Method for producing radioactive isotopes in a fast neutron reactor
A radionuclide and fast neutron technology, applied in the field of nuclear engineering, can solve the problems of rising product cost, large assembly weight, and reduced capacity, and achieve the effect of reducing materials, reducing weight, and simplifying use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
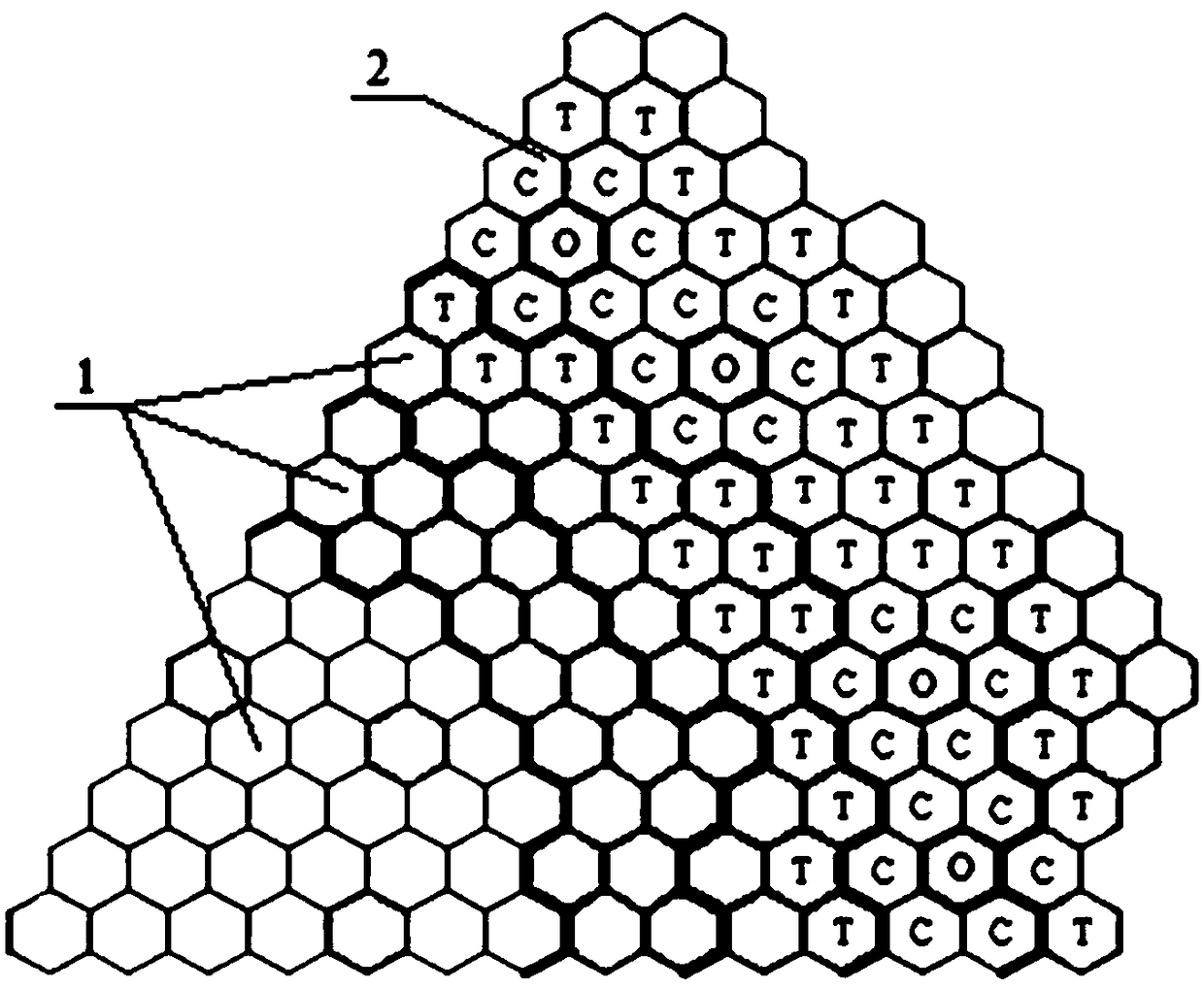
[0032] The method is implemented in a fast neutron reactor, which has an outer shell in which the core 1 and wall tubes 2 are located (see figure 1 ). In the core there are fuel assemblies used to generate the fast neutron flux. Inside the wall tubes of the reactor are the fuel assemblies used to produce plutonium and reduce the neutron flux, preventing the neutron flux from escaping the reactor.
[0033] In order to implement the method according to the invention, a radiant assembly is installed in the wall duct 2, in figure 1 The letter O is used to indicate the radiation component. The radiant assemblies are installed in the fuel assemblies denoted by the letter T and are separated from them by an intermediate steel assembly marked with the letter C, therefore, in order to carry out the invention, the assemblies are installed as follows: the irradiated assemblies are installed in the wall tubes of the reactor, The steel assembly is located around it, and the fuel assem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com