High-temperature, high-strength and low-carbon hot work die steel and preparation method thereof
A high-temperature, high-strength technology, applied in the field of low-carbon hot-work die steel and its preparation, can solve the problems of lowering the high-temperature strength and red hardness of the material, affecting the toughness and fatigue performance of the hot-working die steel, and reducing the service life of the die.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
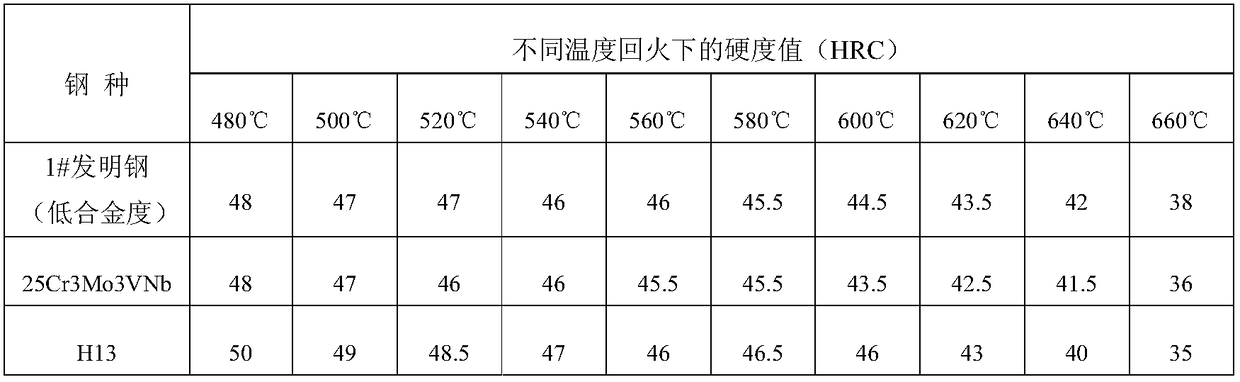
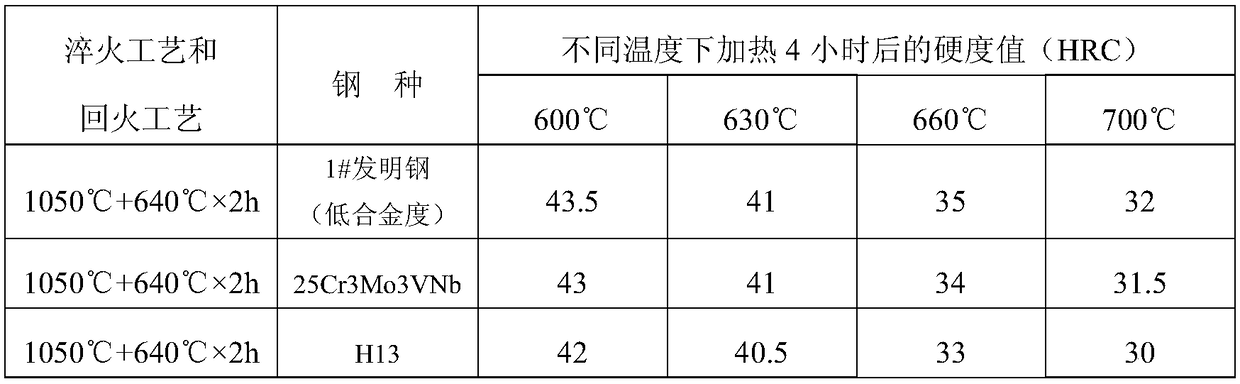
[0039] Place the 1# ingot in a gas furnace and heat it to 1250°C for homogenization annealing for 20 hours, then cool it with the furnace at a rate of 100°C / h to below 500°C and leave the furnace for air cooling; heat it to 1160°C with a trolley and keep it for 4 hours . After the heat preservation is completed, forging is carried out. The initial forging temperature is about 1130°C, the final forging temperature is 810°C, the first heat forging is to Φ90, and the forging ratio is 3.3; Heat to 870°C at a heating rate greater than 100°C / h, hold for 150 minutes, and then cool with the furnace at a rate of 30°C / h to below 500°C and leave the furnace for air cooling. After the 1# steel and the comparison steel were annealed, they were processed into samples, quenched after being kept at 980°C for 60 minutes, and then tempered at 640°C for 2 hours, then the mechanical properties were tested. Compared with the comparison steel, the structure of 1# steel is finer than that of the se...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Place 2# and 3# steel ingots in a gas furnace and heat them to 1280°C for homogenization annealing for 30 hours, then cool with the furnace at a rate of 90°C / h to below 500°C and leave the furnace for air cooling; heat to 1180°C with a trolley Keep warm for 4 hours. After the heat preservation is completed, forging is carried out. The initial forging temperature is about 1150°C, the final forging temperature is 830°C, the first fire forging is to Φ90, and the forging ratio is 3.3; Heat to 870°C at a heating rate greater than 100°C / h, hold for 150 minutes, and then cool to 500°C with the furnace at a rate of 30°C / h, then take out the furnace and air cool. After annealing 2#, 3# steel and the comparison steel, they were processed into samples, and quenched after being kept at 1050°C for 60 minutes, and then tempered at 640°C for 2 hours, then the mechanical properties were tested. Compared with the comparison steel, 2# and 3# steel have finer structure than the second st...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Put the 4# ingot in a gas furnace and heat it to 1300°C for homogenization annealing for 20 hours, then cool it with the furnace at a rate of 80°C / h to below 500°C and leave the furnace for air cooling; heat it to 1200°C with a trolley and keep it for 4 hours . After the heat preservation is completed, forging is carried out. The initial forging temperature is about 1180°C, the final forging temperature is 850°C, the first fire forging is to Φ90, and the forging ratio is 3.3; Heat to 870°C at a heating rate greater than 100°C / h, hold for 150 minutes, and then cool to 500°C with the furnace at a rate of 30°C / h, then take out the furnace and air cool. After the 4# steel and the comparison steel were annealed, they were processed into samples, quenched after being kept at 1050°C for 60 minutes, and then tempered at 640°C for 2 hours, then the mechanical properties were tested. Compared with the comparison steel, the structure of 4# steel is finer than that of the second t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com