Preparation method of cubic structure CoSbS thermoelectric compound
A cubic structure and compound technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of CoSbS-based thermoelectric materials, can solve the problems of high overall cost, inability to obtain high symmetry cubic structure thermoelectric materials, high cost of Sb single substance, etc., and achieve cheap constituent elements and crystal structure symmetry Controllable, short material cycle results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] In this embodiment, the preparation method of the thermoelectric material of the present invention is described in detail by taking the preparation process of CoSbS as an example.
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes the following steps: 1) batching step; 2) wet ball milling step; 3) drying step; 4) pressing step; 5) sintering step.
[0048] The above five steps will be described in detail below.
[0049] 1) Ingredients step
[0050] Co, Sb, and S are used as raw materials, mixed with the molar ratio of CoSbS molecular formula, and placed in a stainless steel ball mill jar. Preferably, the raw materials are Co powder, Sb powder and S powder with a purity ≥ 99.5%; the raw materials are weighed according to the CoSbS stoichiometric ratio, and the total weight is 5g. The ball-to-material ratio can be set to 20:1.
[0051] Preferably, in order to increase the possibility of more CoSbS-based thermoelectric materials, Ni, Se, Te or Fe can be added to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] In this example, the thermoelectric material Ni x co 1-x SbS (x=0-0.15).
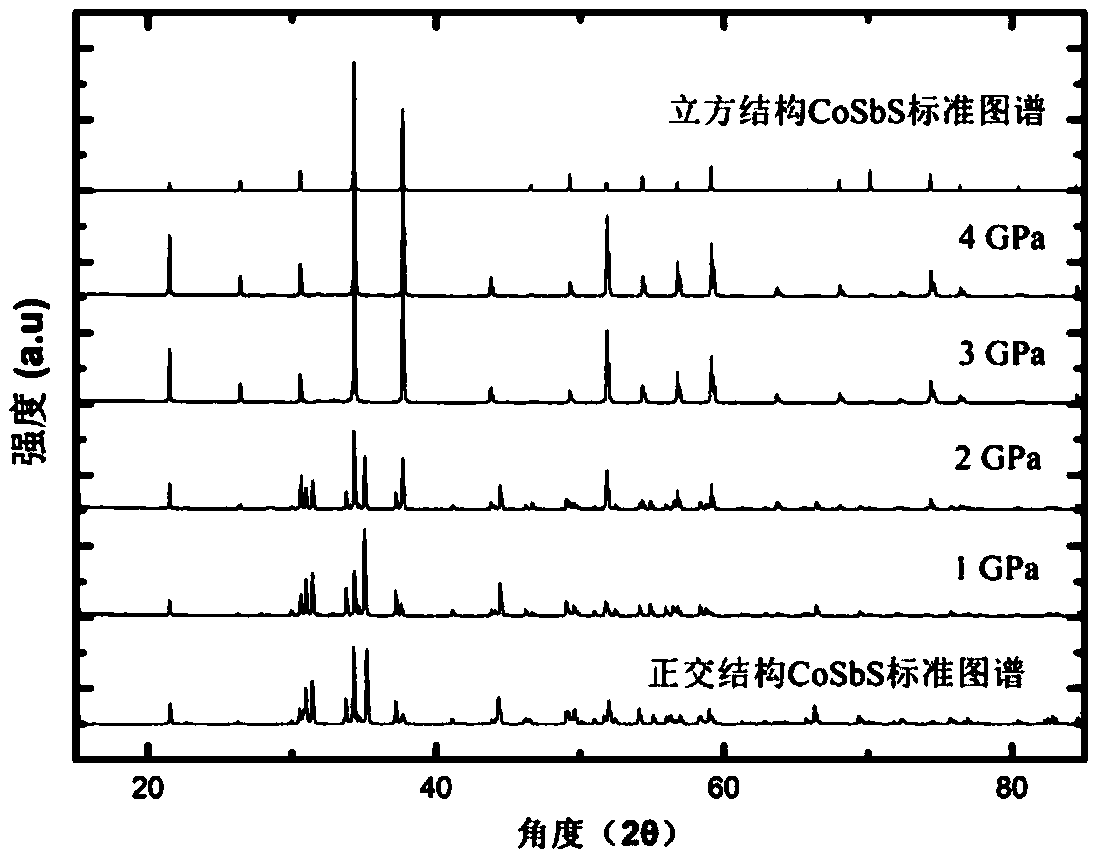
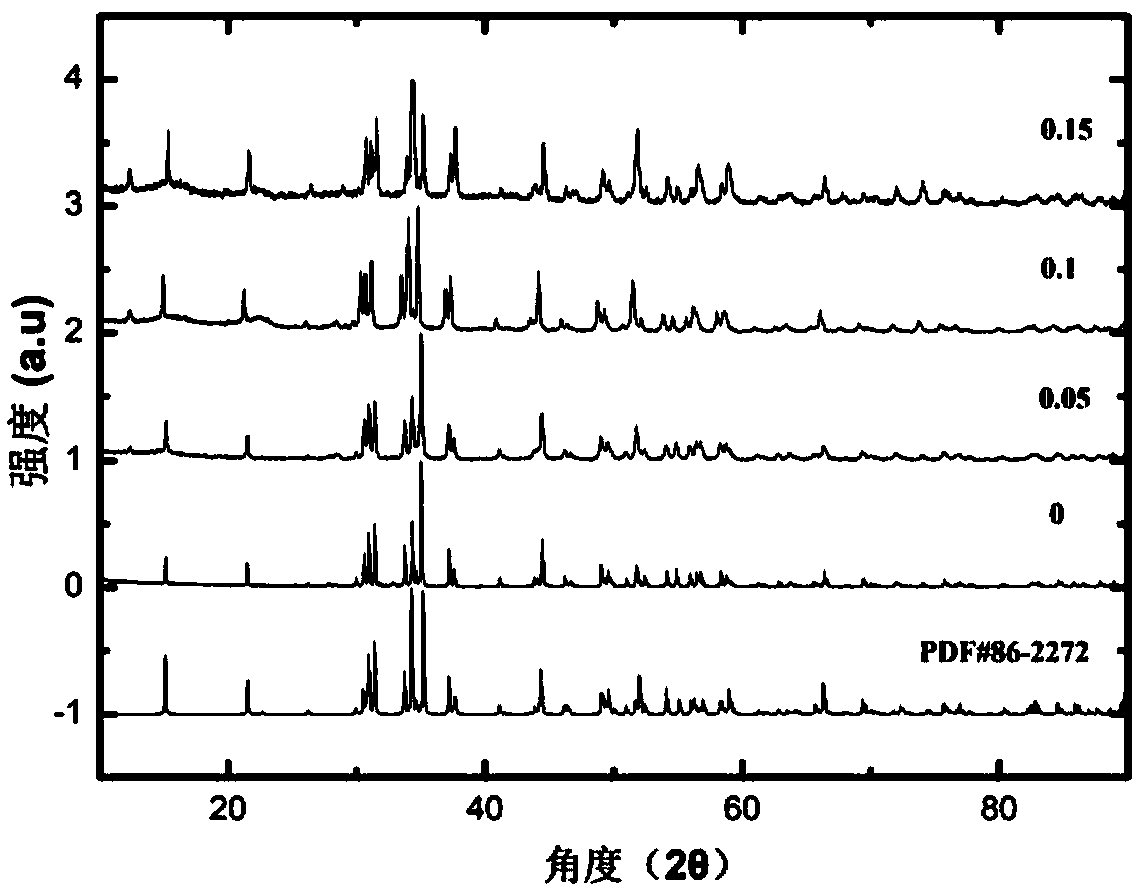
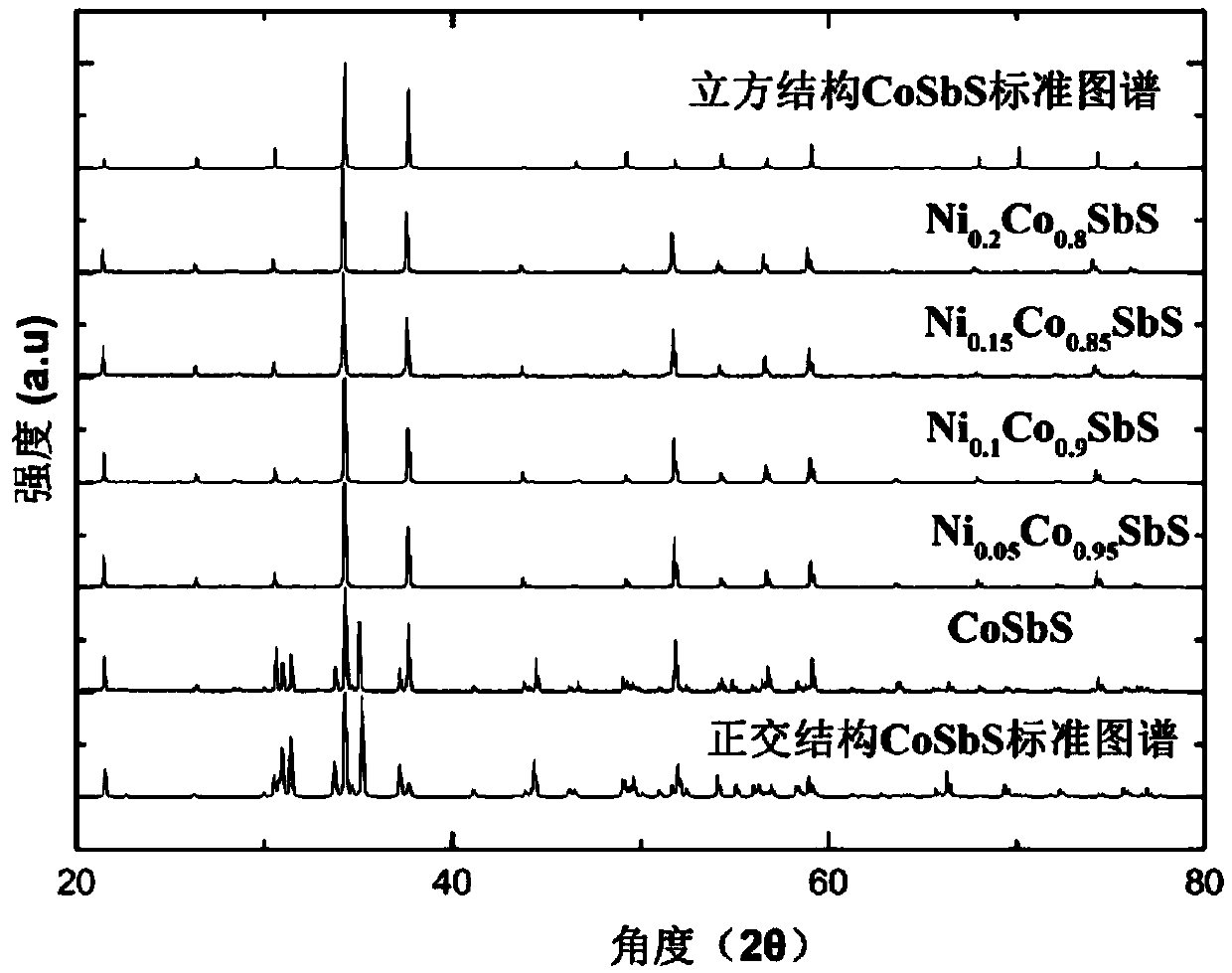
[0063] In the preparation of thermoelectric materials Ni x co 1-x In the process of SbS, the inventor adopted steps similar to those in Example 1, namely 1) batching step; 2) wet ball milling step; 3) drying step; 4) pressing step; 5) sintering step. Wherein the sintering pressure is 1-3GPa. After the sintered samples were tested by X-ray diffraction, it was found that all samples were orthogonal structures under 1GPa conditions (such as figure 2 ), the sample transforms into a cubic structure after doping 5% Ni under the condition of 2GPa (such as image 3 ), that is, Ni doping can reduce the structural transition pressure of CoSbS.
[0064] In order to characterize the properties of samples with different structures, the Ni-doped samples synthesized at 1GPa and 3GPa were cut and polished, and the resistivity, Seebeck coefficient and thermal conductivity of the samples were tested by LSR-...
Embodiment 3
[0068] In this example, the preparation of thermoelectric material Fe x co 1-x SbS (x=0-0.1).
[0069] In the preparation of thermoelectric materials Fe x co 1-x In the process of SbS, the inventor adopted steps similar to those in Example 1, namely 1) batching step; 2) wet ball milling step; 3) drying step; 4) pressing step; 5) sintering step.
[0070] In this embodiment, the sintering pressure is 2GPa. Figure 6 For the X-ray diffraction pattern of the sample, it is found that the Fe-doped CoSbS sample is still an orthorhombic structure, that is, Fe doping cannot reduce the crystal structure transition pressure of CoSbS as Ni does. Since Fe doping does not improve the symmetry of the crystal structure of CoSbS, and provides more electrons to the CoSbS compound, the resistivity of the sample increases and the thermoelectric performance decreases (the power factor of Fe-doped CoSbS at room temperature is only 5×10 -5 μWcm -1 K -2 ).
[0071] Similarly, applicants u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com