A method of inhibiting dna enzyme cleavage
A DNase and double-enzyme cleavage technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of poor temperature control and inability to completely inhibit enzyme cleavage, and achieve the effects of convenient operation, easy acquisition and reasonable cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Preparation of monolayer or multilayer MoS 2 The specific steps are as follows:
[0028] This example prepares 2mg / mL of MoS 2 , Weigh 10 mg of the initial molybdenum disulfide crystal, dissolve it in a glass bottle filled with 5mL ultrapure water, and ultrasonicate for ≥2h, wherein the original molybdenum disulfide crystal is obtained by mechanical exfoliation, that is, the material with a layered structure and Other harder substances are subjected to physical surface friction to obtain a thin layer or monolayer material, and the average diameter of the nanomaterial is maintained at 176nm.
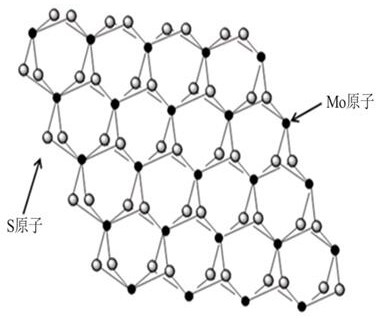
[0029] figure 1 Schematic diagram of the molecular structure of molybdenum disulfide. The monolayer structure of the material consists of a quasi-2D network of covalently bonded S-Mo-S hexahedrons.
[0030] (2) Preparation of Escherichia coli containing the target plasmid:
[0031] a. Preparation of competent cells: Take out the frozen Escherichia coli DH5α strain from th...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) This example prepares 1 mg / mL MoS 2 , Weigh 10mg of the initial molybdenum disulfide crystal, dissolve it in a glass bottle filled with 10mL ultrapure water, and ultrasonicate for 3h, wherein the original molybdenum disulfide crystal is obtained by mechanical exfoliation, that is, the material with a layered structure and other Harder substances are subjected to physical surface friction to obtain thin or monolayer materials, and the average diameter of the nanomaterials is maintained at 214nm.
[0047] (2) Preparation of Escherichia coli containing the target plasmid:
[0048] a. Preparation of competent cells: the steps are the same as in a in Example 1 (2).
[0049] b. Transformation: take the competent cells out of the -70°C refrigerator, thaw on ice, and work in ultra-clean
[0050] In Taichung, take 1 μL of PB2GW7.0 plasmid and add 9 μL of ultrapure water to dilute it, then add it to 100 μL of competent cells, place on ice for 30 minutes, heat shock (water b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com