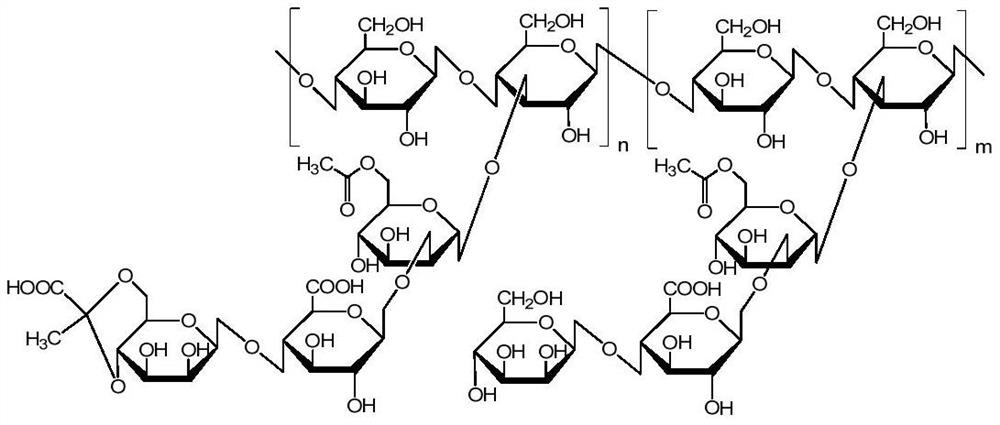
oral care composition
A technology for oral care and composition, which is applied in the field of oral care compositions and can solve the problems of high delivery of gain agents and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
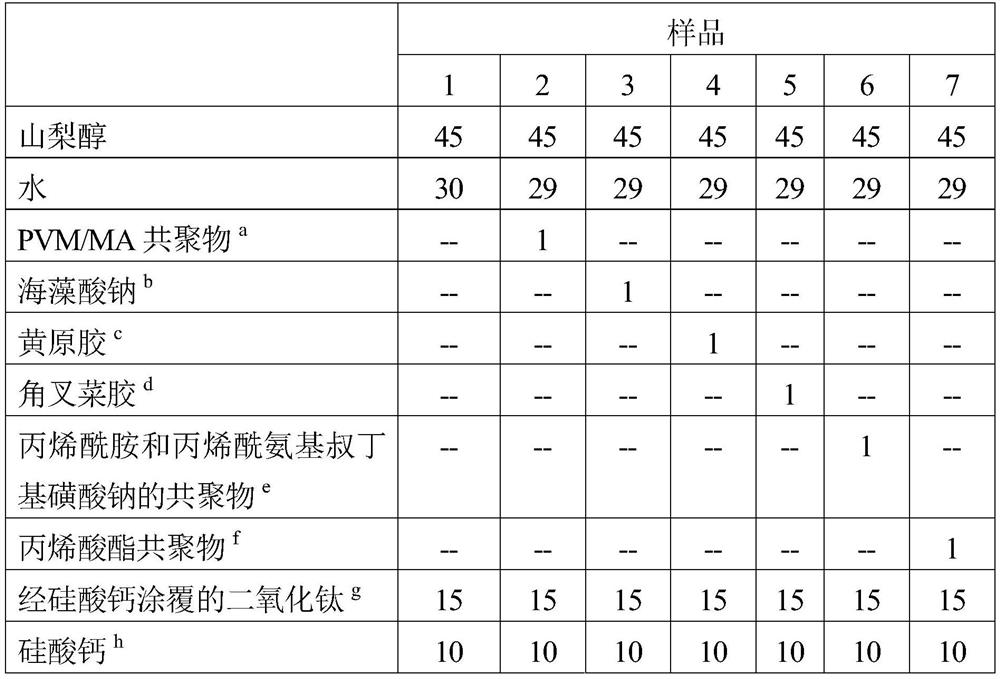
[0126] This example demonstrates improved deposition of particles on tooth surfaces by using calcium silicate in combination with xanthan gum. All ingredients are expressed as percentages by weight of the total formulation and expressed as active ingredient levels.
[0127] Table 1
[0128]
[0129] a. by trade name S-97BF is a commercially available PVM / MA copolymer from Ashland
[0130] b. Commercially available sodium alginate from Sinopharm Group Co.Ltd
[0131] c. by trade name Xanthan Gum Commercially available xanthan gum from CP Kelco
[0132] d. by trade name Carrageenan CL110 Commercially available carrageenan from Danisco
[0133] e. Commercially available copolymer of acrylamide and sodium acrylamido tert-butyl sulfonate available from SNF under the tradename Flopaam AN125
[0134] f. Under the trade name EPITEX TM 66 commercially available acrylate copolymers from Dow Chemical Company
[0135] g. Commercially available calcium silicate coated tit...
Embodiment 2
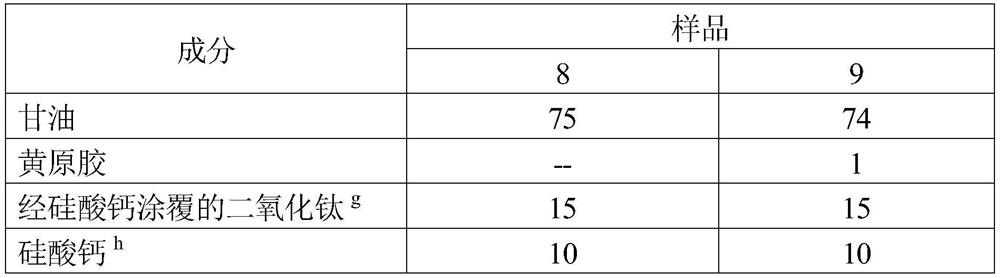
[0154] This example demonstrates the effect of particle concentration on particle deposition efficiency. All ingredients are expressed as weight percent of the total formulation and expressed as active ingredient content.
[0155] Table 6
[0156]
[0157] method
[0158] As described in Example 1, the same protocol was used to evaluate the deposition of particles on tooth surfaces.
[0159] result
[0160] Results after one and three treatment cycles are summarized in Table 7 (errors represent standard errors of repeated measures).
[0161] Table 7
[0162]
[0163] After one cycle of treatment, with TiO containing 0.5% 2 The HAP disks treated with Sample 10 show almost no titanium deposition, while those treated with samples containing more than 5% TiO 2 The HAP disks treated with Samples 13 and 14 exhibited much higher Ti deposition. Furthermore, Sample 15 containing composite particles exhibited better particle deposition than those containing uncoated TiO...
Embodiment 3
[0165] This example demonstrates the effect of xanthan gum concentration on particle deposition efficiency. All ingredients are expressed as weight percent of the total formulation and expressed as active ingredient content.
[0166] Table 8
[0167]
[0168] method
[0169] As described in Example 1, the same protocol was used to evaluate the deposition of particles on tooth surfaces.
[0170] result
[0171] The results after one processing cycle are summarized in Table 9 (errors represent the standard error of repeated measures).
[0172] Table 9
[0173]
[0174] From the XRF results, it can be seen that the concentration of xanthan gum is important for particle deposition efficiency. Sample 16 without xanthan gum was used as a control. Samples 17 to 19 containing 0.3% or less of xanthan gum showed comparable titanium deposition to sample 16, indicating that small amounts of xanthan gum did not contribute to particle deposition. Compared to Sample 16, Samp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com