Ginseng and American ginseng cis-hybridization and trans-hybridization F1-generation young embryo rescue method
A technology for American ginseng and embryo rescue, applied in the field of plant breeding, can solve problems that have not yet been seen, and achieve the effect of high regeneration frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
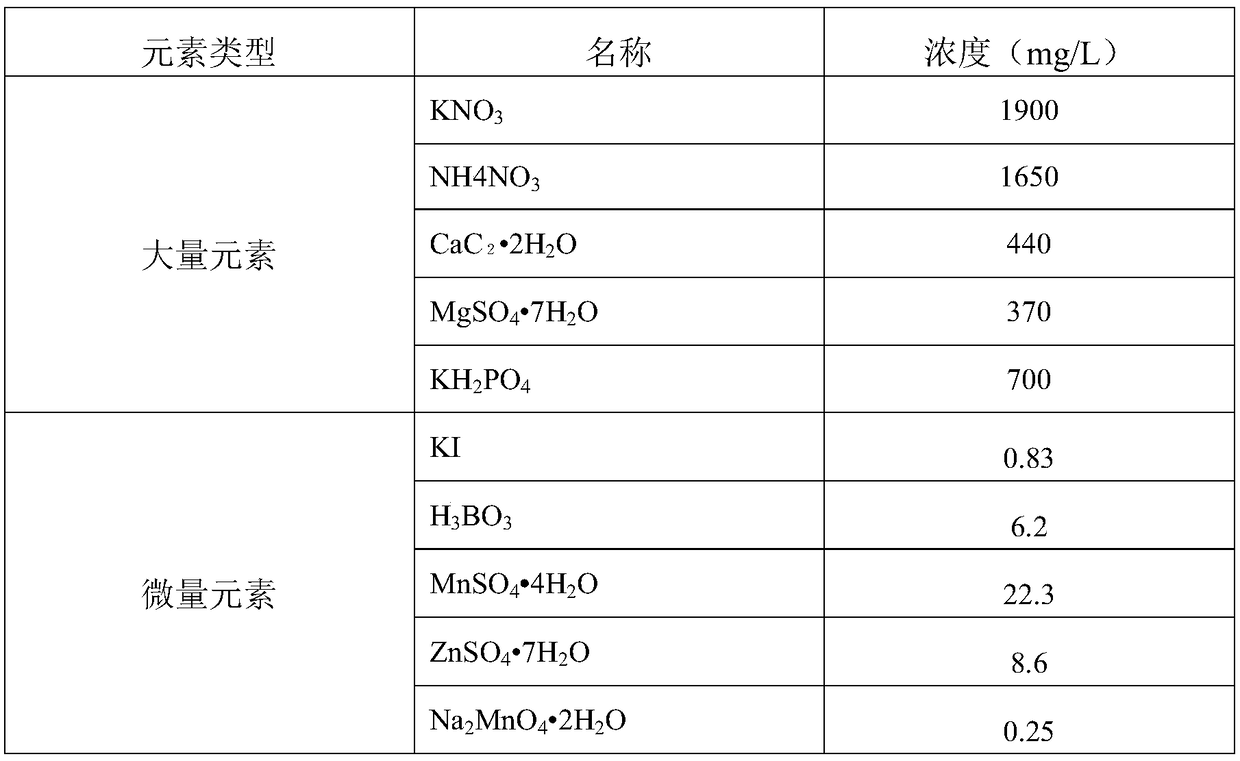
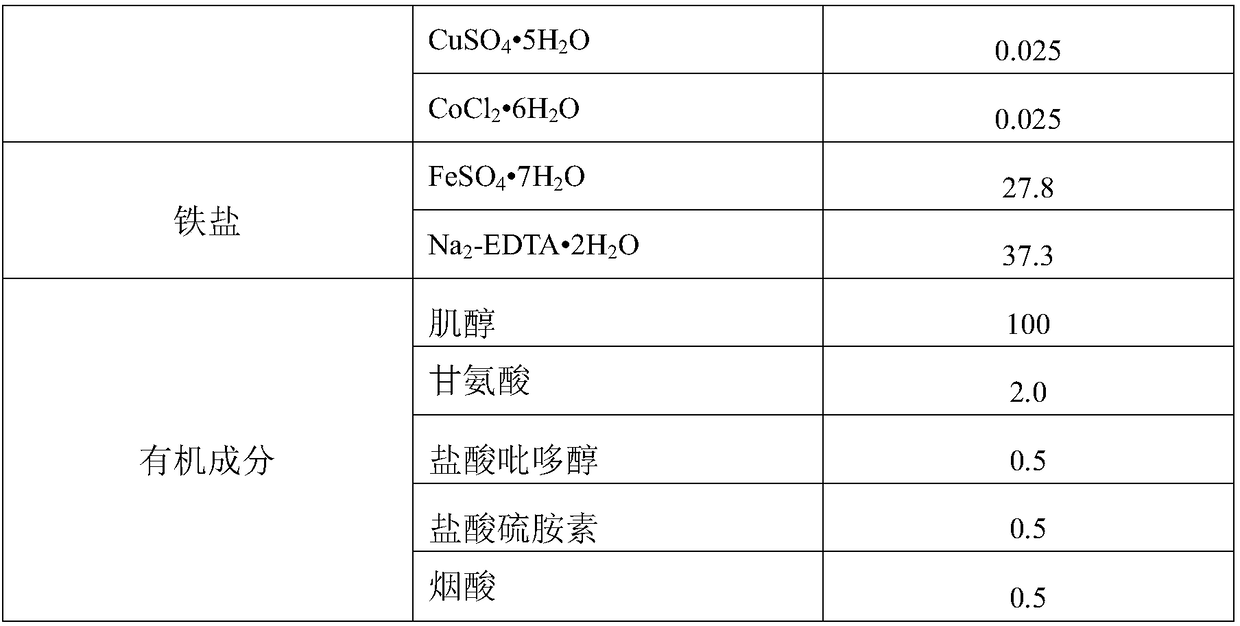
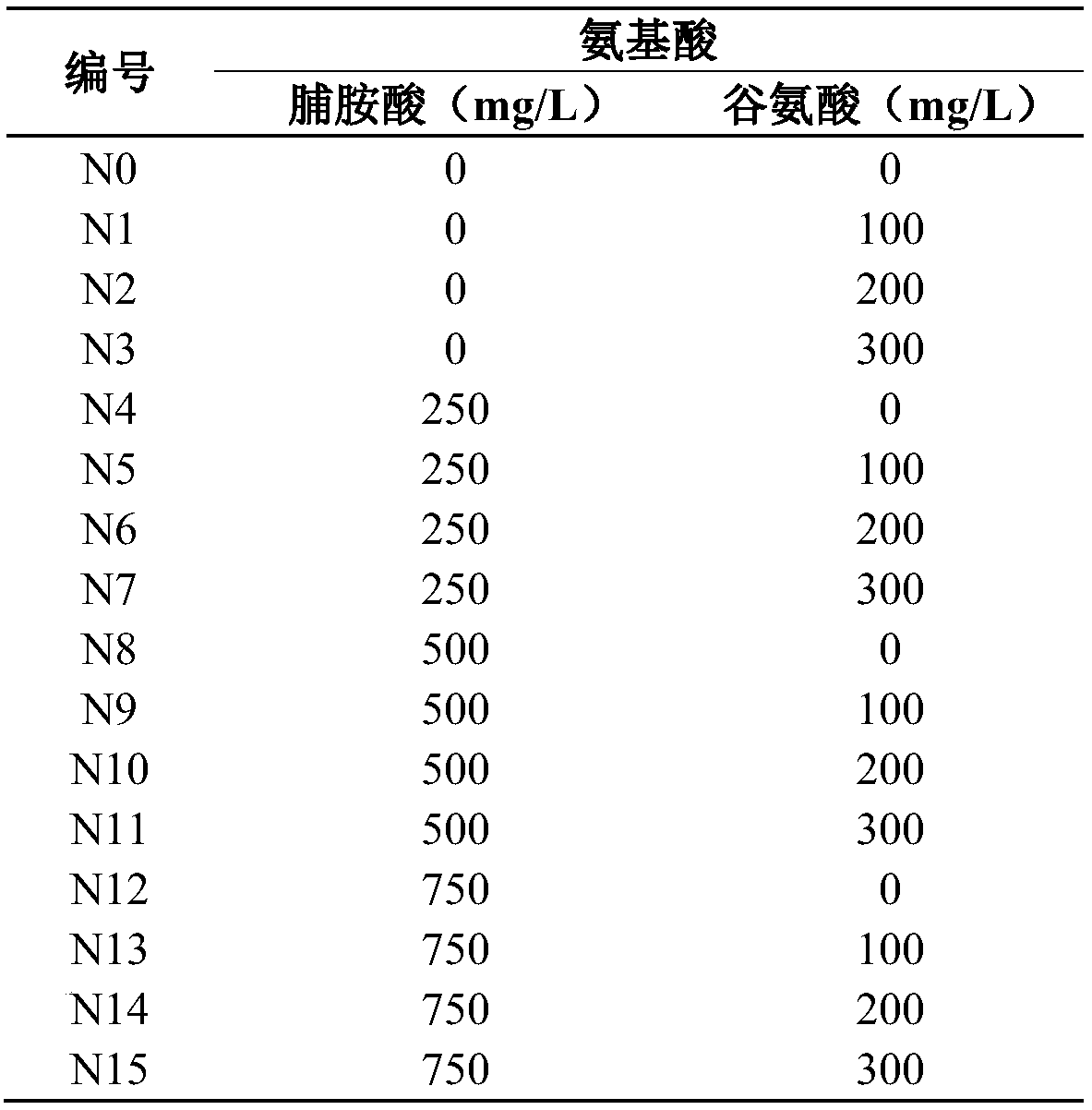
[0049] The method for rescuing immature embryos of the F1 generation of reciprocal crosses of ginseng and American ginseng comprises the following steps:
[0050] Step 1, parental emasculation and pollination: In the early flowering stage of the female parent, select a healthy and disease-free plant, use tweezers to remove all the inner florets, and only leave the outer 2-3 layers of florets that are about to open for emasculation. Immediately after emasculation, dip the pollen of the male parent collected in advance with a clean brush, and gently smear it on the stigma of the female parent. After the pollination is completed, bag it and put it on the record.
[0051] Step 2: Observing and collecting reciprocal cross F1 young species: observe and record the development of young hybrid embryos 7 days, 15 days and 30 days after pollination respectively. After 35 days of pollination, collect immature orthogonal species, and 45 days later, collect immature reciprocal species, wash...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The method for rescuing immature embryos of the F1 generation of reciprocal crosses of ginseng and American ginseng comprises the following steps:
[0057] Step 1, parental emasculation and pollination: In the early flowering stage of the female parent, select a healthy and disease-free plant, use tweezers to remove all the inner florets, and only leave the outer 2-3 layers of florets that are about to open for emasculation. Immediately after emasculation, dip the pollen of the male parent collected in advance with a clean brush, and gently smear it on the stigma of the female parent. After the pollination is completed, bag it and put it on the record.
[0058] Step 2: Observing and collecting reciprocal cross F1 young species: observe and record the development of young hybrid embryos 7 days, 15 days and 30 days after pollination respectively. After 45 days of pollination, collect immature orthogonal species, and 55 days later, collect immature reciprocal species, wash...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The method for rescuing immature embryos of the F1 generation of reciprocal crosses of ginseng and American ginseng comprises the following steps:
[0064] Step 1, parental emasculation and pollination: In the early flowering stage of the female parent, select a healthy and disease-free plant, use tweezers to remove all the inner florets, and only leave the outer 2-3 layers of florets that are about to open for emasculation. Immediately after emasculation, dip the pollen of the male parent collected in advance with a clean brush, and gently smear it on the stigma of the female parent. After the pollination is completed, bag it and put it on the record.
[0065] Step 2: Observing and collecting reciprocal cross F1 young species: observe and record the development of young hybrid embryos 7 days, 15 days and 30 days after pollination respectively. After 40 days of pollination, collect immature orthogonal species, and 50 days later, collect immature reciprocal species, wash...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com