Method and kit for detecting pathogenic gene of fetal thalassemia
A technology for thalassemia and disease-causing genes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of false negative PCR and the inability to further determine the existence of maternal mutations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Construction of embodiment 1 haplotype (i.e. haploid genotype)
[0045] (1) Thalassemia primer and probe design
[0046] Design region for α-thalassemia (chr16:60022-2233661): downstream (10Kb) + HBA gene + upstream (10Kb), and design region for β-thalassemia (chr11:3236690-7177304): downstream (10Kb) + HBB gene + upstream (10Kp), and then use the dbSNP database to screen out 195 α-thalassemia SNP sites and 275 β-thalassemia SNP sites. Among them, the SNP site screening conditions: the SNP site has MAF>=20% at the same time in the Thousand Genomes Chinese Southerners and Northerners database; the 100bp sequence above and below the SNP site is a specific region and has no homology on the genome; and 45 %<GC<70% SNP sites do not have 3 consecutive identical bases. According to the SNP sites screened above, the amplification primer pair was designed through the Ampliseq Designer website (https: / / www.ampliseq.com / login / login.action), and the Agilent SureDesign website (ht...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3 maternal genetic situation analysis
[0073] Based on the analysis of paternal inheritance, the analysis of maternal inheritance was carried out. Select the locus (MN) whose genotype is homozygous father (MM) and heterozygous mother (MN), and determine whether the maternal pathogenic haplotype is inherited according to RHDO-SPRT, wherein the SPRT curve is calculated according to the following formula:
[0074]
[0075] in,
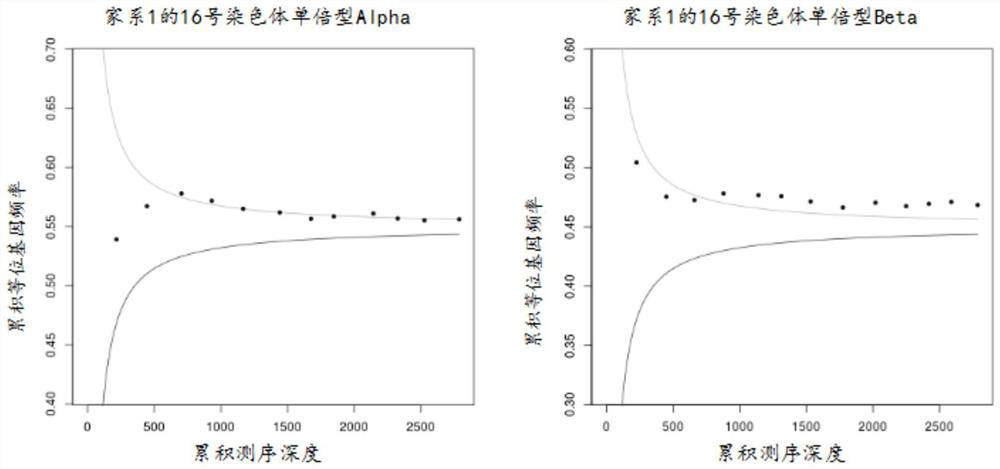
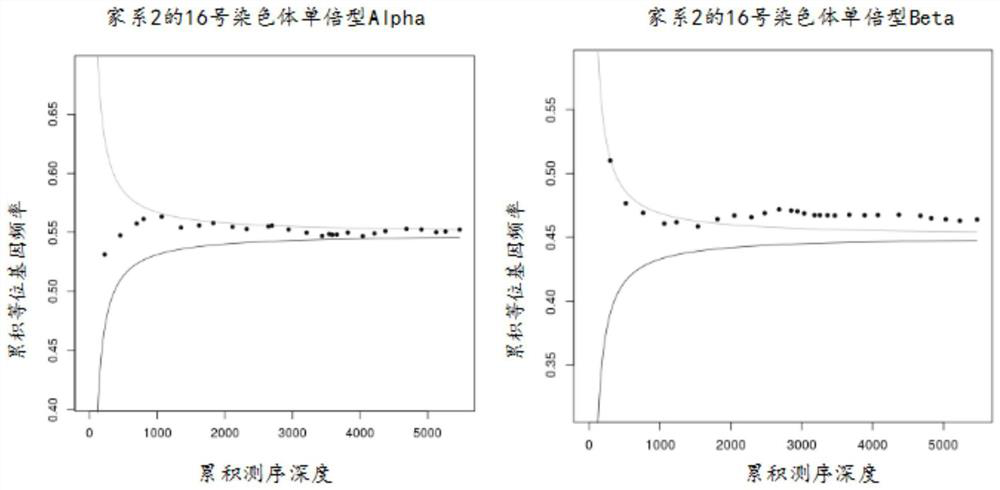
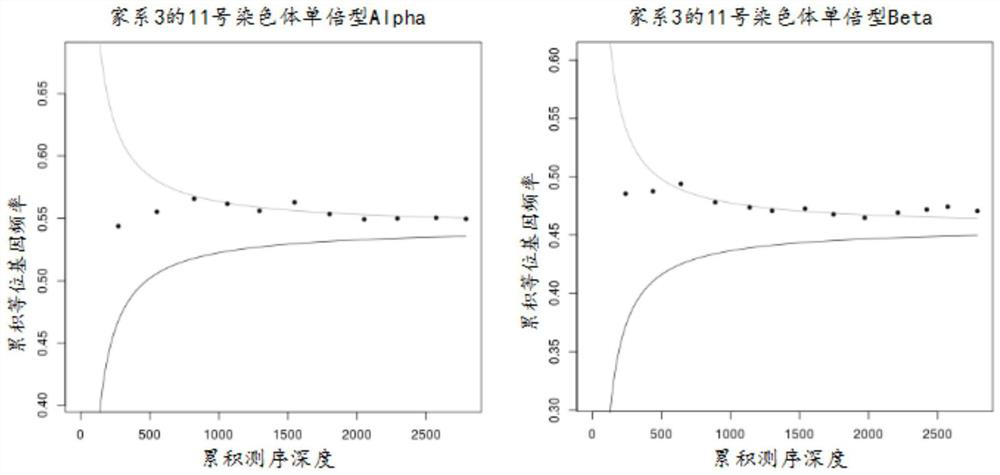
[0076] Upper boundary and Lower boundary refer to the upper bound and the lower bound respectively. In this detection method, the inventor defines haplotype 1 as the upper bound, and defines haplotype 2 as the lower bound. Use the SPRT algorithm to calculate the sum of the sum of the variation frequencies of the selected sites corresponding to the depth. If the screened loci are all between the upper and lower bounds, then it is impossible to tell which haplotype the fetus has inherited from the mother; if one or more of the acc...
Embodiment 4
[0078] Example 4 Test results of 5 thalassemia families
[0079] (1) Thalassemia test results
[0080] Families 1-5 were detected by the method of Example 2, and the haplotype construction results of families 1-5 are shown in Table 3-7. According to Mendel's law of inheritance, combined with family sample phenotype and known mutation type information, the pathogenic mutation is associated with the haplotype (for example: the father's genotype is MN, the mother's genotype is MN, and the child's genotype is NN (M is the disease-causing locus, N is the normal locus. M and N represent the bases A, T, C, G), and the child has inherited the father's haplotype 1 and the mother's haplotype 1 respectively, then The father's pathogenic locus M is on haplotype 2, and the mother's pathogenic locus M is on haplotype 2). Table 8 shows the results of the association of pathogenic loci in the father and mother of families 1-5 with haplotypes.
[0081] Table 3 Haplotype construction results...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com