Obligate attractant for controlling oriental fruit moths and control method
A technology of pear small borer and attractant, which is applied in the fields of attracting pests, pest control, botanical equipment and methods, etc. The effect of increasing lure efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
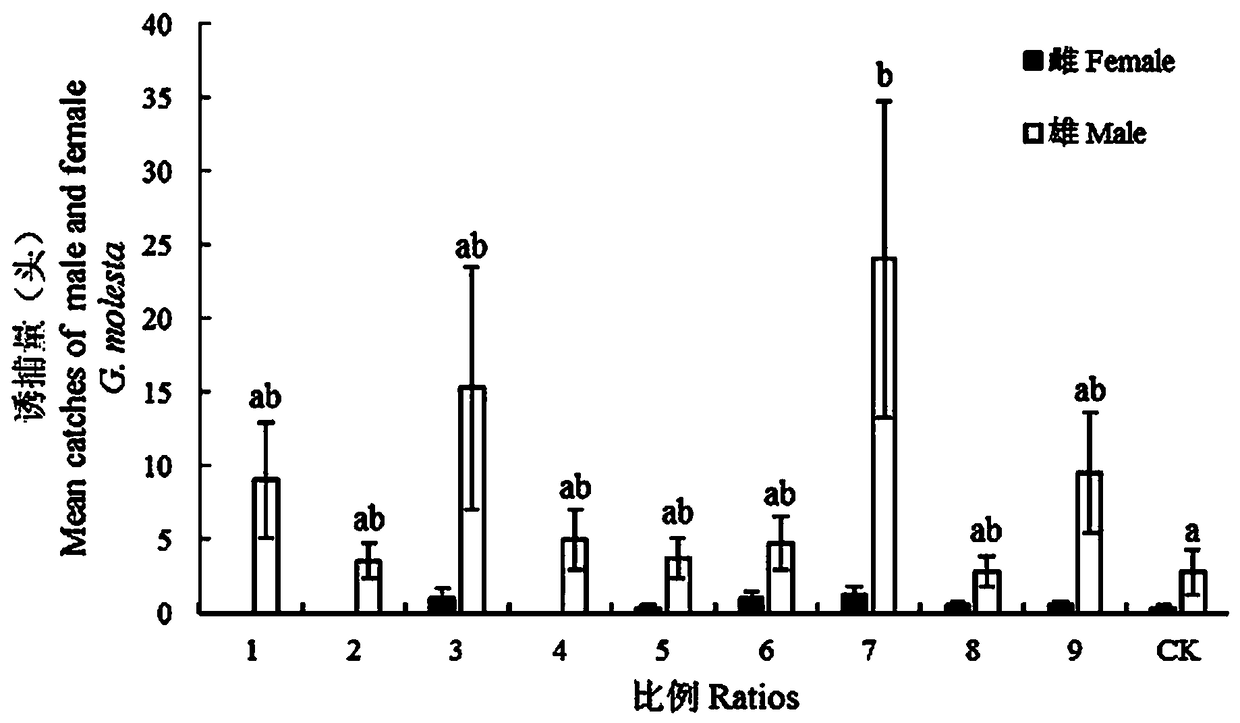
[0013] Example 1: Field trapping effect experiment of different ratios of sweet and sour liquor on the male and female pear borer worms. The different ratios of sweet and sour liquor are shown in Table 1. The ratio of sweet and sour liquor with the best trapping effect on both male and female pear borer worms was 3 : 1 : 3 : 80 through screening.
[0014] Table 1 Different ratios of sweet and sour liquor
[0015]
[0016] There were significant differences in the trapping amount of male pear borer moths with different ratios of sweet and sour liquor in the field ( F =2.24, df=9,39, P =0.047), there was no significant difference in the amount of trapping females ( F =1.889, df=9,39, P =0.093). Among them, the average trapping quantity of both male and female insects reached the maximum at ratio 7 (1.25±0.48 and 24.00±10.70). Ratio 1, 2 and 4 failed to trap females, and the trapping amount of males in the blank control was the smallest. ( figure 1 )
Embodiment 2
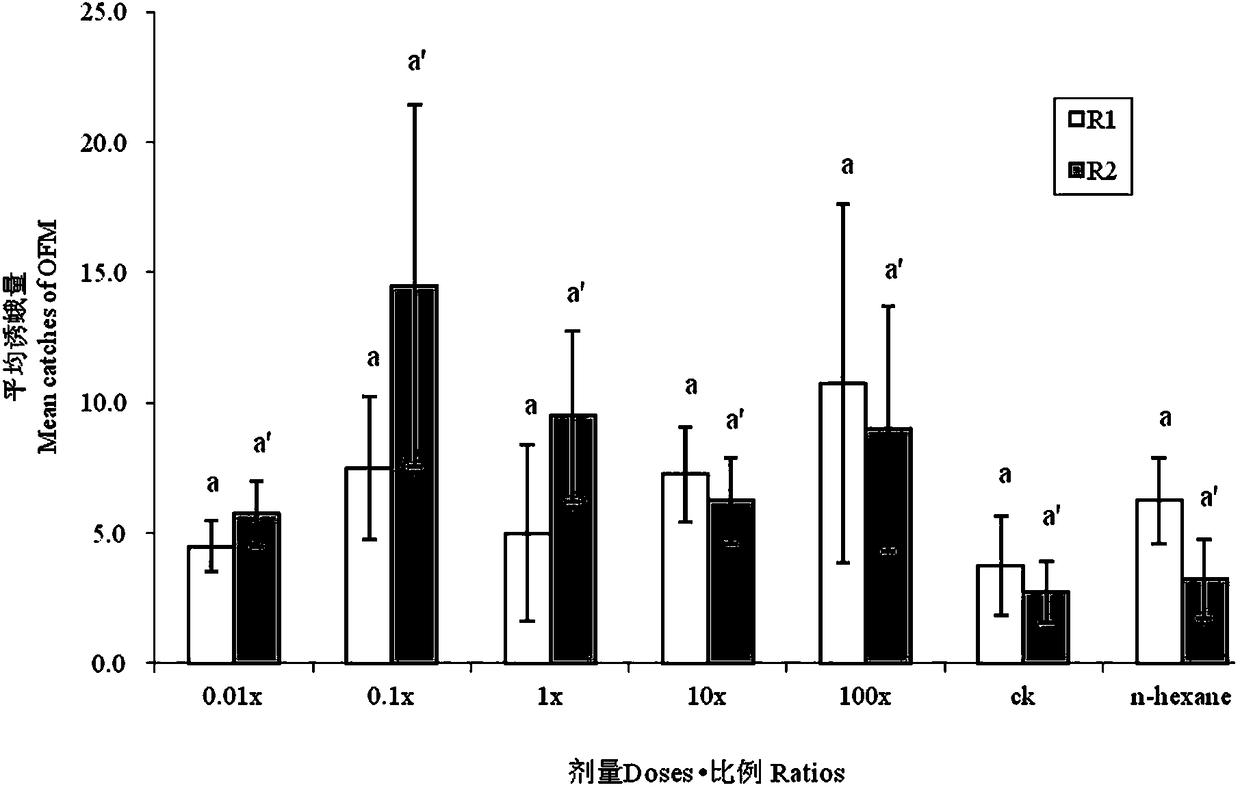
[0017] Example 2: Experiments on the effect of different ratios and doses of host plant volatiles on the field trapping effect of female and male moths of pear borer moths. The ratio and dose of host plant volatiles are shown in Table 2. The proportion and dose of volatiles in host plants with the best trapping effect on both male and female pear borer worms were obtained through screening: nonanal: cis-3-hexenol acetate: 6-methyl-5-heptene -2-keto:(Z)-β-ocimene=14:100:1:86 ratio, 0.201mg dose.
[0018] Table 2 The ratio and dose of volatiles in host plants
[0019]
[0020] The field moth-attracting effect of host plant volatile components was not significantly different under the combined effects of ratio and dosage ( F =0.560, df= 6, 56, P = 0.76), the same difference was not significant under individual ratio or dose effects (dose: F =0.217, df = 1, P = 0.446; Scale: F = 1.317, df = 6, P = 0.271). In terms of dosage, 0.1× has the highest moth-attracting am...
Embodiment 3
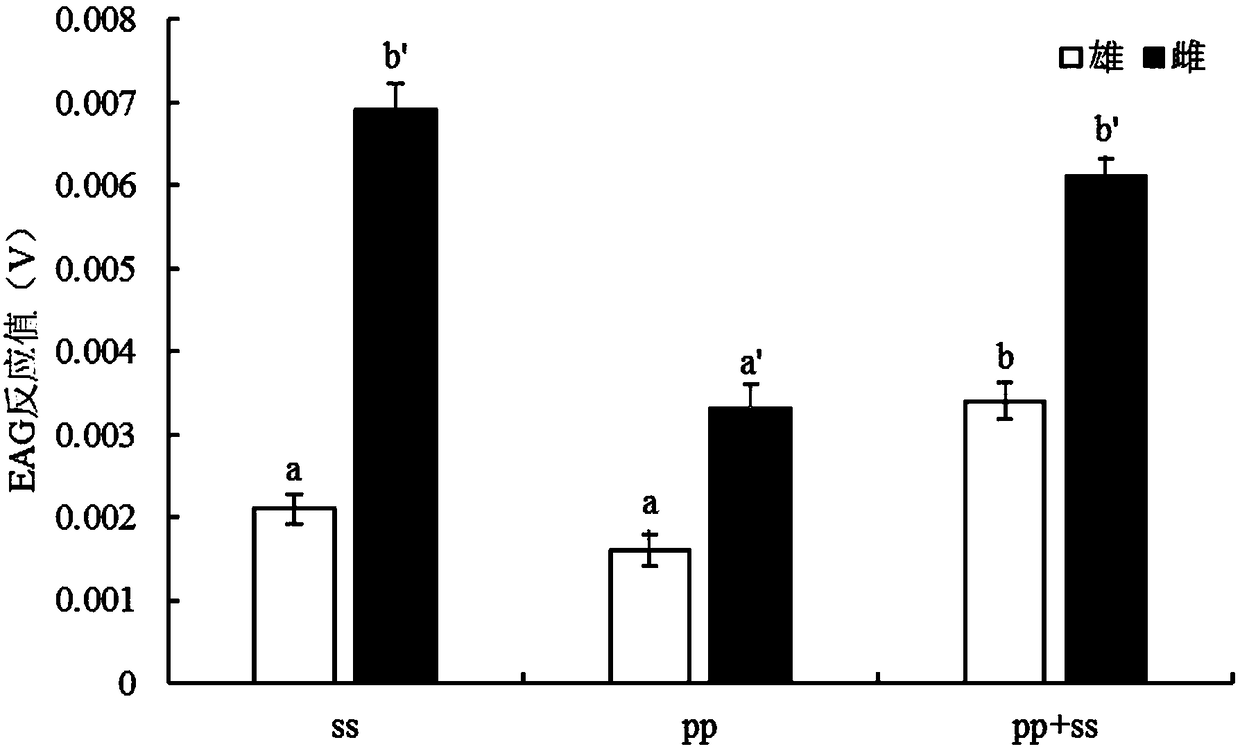
[0021] Embodiment 3: Contrast experiment of sweet and sour liquor, host plant volatile matter and the obligate lure method used in combination on the lure of pear borer. The antennal potential was used to detect the reactivity of the antennae to the odor indoors, and the flight behavior induced by the odor was measured through the wind tunnel to simulate the field activity space, and finally the trapping effect was tested in the field. See image 3 . The directional flight response rate of the female and male moths of the pear borer moth, see Figure 4 . The response rate of the female and male moths of the pear borer moth flying to more than 1 / 2 distance in the wind tunnel is shown in Figure 5 . The female and male moths of the pear borer moth approach the odor source within 10cm or the landing reaction rate see Figure 6 . Specific lure method in the field to attract moths of the small pear borer, see Figure 7-9 . In the figure: PP means host plant volatile matter,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com