Preparation method for self-assembly nanoparticle with targeting function and application thereof
A self-assembling nanoparticle and functional technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as easy decomposition, and achieve the effect of simple and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of self-assembled nanoparticles UA@EGCG-Apt NPs with targeting function
[0031] Take 100 µL of 20, 10, 5, and 1 mM ursolic acid methanol solutions at room temperature, and slowly add them dropwise to 1 mL of water under ultrasonic conditions to completely volatilize the methanol, and then add 100 µL of 1 mM EGCG aqueous solution, ultrasonic for 45 minutes, to obtain UA@EGCG self-assembled nanocomposites, then add 10 µL 10 μM nucleic acid aptamer aqueous solution, shake on a shaker for 4-6 hours, and after standing at room temperature, you can get Function-oriented self-assembled nanoparticles UA@EGCG-Apt NPs.
Embodiment 2
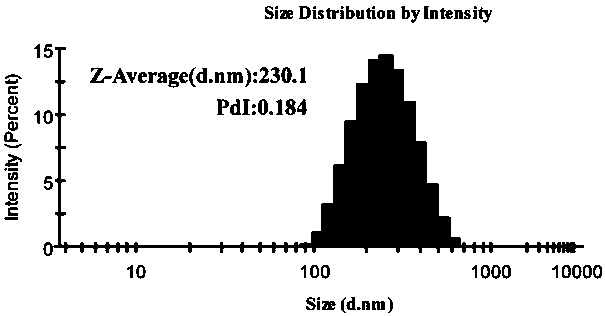
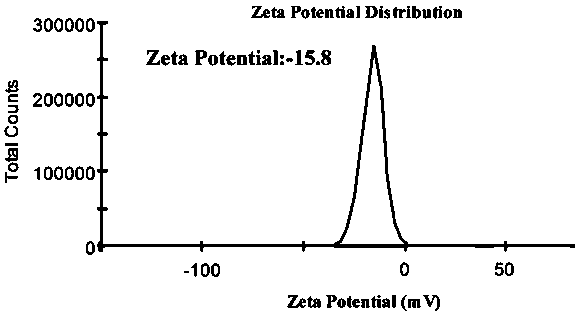
[0032] Example 2 Particle size and potential analysis and detection of UA@EGCG self-assembled nanocomposites
[0033] The particle size distribution and Zeta potential of the nanocomposite prepared by the ratio of the amount of substances were measured using a Malvern particle sizer.
[0034] Table 1 Particle size distribution of UA@EGCG self-assembled nanocomposites with different molar ratios
[0035]
[0036] UA@EGCG self-assembled nanocomposites were prepared by "solvent exchange method". The ratio of substances is an important factor affecting the particle size of UA@EGCG nanocomposites, and the PDI value can reflect the distribution of nanoparticle sizes. UA@EGCG nanocomposites The optimum substance molar ratio was 10:1 (Table 1). When the molar ratio of substances is 1:1, the average particle size of UA@EGCG nanocomposites is 358.1 nm, the PDI is 0.376, and the potential is -27.3 mV; when the molar ratio of substances is 5:1, the UA@EGCG nanocomposites The average ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3 Agarose electrophoresis experiment
[0038] In order to verify whether Aptamer targeting tumor cell EpCAM can be adsorbed on the nano drug delivery system UA@EGCG self-assembled nanocomposite, an agarose electrophoresis experiment was carried out.
[0039] (1) Add 0.5 g of agarose to 50 mL of 0.5×TBE electrophoresis buffer and shake well. Heat in a microwave oven for 1 min until the agarose dissolves, take it out, shake it by hand, and continue heating in the microwave oven for 30 s until the agarose is completely dissolved to make a 1% agarose gel.
[0040] (2) Cool the dissolved agarose to about 60°C, pour it into the agarose gel mold with the comb inserted, cool and solidify at room temperature, and carefully pull out the comb vertically.
[0041] (3) Put the gel into the electrophoresis tank, add 0.5×TBE electrophoresis buffer solution into the electrophoresis tank until the liquid surface covers the gel by 1-2 mm.
[0042] (4) Sample treatment: 8 μL DNA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com