Detection method for evaluating intestine toxicity of medicine by utilizing 3D organ
An organoid, enterotoxic technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of unreported safety evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Example 1 Sorting of C57BL / 6 mouse crypts and culture of 3D organoids
[0114] (1) Take the small intestine of 6-8 week-old C57BL / 6 mice, divide the small intestine into several 5-8cm long segments from the position 1-2cm away from the duodenum, remove the connective tissue on the small intestine, and Cut it in the middle, wash it with pre-cooled phosphate buffered saline (Phosphate buffered saline, PBS), then transfer it to a 50ml centrifuge tube containing an appropriate amount of PBS, and place it on ice.
[0115] (Note: All the following steps are performed in a sterile environment, and the crypts must be placed on ice as much as possible.)
[0116] (2) In a biological safety cabinet, wash the small intestine fragment with PBS containing penicillin / streptomycin (P / S) for 3-4 times, then transfer it to a 50ml centrifuge tube, add 25ml of PBS containing 2mM EDTA , digested in a refrigerator at 4°C, and after 10 minutes, transfer the small intestine fragments to a new...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Embodiment 2 Verification of 3D organoid model
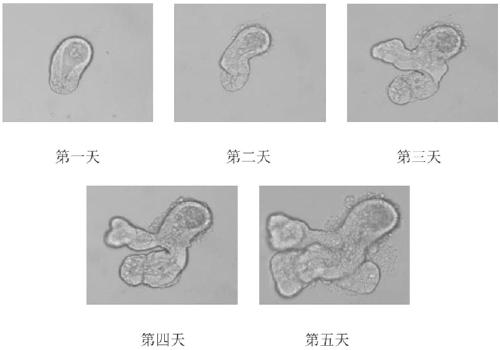
[0125] 2.1 Observation of 3D organoid morphology
[0126] The crypt culture of C57BL / 6 mice was observed and photographed under the Olympus IX 71 microscope equipped with the Olympus DP 71 camera system every day from the first day to the fifth day of culture. The result is as figure 1 shown. From figure 1 Organoid structures derived from crypt differentiation can be seen in . A villous spherical cavity formed in the center of the organoid, surrounded by newly formed crypts.
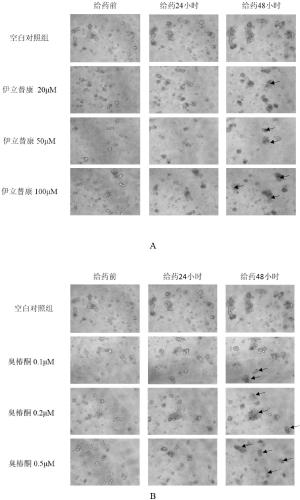
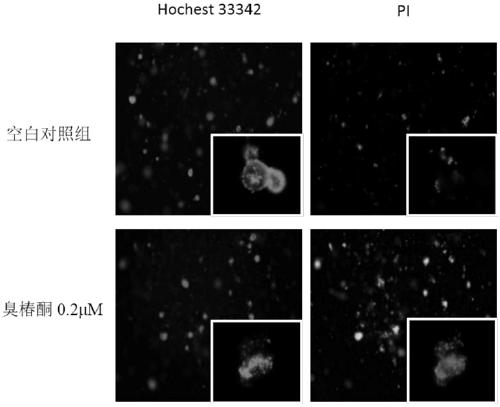
[0127] 2.2 Evidence of enterotoxicity of drugs from changes in organoid morphology
[0128] (1) Preparation of drug-containing medium. A 100 mM stock solution of irinotecan was prepared in DMSO and diluted to 5 μM, 10 μM, 20 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM with complete medium containing growth factors (Responding, m-noggin, m-EGF). 10 μM stock solution of ailanthone was prepared in DMSO and diluted to 0.02 μM, 0.05 μM, 0.1 μM, 0.2 μM, 0.5 μM with complete...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3 Using 3D organoids to study the enterotoxic dose of drugs
[0138] (1) Preparation of drug-containing medium. The preparation method and concentration setting are the same as "Example 2.2".
[0139] (2) On the third day of organoid culture, aspirate the original medium in the cell plate, add complete medium containing different concentrations of irinotecan or ailanthonone, set 3 parallel groups for each concentration, and set 3 blanks at the same time For medium control wells, the cell plate was placed in a 37°C cell culture incubator to continue culturing.
[0140] (3) After 48 hours of administration, the cell plate was taken out from the incubator and added to the MTS kit in the dark. Add 20 μl of MTS solution to 100 μl of culture medium in each well, shake gently after adding, and incubate for 2 hours in a 37°C cell culture incubator protected from light.
[0141] (4) After the incubation, the absorbance value of each well (the absorbance wavelength is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com