Thin-walled structure with large temperature gradient and its preparation method by laser direct deposition
A laser direct deposition, temperature gradient technology, applied in the direction of additive manufacturing, process efficiency improvement, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of different melting and solidification processes, easy to produce harmful impurities, affect structural accuracy, etc., to eliminate the risk of cracking , reduce stress and thermal stress, and suppress the deformation of thin-walled structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
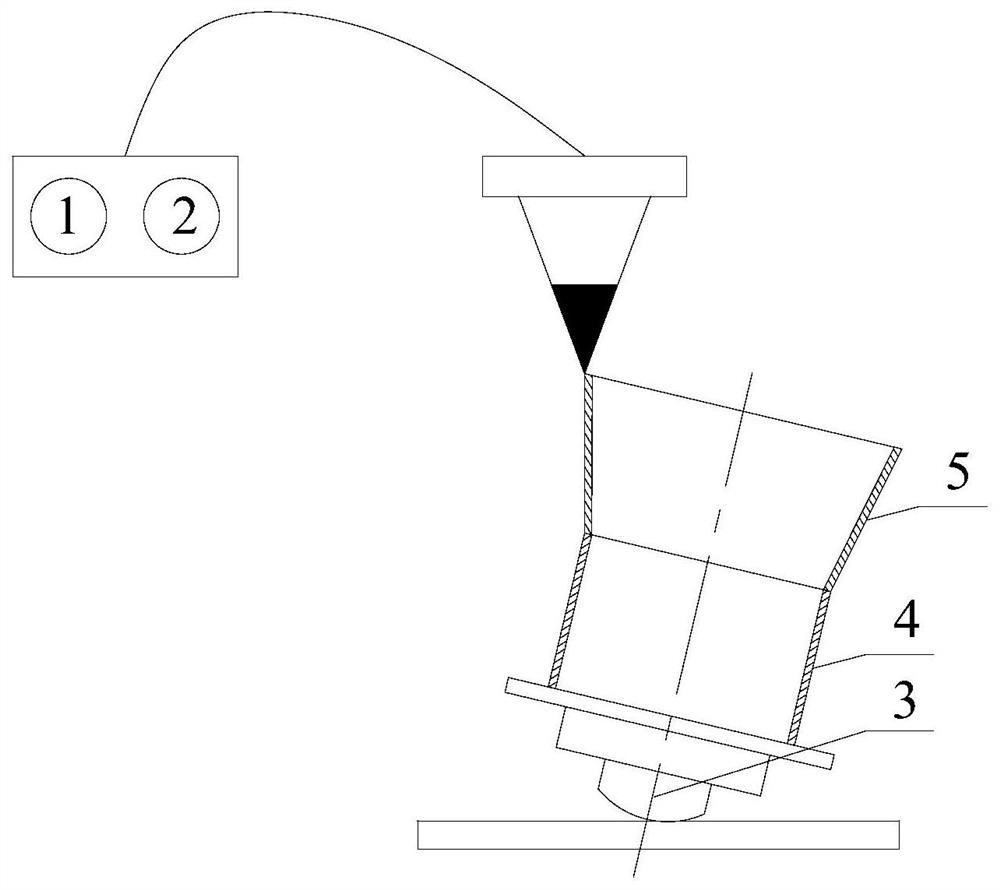
[0048] TA15 / Ti2AlNb thin-walled large temperature gradient cone structure was prepared by laser direct deposition, as shown in the attached figure 2 As shown, the hollow rotary body formed by connecting the cylindrical surface 4 and the conical surface 5 (that is, the cone structure) is prepared by laser direct deposition equipment, the wall thickness is 2mm, the cylindrical surface material (tube material) is TA15 alloy, and the conical surface material is TA15 alloy. (Material of the cone part) is Ti2AlNb alloy, the diameter of the cylindrical end (tube part) is φ160mm, the height is 100mm, the diameter of the big end of the cone surface (the big end of the cone part) is φ200mm, and the total height of the rotary body is 200mm. 3 is the turntable for making the rotary body structural parts .
[0049] The first step is to initialize the laser forming equipment.
[0050] Carry out the inspection and preparation of each system of the laser direct deposition equipment LSF-Ⅲ (l...
Embodiment 2
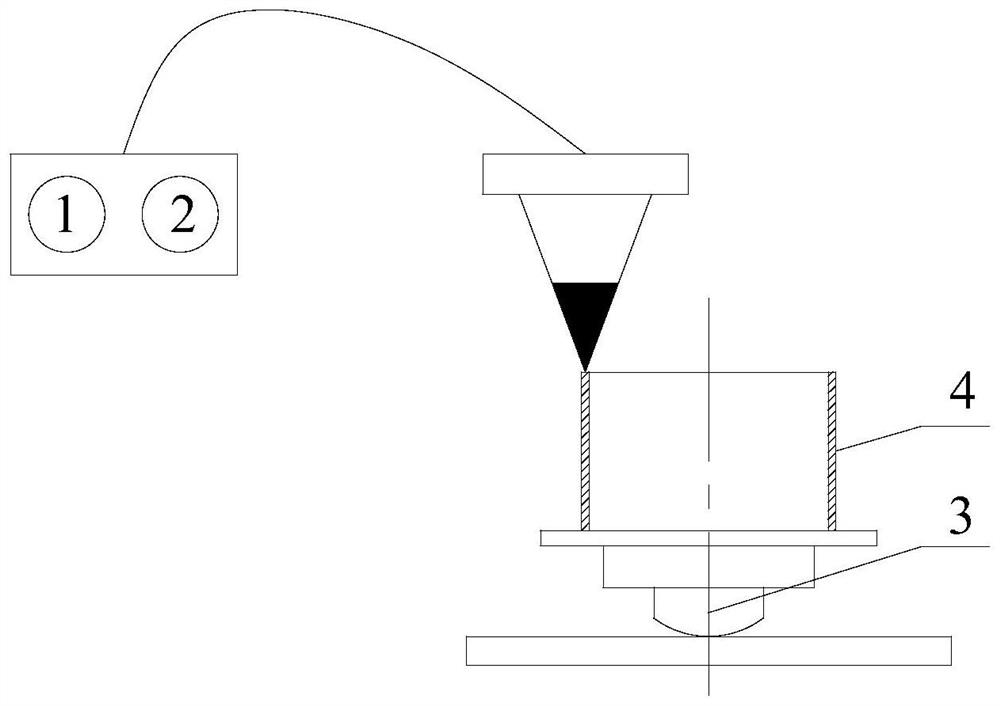
[0068] The TA15 / Ti2AlNb thin-walled large temperature gradient cylindrical structure is prepared by laser direct deposition, with a diameter of φ150mm and a wall thickness of 2mm. The lower material is TA15 and the height is 100mm. The upper material is Ti2AlNb and the height is 50mm.
[0069] The first step is to initialize the laser forming equipment.
[0070] Carry out the inspection and preparation of each system of the laser direct deposition equipment LSF-Ⅲ (laser CP4000), turn on the atmosphere protection system, keep the oxygen content below 50ppm, and load the TA15 and Ti2AlNb alloy powder into the powder feeder 1 and 2 respectively;
[0071] The second step is to generate the laser scanning path.
[0072] Use the 3D modeling software Siemens NX to establish a 3D model of the gradient structure, use the subdivision software that comes with the laser direct deposition equipment to subdivide the 3D model, and input the CNC program (laser scanning path) generated by the ...
Embodiment 3
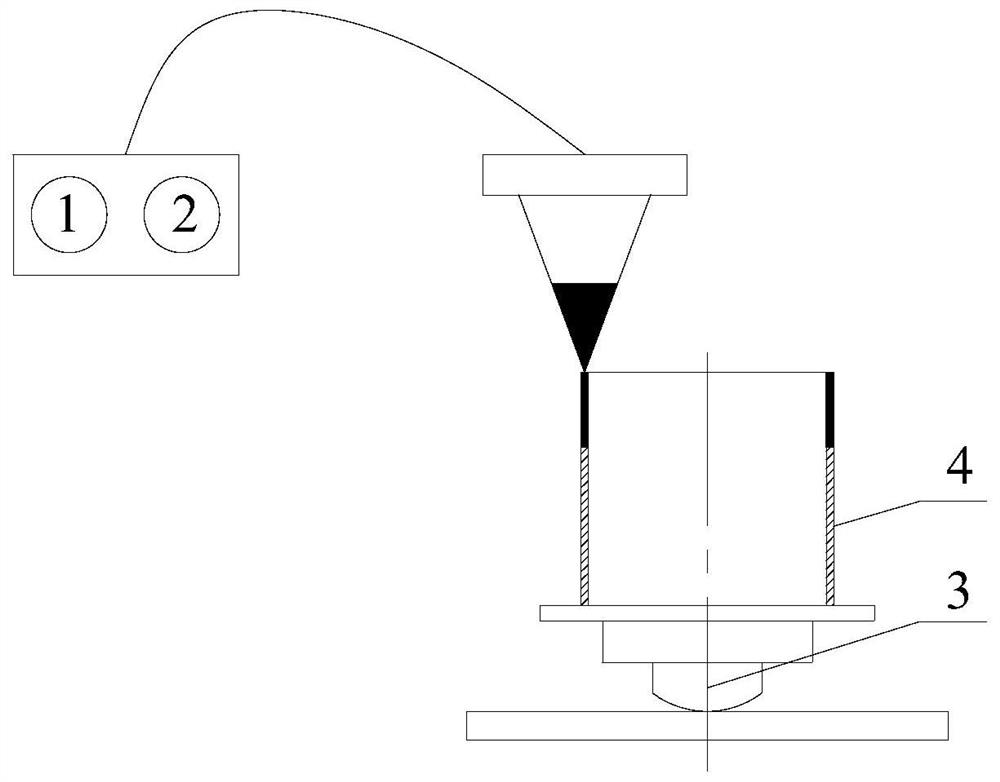
[0088] In this embodiment, except that the total thickness of the transition layer is 0.6 mm (those of the three transition layers are all 0.2 mm), and the total thickness of the high-temperature base layer is 0.5 mm, other steps are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0089] The gradient transition layer and the high-temperature base layer are prone to cracks or deformation of the structural part during the preparation process of the structural part obtained in this embodiment, which affects the product qualification rate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com