Method for enlarging genetic variation range of brassica napus
A Brassica napus, genetic variation technology, applied in the field of biological breeding, can solve the problems of slow progress of genetic stability of hybrid offspring, poor compatibility of hybrid offspring, complicated procedures, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
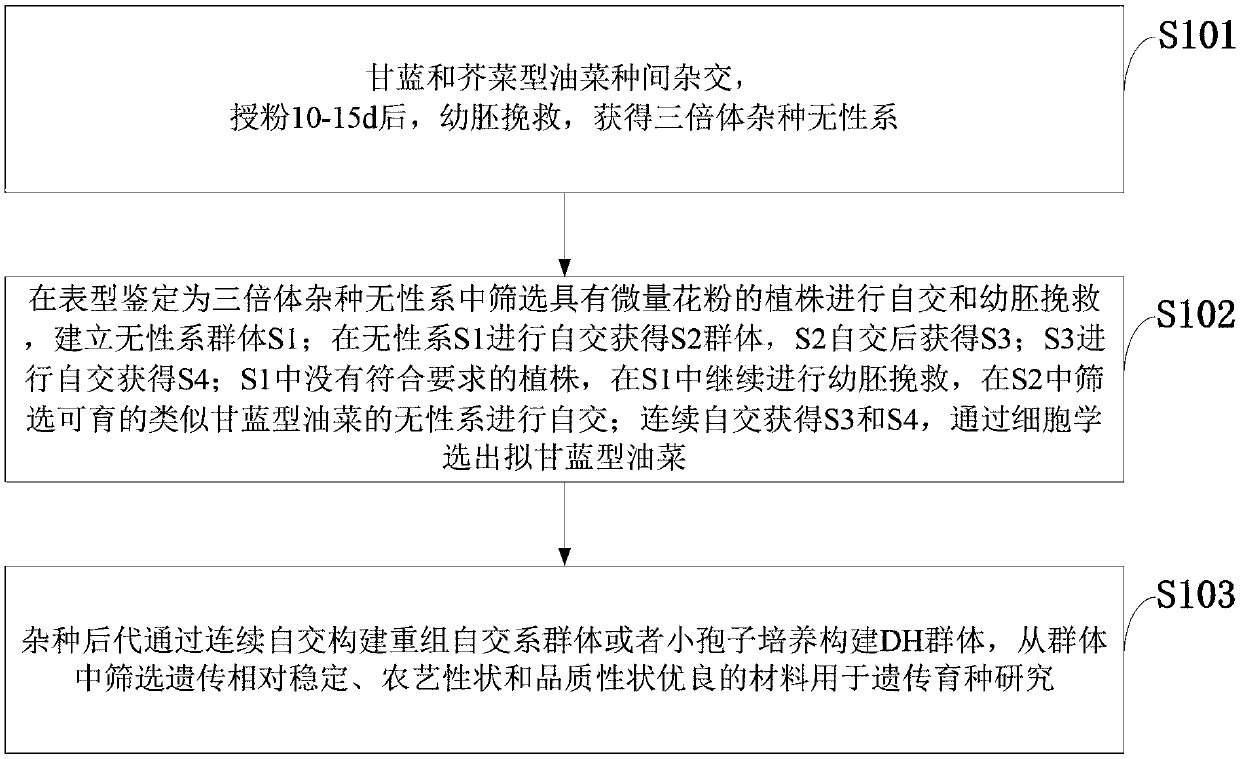
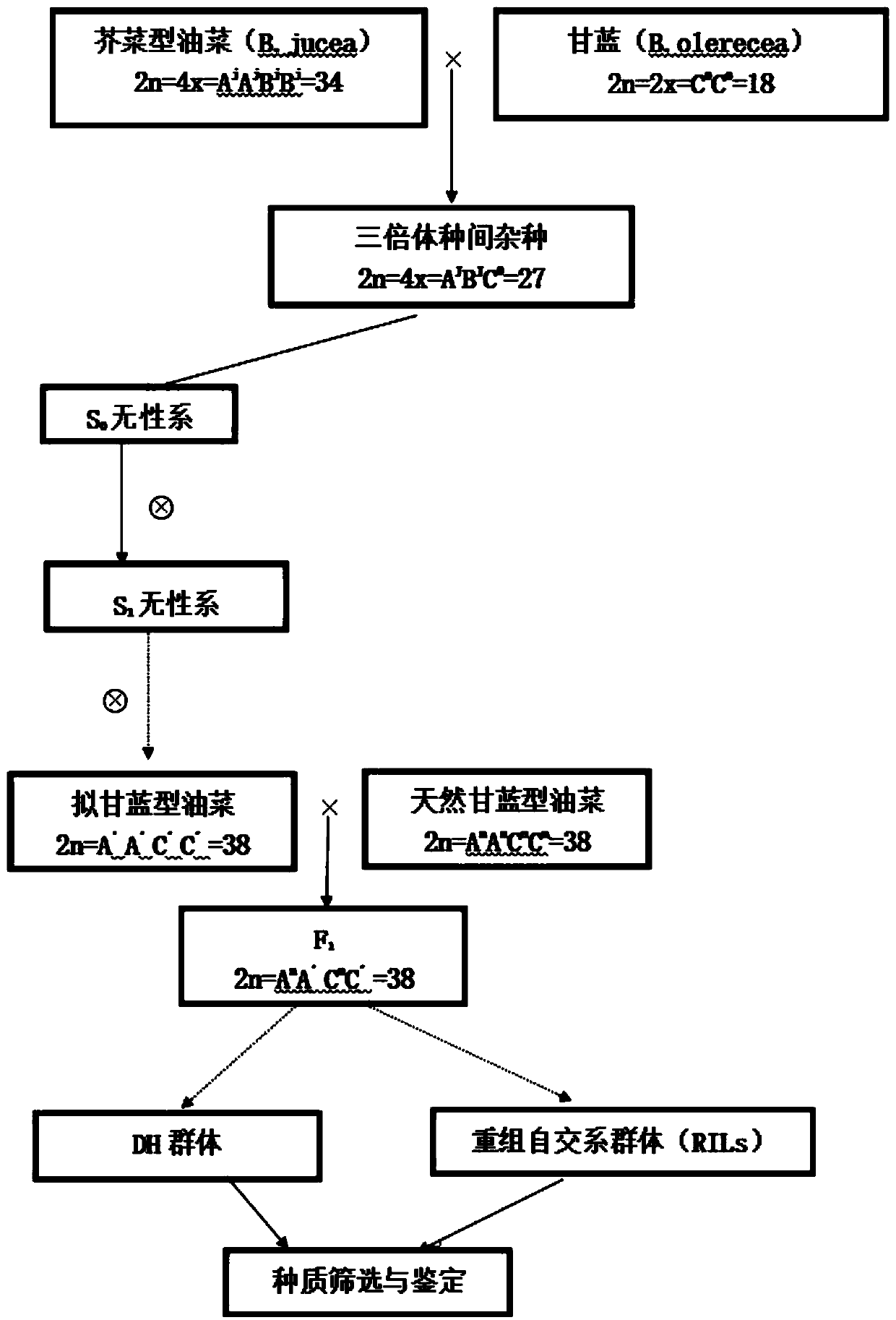
[0045] The method for widening the Brassica napus mutant library provided by the embodiments of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0046]Step 1: Select Brassica napus and cabbage (kale, kale, head cabbage, etc.) with excellent properties as experimental materials, and adjust the sowing date appropriately so that the two flowering stages meet. Select a robust Brassica napus strain as the female parent, remove the flower buds that have already bloomed or are too small, and keep the flower buds that can bloom after 2-3 days for peeling and emasculation, and smear the stigma with a 10% NaCl solution by mass ratio , after the stigma is slightly air-dried, give fresh cabbage pollen. Repeat pollination the next day. Bagging was done immediately after each pollination. After 30 days of pollination, the mature immature embryos will be sterilized with 75% alcohol (30-60s) and 10% NaClO in turn, and inoculated on Ms or 1 / 2Ms medium under aseptic conditions, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Brassica napus 09K26 and 09D311 were used as female parents, kale 09D427 and 09DK005 were used as male parents, about 1,200 flower buds were pollinated, and 71 immature embryos were obtained. After cultivation, 10 clones were obtained, including 3 true hybrids. Brassica napus 09D454, 09D217 was used as the female parent, and Chinese kale AY169, D229, D230 was used as the male parent. About 3,300 flower buds were pollinated, and about 800 immature embryos were obtained. Finally, 31 clones were obtained by inoculating some of the immature embryos. These clones can be divided into three categories according to the number of pollen grains: A, highly sterile; B, partially sterile (with trace amount of pollen); C, fully fertile (morphological performance similar to the female parent, pseudo-hybrid). Among them, type B can obtain a small amount of shriveled seeds through assisted pollination at the bud stage, and a small amount of clones can be obtained through the rescue of im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com