An ultra-lightweight two-way authentication method for mobile RFID systems
A two-way authentication, lightweight technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of non-reusable, low efficiency, short service life, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
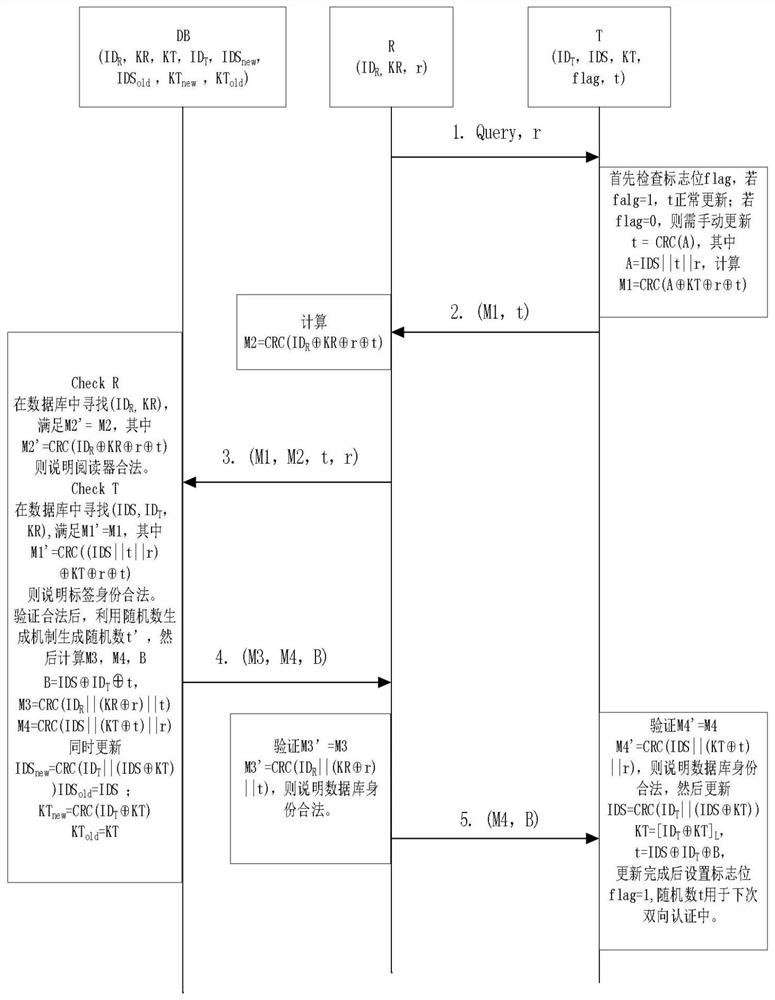
[0041] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the implementation manners.
[0042] Step 1: The reader generates a random number r, then sends a Query request to the tag, and sends the random number to the tag.
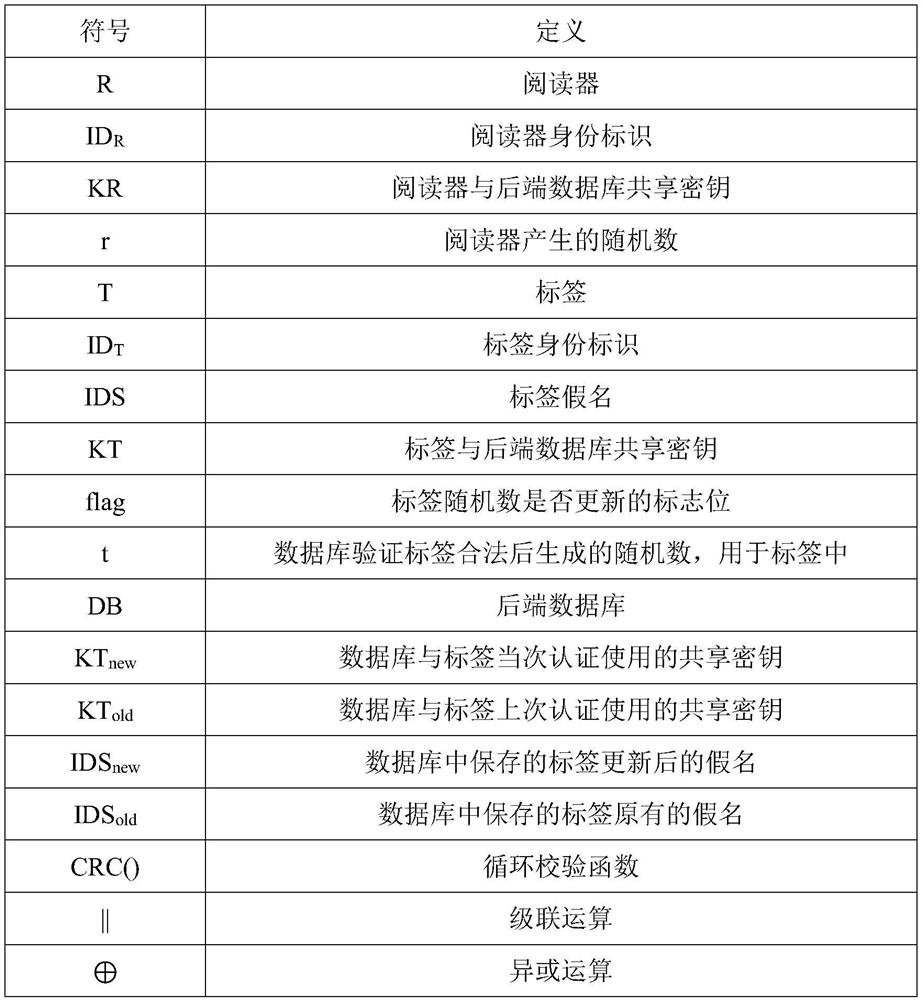
[0043] Step 2: After receiving the request initiated by the reader, the tag first judges the value of the random number flag bit to determine whether the random number is legally updated. If flag=1, it means that the last random number update was successful, then t will be used as a normal random number and set flag to 0; if flag=0, it means that there was an exception in the last authentication, and the CRC() algorithm in the tag is used at this time Update the random number, that is, t=CRC(A), where A=IDS||t||r, and use it as the random number this time. After the random number update is completed, the flag is still set to 0. Then calculate M1=CRC(A ⊕KT⊕r⊕t), and send the message (M1, t) to the reader.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com