Method for performing full genome sequence hole filling by means of long sequencing read segment
A whole-genome and sequencing technology, applied in the field of genomics and bioinformatics, can solve problems such as large memory requirements, long running time, and limited applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] Using C. elegans PacBio sequencing data to fill holes in the C. elegans genome
[0154] Materials: From the website of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information) ( https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to download the next-generation genome sequencing data of C. elegans (NCBI SRA database numbers: DRR023912 and DRR023913). PacBio raw sequencing data of C. elegans were downloaded from the website (http: / / datasets.pacb.com.s3.amazonaws.com / 2014 / c_elegans / list.html). The obtained data format is fastq format, about 7.4G data volume, and the average read length is 10,958 bases. Preprocess the downloaded PacBio data and convert the files in fastq format to fasta format. First, the next-generation sequencing data was assembled with Platanus (platanus.bio.titech.ac.jp) to obtain the nematode genome. The genome size was 95.5Mb, including 4256 holes, and the total length of the holes was 3.6Mb. In order to fill the unknow...
Embodiment 2
[0164] Using C. elegans Nanopore sequencing data to fill holes in the C. elegans genome
[0165] Materials: Same as Example 1, download the next-generation genome sequencing data of C. elegans and assemble it into a genome. Genome size and number of holes are consistent with Example 1. From the National Center for Biotechnology Information website ( https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to download the Nanopore raw sequencing data of C. elegans (NCBI SRA database numbers: ERR2092776 and ERR2092777). The amount of data is about 9.9G, and the average read length is 11,537 bases. In order to fill the unknown bases in the hole, follow the steps below to fill the hole, and perform three iterations to fill the hole.
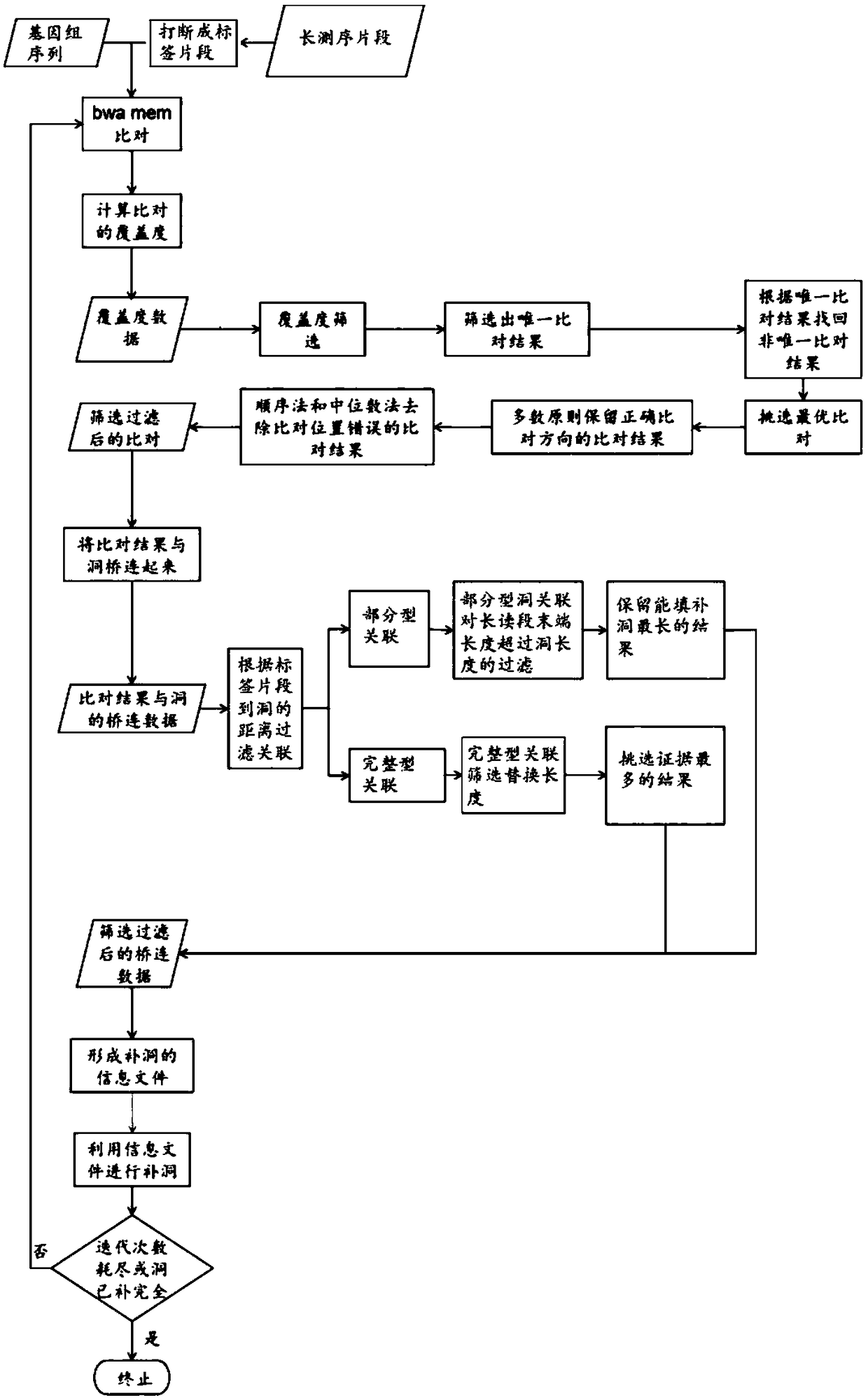
[0166] 1. Break each Nanopore long sequencing read into equal-length 300-base index fragments.
[0167] 2. Align the tag fragments to the genome with bwa-mem, and run bwa-mem with the parameter -k14-W20-r10-A1-B1-O1-E1-L0.
[0168] 3. The remaining steps are the sam...
Embodiment 3
[0173] Using Yeast Nanopore Sequencing Data to Fill in Holes in the Yeast Genome
[0174] Materials: From the website of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information) ( https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) to download the next-generation genome sequencing data of yeast (NCBI SRA database numbers: ERR225691, ERR225692, and SRR507778). In addition, download the original Nanopore sequencing data of yeast from this website (SRA database numbers: ERR1883389, ERR1883402, ERR1883399, ERR1883400 and ERR1883401). The obtained data format is fastq format, about 440M data volume, and the average read length is 8,000 bases. Preprocess the downloaded Nanopore data and convert the files in fastq format to fasta format. First, the next-generation sequencing data was assembled with Platanus (platanus.bio.titech.ac.jp) to obtain the yeast genome. The genome size was 11.27Mb, including 472 holes, and the total length of the holes was 290.8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com