Low-strength martensitic stainless steel ring forging and its forging method
A martensitic stainless steel and ring forging technology, applied in the field of martensitic stainless steel, can solve the problems of low tensile strength and unattainable QT650, and achieve the effect of improving the qualification rate and avoiding energy waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment provides a low-strength martensitic stainless steel ring forging, the chemical composition of which is shown in Example 1 in Table 1. The strength grade of the martensitic stainless steel ring forging is QT650. Tensile strength: 650~830Mpa, yield strength ≥520Mpa, elongation ≥15%, made by the following forging methods:
[0041] The steel ingot is made by vacuum degassing ingot casting, and then the steel ingot is forged. The specific steps are as follows:
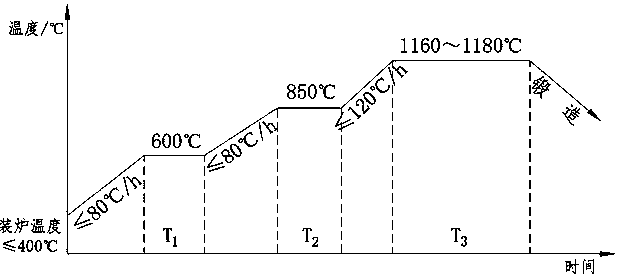
[0042] a. Pre-forging heating: put the steel ingot into the gas furnace, heat treatment in sections, reduce the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the steel ingot, and avoid cracking: first heat up to 600 °C at a rate of 80 °C / h or less, and keep it for 3 hours; Equal to 80°C / h heating up to 850°C, holding for 5h; then heating at 120°C / h or less to 1160°C, holding for 7h, to avoid cracking of the forging billet caused by δ ferrite caused by excessive heating temperature, and then s...
Embodiment 2
[0052] This embodiment provides a low-strength martensitic stainless steel ring forging, the chemical composition ratio of which is shown in Example 2 in Table 1. The strength grade of the martensitic stainless steel ring forging is QT650. Tensile strength: 650~830Mpa, yield strength ≥520Mpa, elongation ≥15%, made by the following forging methods:
[0053] The steel ingot is made by vacuum degassing ingot casting, and then the steel ingot is forged. The specific steps are as follows:
[0054] a. Pre-forging heating: put the steel ingot into the gas furnace, heat treatment in sections, reduce the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the steel ingot, and avoid cracking: first heat up to 600 °C at a rate of 80 °C / h or less, and keep it for 3 hours; Equal to 80°C / h heating up to 850°C, holding for 5h; then heating up to 1165°C at 120°C / h or less, holding for 8h, to avoid cracking of the forging billet caused by δ ferrite caused by excessive heating temperature,...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment provides a low-strength martensitic stainless steel ring forging, the chemical composition of which is shown in Example 3 in Table 1. The strength grade of the martensitic stainless steel ring forging is QT650. Tensile strength: 650~830Mpa, yield strength ≥520Mpa, elongation ≥15%, made by the following forging methods:
[0065] The steel ingot is made by vacuum degassing ingot casting, and then the steel ingot is forged. The specific steps are as follows:
[0066] a. Pre-forging heating: put the steel ingot into the gas furnace, heat treatment in sections, reduce the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the steel ingot, and avoid cracking: first heat up to 600 °C at a rate of 80 °C / h or less, and keep it for 3 hours; Equal to 80°C / h heating up to 850°C, holding for 5h; then heating up to 1175°C at ≤ 120°C / h, holding for 7h, to avoid cracking of the forging billet caused by δ ferrite caused by excessive heating temperature, and then st...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com