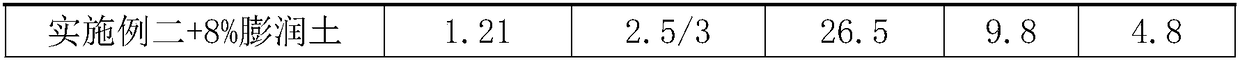Compound drilling fluid applied to stratums with natural gas hydrates in seafloor
A drilling fluid and hydrate technology, which is applied to drilling compositions, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of reduced fracture pressure, damage of temperature and pressure conditions, easy collapse and fracturing of the well wall, and achieves the formation of hydrates. Inhibition effect increases, reduces and prevents repeated crushing, avoids the effect of serious enlargement of pore size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1, the content of each component in the drilling fluid is: polyethylene glycol mass ratio is 5%, sodium chloride mass ratio is 14%, ethylene glycol mass ratio is 14%, low viscosity carboxymethyl cellulose LV- The mass ratio of CMC is 1.8%, the mass ratio of potassium polyacrylate is 1.8%, the mass ratio of xanthan gum is 0.4%, the mass ratio of polyvinyl caprolactam is 0.8%, the mass ratio of propylene glycol phenyl ether is 0.8%, and the tetra-n-butyl ammonium phosphate The mass ratio is 0.8%, and the remaining components are water for preparation.
Embodiment 2
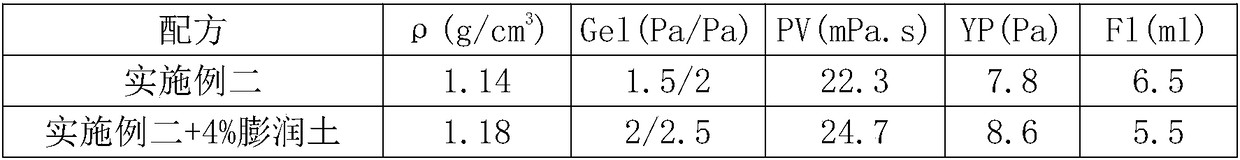
[0035] Embodiment two, the contents of each component in the drilling fluid are: polyethylene glycol mass ratio is 6%, sodium chloride mass ratio is 15%, ethylene glycol mass ratio is 15%, low viscosity carboxymethyl cellulose LV- The mass ratio of CMC is 2%, the mass ratio of potassium polyacrylate is 2%, the mass ratio of xanthan gum is 0.5%, the mass ratio of polyvinyl caprolactam is 1%, the mass ratio of propylene glycol phenyl ether is 1%, tetra-n-butyl ammonium phosphate The mass ratio is 1%, and the remaining components are water for preparation.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment three, the contents of each component in the drilling fluid are: polyethylene glycol mass ratio is 7%, sodium chloride mass ratio is 16%, ethylene glycol mass ratio is 16%, low viscosity carboxymethyl cellulose LV- The mass ratio of CMC is 2.2%, the mass ratio of potassium polyacrylate is 2.2%, the mass ratio of xanthan gum is 0.6%, the mass ratio of polyvinyl caprolactam is 1.2%, the mass ratio of propylene glycol phenyl ether is 1.2%, and the tetra-n-butyl ammonium phosphate The mass ratio is 1.2%, and the rest is water for preparation.
[0037] The drilling fluid configuration methods of the above-mentioned examples 1, 2, and 3 are conventional drilling fluid configuration methods, and are evaluated by the following experimental methods:
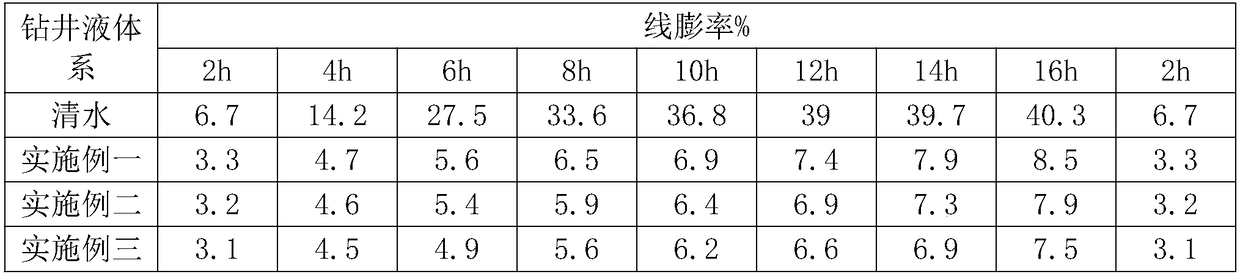
[0038] 1 Evaluation of drilling fluid shale hydration inhibition
[0039] Inhibition evaluation experiment is an important part of the indoor evaluation of drilling fluid related performance. The present invention adopt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com