Acid gas treatment agent and acid gas treatment method
An acid gas and treatment agent technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal carbonates to prevent moisture absorption, etc. Increased pressure loss, high processing efficiency, and easy peeling effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~5
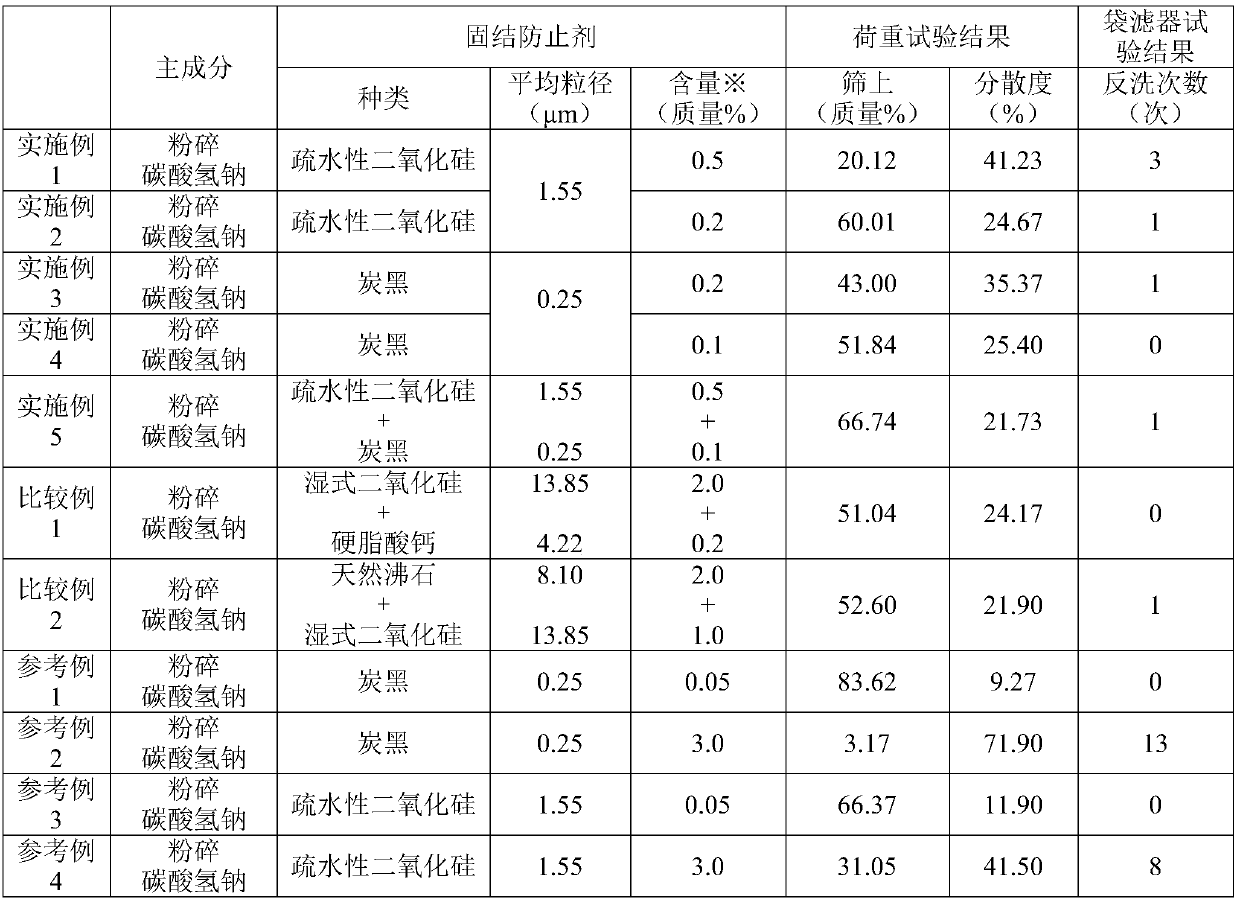
[0069] [Examples 1 to 5, Comparative Examples 1 and 2, Reference Examples 1 to 4]
[0070] The acid gas treating agent was prepared by blending the chemicals shown in Table 1. For each acid gas treatment agent, the following load test and bag filter test were performed. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0071]
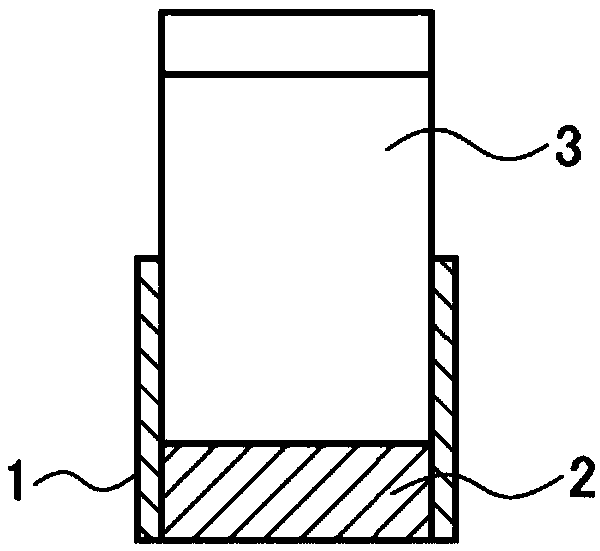
[0072] use figure 1 With the load test apparatus shown, fixability was evaluated by the following method.
[0073] 100 g of acid gas treating agent 2 was filled in frame-shaped box 1 of 100 mm×100 mm, and load 3 of 10 kg was applied for 3 hours. Afterwards, the acid gas treatment agent was placed on a stainless steel sieve with a mesh size of 355 μm, the fine powder was partially dropped, and the mass of the coarse particles remaining on the sieve was measured, and the ratio (mass %) relative to the mass for the test was calculated. ). The smaller the ratio on the sieve, the more the caking can be prevented, and the more the fine powder part falls.
[0074] D...
Embodiment 2
[0094] In Example 2, by making the blending ratio of the anti-caking agent lower than in Example 1, the anti-caking effect and pressure loss equivalent to those in the comparative example were obtained. The advantage is that the blending ratio of the anti-caking agent is lower than that of the comparative example, and the blending ratio of the pulverized sodium bicarbonate component of the acid gas treatment component is increased.
[0095] In Example 3 and Example 4, it was confirmed in the load test that the anti-coagulation effect was superior to that of the comparative example, and the pressure loss of the bag filter was equivalent to that of the comparative example. The advantage is that the blending ratio of the anti-caking agent is smaller than that of the comparative example, and the blending ratio of the pulverized sodium bicarbonate, which is an acid gas treatment component, is increased.
Embodiment 5
[0096] Example 5 is a result of using two kinds of anti-caking agents, and exhibited the same anti-caking effect and pressure loss as those of the comparative example. The advantage is that the blending ratio of the anti-caking agent is smaller than that of the comparative example, and the blending ratio of the pulverized sodium bicarbonate, which is an acid gas treatment component, is increased.
[0097] For reference examples 1 and 3, the blending amount of carbon black or hydrophobic silica is small, and the anti-consolidation effect is poor, but the pressure loss is small.
[0098] For reference examples 2 and 4, the blending amount of carbon black or hydrophobic silica is large, and the anti-caking effect is extremely high, but the pressure loss is large.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com