A kit for detecting minimal residual disease mrd
A minimal residual disease and kit technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as high requirements for experimental conditions and operating techniques, low standardization, and inability to quantify
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
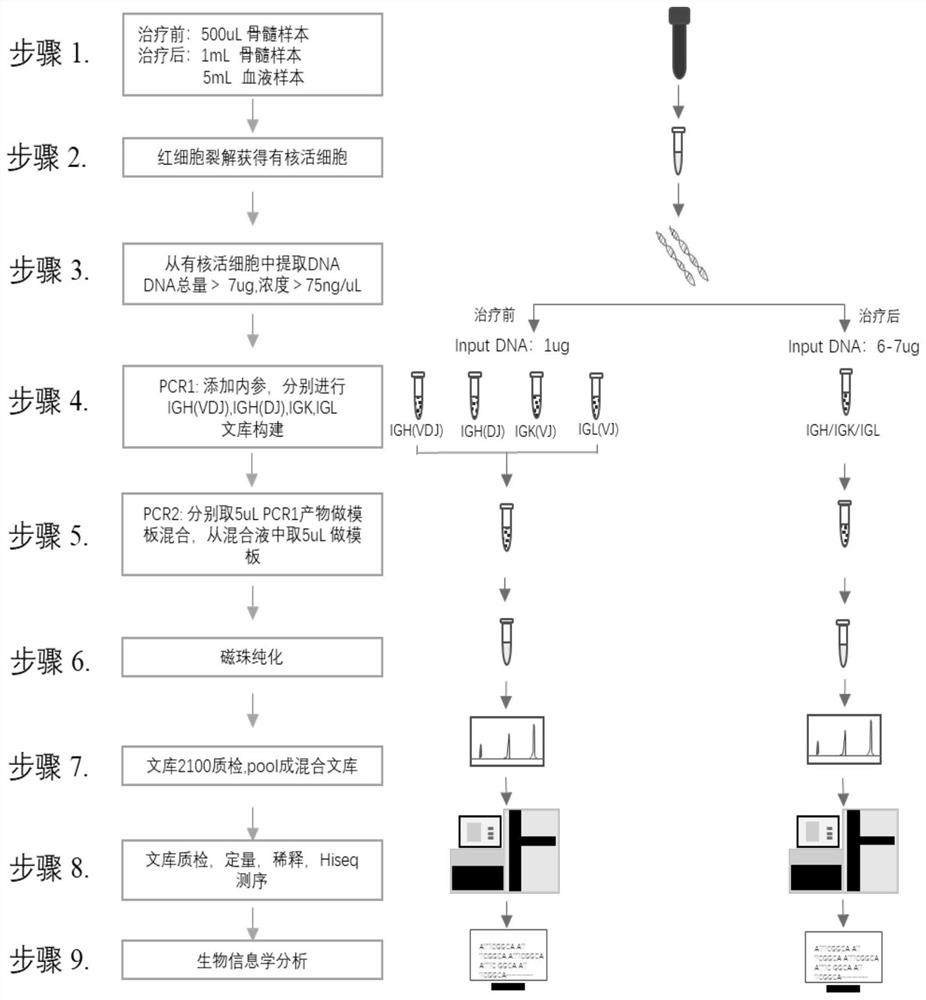
[0068] Example 1: Obtaining the sample genome
[0069] 1. According to before and after treatment and sample specificity, it can be divided into:
[0070] 100uL, 200uL, 300uL, 400uL, 500uL of human bone marrow samples before treatment were placed in EDTA anticoagulation tubes;
[0071] 100uL, 200uL, 300uL, 400uL, 500uL, 600uL, 700uL, 800uL, 900uL, 1mL, 2mL of bone marrow samples after human treatment were placed in EDTA anticoagulation tubes;
[0072] Human peripheral blood samples of 5mL, 6mL, 7mL, 8mL, 9mL, and 10mL were placed in EDTA anticoagulation tubes.
[0073] 2. Use the red blood cell lysate to lyse the red blood cells in the sample and separate the nucleated live cells.
[0074] 3. The obtained nucleated live cells were counted and the genomic gDNA was extracted.
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: Multiplex PCR Amplification and Library Construction
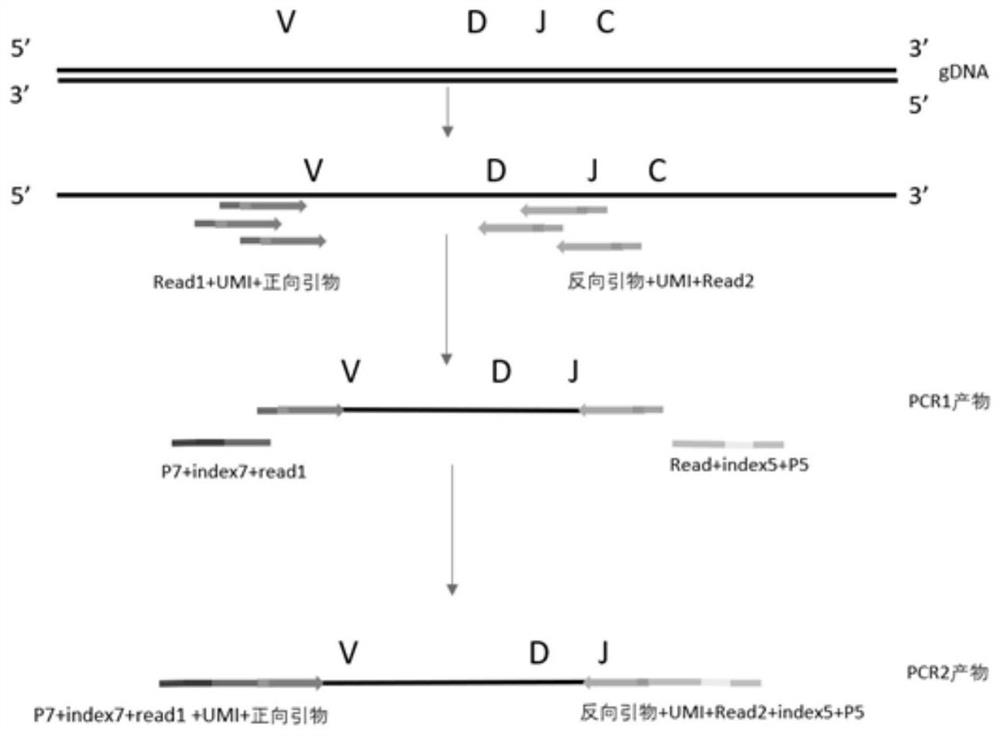
[0076] Using the library building kit in the kit, add multiple pairs of primers of V gene fragment and J gene fragment with UMB into the multiplex PCR reaction system, and add any three corresponding 1% input DNA template amount of known The internal reference DNA or House Keeping gene of the sequence is specifically amplified at the same time as the sample.
[0077] The primer set sequences are shown in Table 1
[0078] Table 1 Multiplex PCR primers
[0079]
[0080]
[0081]
[0082]
[0083] The primer sequence structure is as figure 2 shown, wherein the Read1 sequence is SEQ ID NO: 248, and the Read2 sequence is SEQ ID NO: 249.
[0084] The sequence of the internal reference DNA is shown in SEQ ID NOs: 128-226.
[0085] The PCR primer sequences for amplifying the House Keeping gene are shown in SEQ ID NOs: 250-253.
[0086] Multiplex PCR system, including 25μL, 50μL, the following is...
Embodiment 3
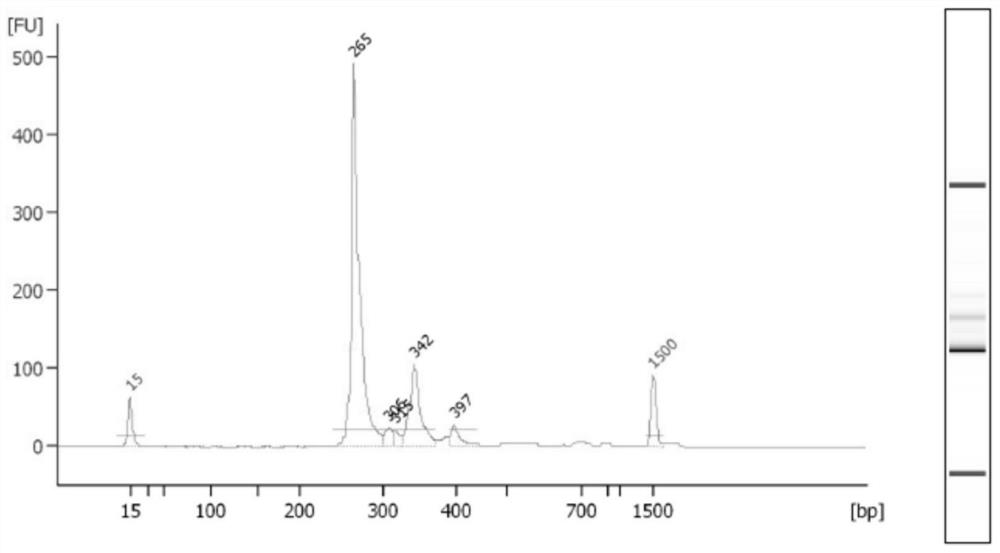
[0092] Example 3: High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
[0093] The method of the present invention uses the Hiseq system from illumina company. Hiseq is a single-molecule cluster-based sequencing-by-synthesis technology based on a proprietary reversible termination chemical reaction principle. During sequencing, random fragments of DNA are attached to the optically transparent glass surface (Flow cell). After extension and bridge amplification, these DNA fragments form hundreds of millions of clusters (clusters) on the Flow cell. Thousands of single-molecule clusters of the same template. Then, four kinds of special deoxyribonucleotides with fluorescent groups are used to sequence the template DNA to be tested by reversibly terminated sequencing by synthesis (Sequencing by Synthesis, SBS) technology.
[0094] First, the primers and tags of the illumina high-throughput sequencer were added to both ends of the PCR1 product, and amplified at the same time (see...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com