Method for quickly separating liver cells in portal area and central vein area from liver
A central vein and hepatocyte technology, applied in the medical field, can solve the problem of inability to separate hepatocytes in the portal duct area from the liver, and achieve the effects of simple operation, high purity and high viable cell rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Embodiment 1 Liver tissue processing
[0065] 1. Disinfect all consumables with 70% ethanol, including the inside of the constant flow pump;
[0066] 2. Inject pentobarbital sodium solution (0.5%, about 0.7ml for 50g mice) intraperitoneally to anesthetize the mice;
[0067] 3. Open the abdominal cavity, ligate the branches of the portal vein, ligate the subhepatic vena cava (live), and ligate the arteries if possible;
[0068] 4. Insert the catheter into the portal vein;
[0069] 5. Wash the intrahepatic blood with solution Krebs / Henseleit buffer at a rate of 35ml / min (210ml / h) at 37°C;
[0070] 6. Continuous perfusion for about 10 minutes, while inserting a second catheter into the inferior hepatic vena cava;
[0071] 7. Use a syringe to push Digitonin solution (1ml); (to separate portal area cells, the perfusion direction is reverse perfusion from the inferior vena cava; to separate central venous area cells, the direction is to perfuse forward from the portal vein...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2 Purification of hepatocytes
[0088] 1. The cells obtained in Example 1 were prepared into a suspension with solution A containing Percoll cell separation fluid, put into a 50ml centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 50g for 3.5min, and removed the supernatant;
[0089] 2. Resuspend with solution A containing Percoll cell separation medium, and centrifuge again;
[0090] 3. Repeat step 2 twice;
[0091] 4. Collect cells and resuspend cells in basal medium;
[0092] 5.50g, centrifuge for 5min, repeat the centrifugal purification twice, the cells are stained with trypan blue, counted, according to 1x10 6 / 25cm 2 The number of cells in the bottle, using complete medium + 20% FBS in 5% CO 2 incubator at 37°C.
[0093] 6. Change the liquid after 18 hours, and change the liquid every day thereafter.
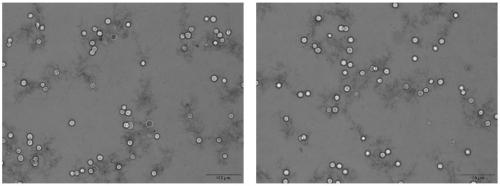
[0094] Trypan blue staining results figure 2 . Viable cell rate >95%.
Embodiment 3
[0095] Example 3 Marker gene expression
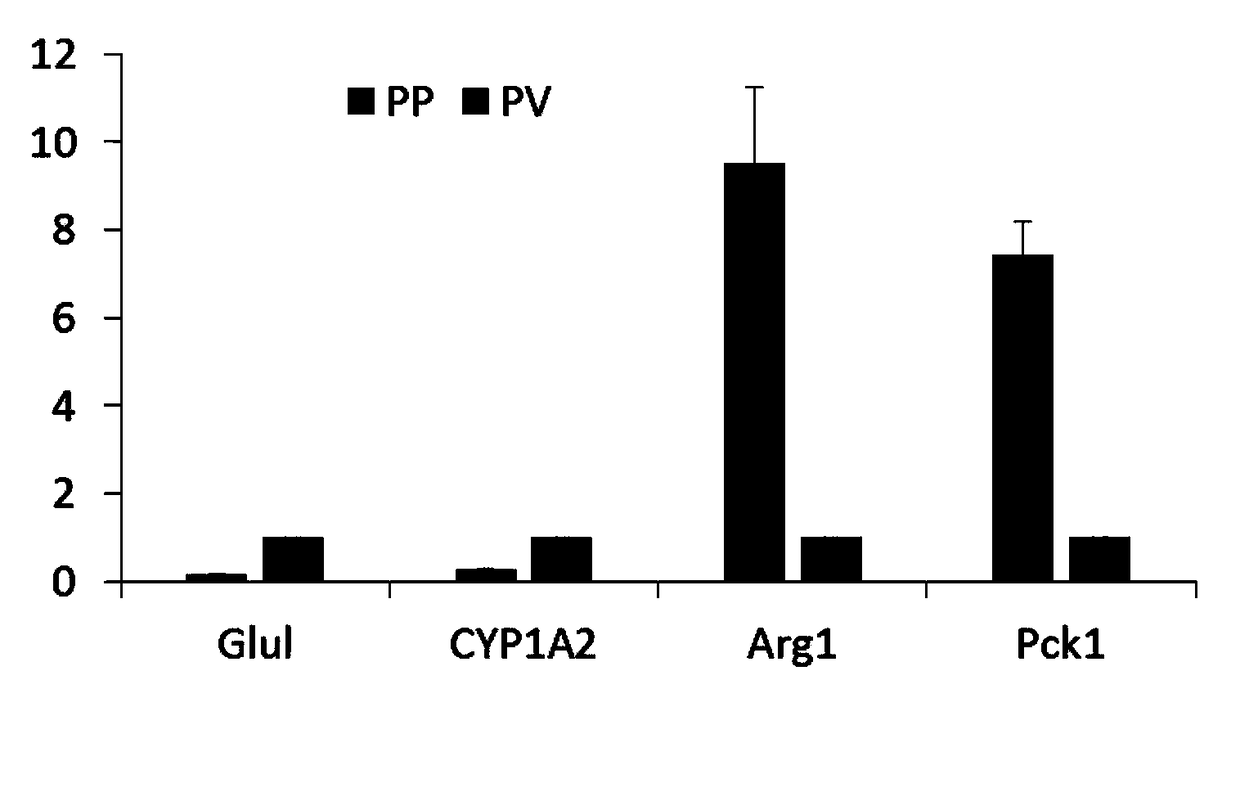
[0096] qRT-PCR detection of liver cell marker genes Glul and CYP1A2 in the central venous region (PV), and liver cell marker genes Arg1 and Pck1 in the portal region (PP) in two groups of isolated hepatocytes. See the test results image 3 .
[0097] The expression of hepatocyte marker genes Glul and CYP1A2 in the central venous area was much higher than that in the hepatocytes in the portal area. On the contrary, the expression of liver cell marker genes Arg1 and Pck1 in the portal area was much higher than that in the central venous area. This indicates that the cells we isolated are of high purity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com