Self-luminous tobacco and genetic modification method
A luminescent gene, self-luminous technology, applied in horticultural methods, genetic engineering, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of inconspicuous plant luminescence, lack of luminous tobacco, low transformation rate, etc., to achieve safe plant growth, The effect of constant luminous intensity for easy observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Using Nicotiana benthamiana (diploid) as the recipient, the LUX gene was transferred into its chloroplast to develop self-luminous tobacco
[0046] Step (1) Search and obtain the LUX gene sequence on NCBI, and synthesize the LUX gene in the carrier p-GH-LUX in Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. The nucleotide sequence can be found in NCBI), design IN-fusion connection primers, and amplify by PCR to obtain the target band. The PCR primers are as follows:
[0047] primer-F: AGGGAGGGATCCATGGGAATACCAAAGGAGATTAC;
[0048] primer-R: TAATGTCTACTCTAGAAATATCCCTATAAATAGAAC;
[0049] When the luminescent gene LUX is subjected to PCR amplification, the PCR reaction system (25ul) is shown in Table 1.
[0050] Table 1
[0051]
[0052] The PCR reaction conditions are shown in Table 2.
[0053] Table 2
[0054]
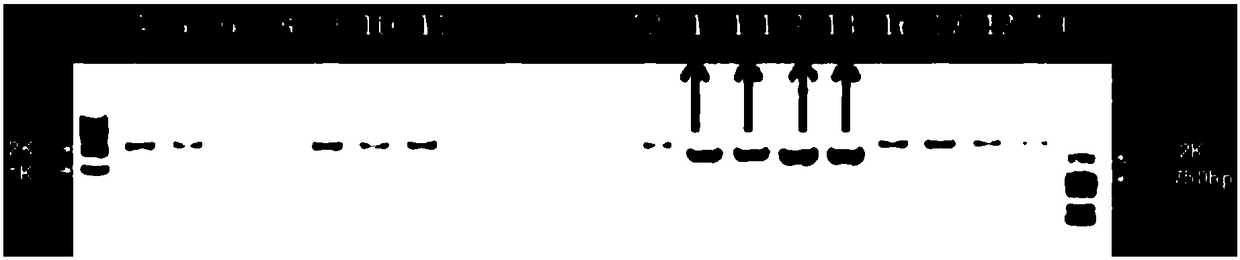
[0055] Perform gel electrophoresis after the PCR reaction results, and use 1.2% gel to recover the target fragment, such as figure 1 shown. figur...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Example 2 Using noble tobacco (tetraploid) as the recipient, the LUX gene was transferred into the air chloroplast genome to develop self-luminous tobacco
[0146] Step (1) The source and amplification system of the LUX gene are the same as in Example 1.
[0147] Step (2) The construction method of the p-LUX vector is the same as that in Example 1.
[0148] Step (3) import the p-LUX carrier into tobacco by means of "gene gun bombardment": the hyperosmotic medium and leaf hyperosmotic treatment methods are the same as in Example 1, and the sterilization treatment of gene gun accessories and the preparation of microcarriers are also the same as in Example 1 1. The only difference between the bombardment of leaves by the gene gun method and that of Example 1 is that the bombardment distance of Example 2 is only 6 cm, and the recovery medium formula and recovery culture method are the same as in Example 1.
[0149] The leaves after step (4) recovery culture are screened on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com