Lithium ion battery gradient anode material and preparation method thereof
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and positive electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as poor material stability, crystal structure defects, and material failure, and achieve enhanced stability, enhanced rate performance, intercalation/ The effect of unimpeded exit channel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A Ti gradient doped multi-element positive electrode material, the initial ratio of metal ions in the material is Ni:Co:Mn =0.80:0.10:0.10, and the change rule of the doping element D from the particle center to the particle surface is 0~0.02. The average particle size of the positive electrode material is about 12.0 μm, and the tap density is about 2.6 g / cm 3 .
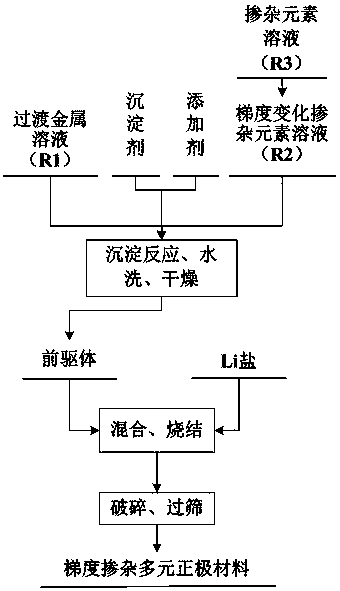
[0050] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0051] Prepare a 1.5 mol / L mixed solution with a molar ratio of nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese sulfate of 0.80:0.10:0.10 and record it as solution (1) and put it into sub-tank R1. Prepare the solution containing titanium sol stabilizer as solution (2) and put it into sub-tank R2, and then prepare the 2mol / L solution of titanium sol as solution (3) and put it into sub-tank R3. Add the solution in the sub-tank of R3 into R2 with stirring at a flow rate of 0.1 L / h to obtain a dopant element solution (4) with a continuously increasing concentr...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A Ti gradient doped multi-component positive electrode material, the initial metal ion ratio in the material is Ni:Co:Mn =0.60:0.20:0.20, and the change rule of the doping element D from the particle center to the particle surface is 0~0.03. The average particle size of the positive electrode material is about 16.0 μm, and the tap density is about 2.9 g / cm 3 .
[0055] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0056] Prepare a 1.5 mol / L mixed solution with a molar ratio of nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese sulfate of 0.60:0.20:0.20 and record it as solution (1) and put it into sub-tank R1. Prepare the solution containing titanium sol stabilizer as solution (2) and put it into sub-tank R2, and then prepare the 2mol / L solution of titanium sol as solution (3) and put it into sub-tank R3. Add the solution in the sub-tank of R3 into R2 with stirring at a flow rate of 0.1 L / h to obtain a dopant element solution (4) with a continuously increasing concentrat...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A Ti gradient doped multi-component positive electrode material, the initial metal ion ratio in the material is Ni:Co:Mn =0.50:0.20:0.30, and the change rule of the doping element D from the particle core to the surface is 0~0.04. The average particle size of the gradient material is about 6.3 μm, and the tap density is about 2.1 g / cm 3 .
[0060] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0061] Prepare a 1.5 mol / L mixed solution with a molar ratio of nickel sulfate, cobalt sulfate and manganese sulfate of 0.50:0.20:0.30 and record it as solution (1) and put it into sub-tank R1. Prepare the solution containing titanium sol stabilizer as solution (2) and put it into sub-tank R2, and then prepare the 2mol / L solution of titanium sol as solution (3) and put it into sub-tank R3. Add the solution in the sub-tank of R3 into R2 with stirring at a flow rate of 0.1 L / h to obtain a dopant element solution (4) with a continuously increasing concentration. Then metal salt ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com