxyl value of 190-200mgKOH / g, a viscosity of 2000-3500MPa·s / 25°C, and an acid value≤1mgKOH / g;
[0056] Described smoke suppression flame retardant is FR808, and FR808 is the commercially available product of Qingdao Lianmei Chemical Co., Ltd.;
[0057] The physical ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A polyurethane combination polyether, including component A; said component A includes the following components in parts by weight: 70 parts of melamine polyol, 70 parts of phosphorus-containing polyester diol, 20 parts of smoke suppressing flame retardant , 20 parts of physical foaming agent, 3 parts of foam stabilizer, 2 parts of chemical foaming agent and 5 parts of catalyst;
[0063] Melamine polyol is a polyol similar to multi-melamine as the initiator, the hydroxyl value is 210±10mgKOH / g, the viscosity is 6000±1000mPa·s / 25℃, and the acid value is ≤1.0mgKOH / g;
[0064] The phosphorus-containing polyester diol is a phosphorus-containing aromatic diol, and the phosphorus-containing aromatic diol has a hydroxyl value of 190-200mgKOH / g, a viscosity of 2000-3500MPa·s / 25°C, and an acid value≤1mgKOH / g;
[0065] Described smoke suppression flame retardant is FR808, and FR808 is the commercially available product of Qingdao Lianmei Chemical Co., Ltd.;
[0066] The physic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com