Vegetable oil degumming method
A vegetable oil and degumming technology, applied in the field of vegetable oil degumming, can solve the problems of low degumming efficiency and achieve the effect of continuous production, high-efficiency separation and improved yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
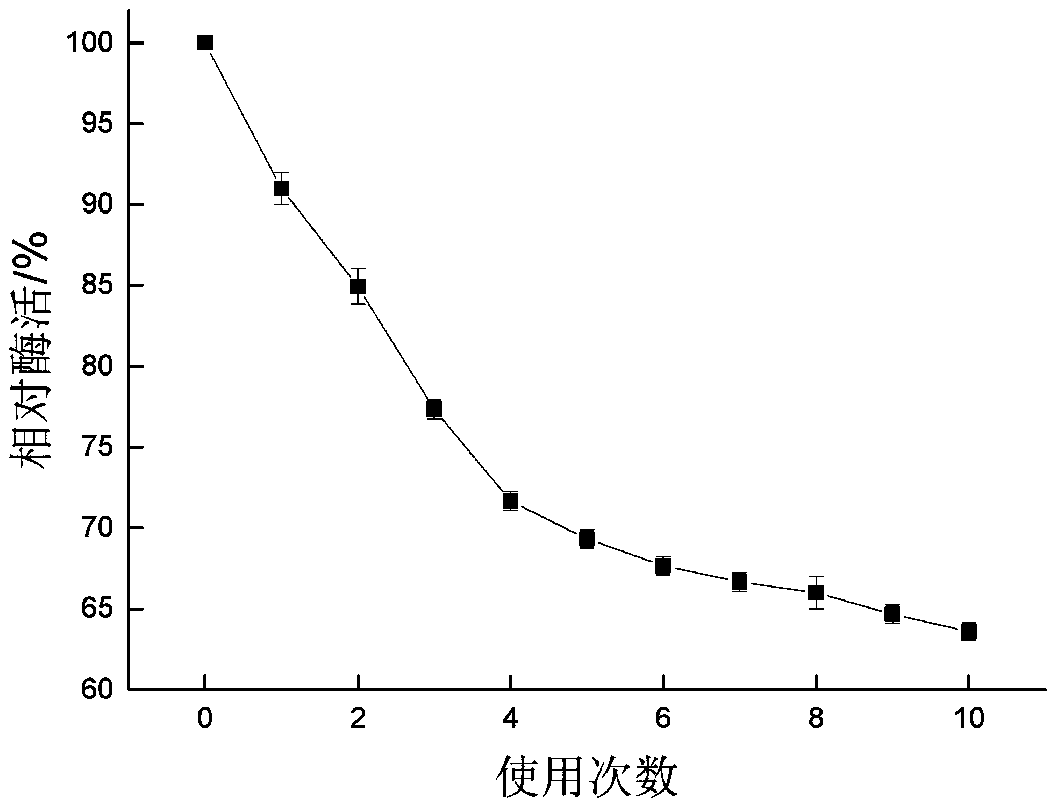
[0043] Preparation of immobilized phospholipase C: Weigh the cross-linked Fe 3 o 4 50 mg of the composite carrier was put into an Erlenmeyer flask, and 8.0 mL of 0.02 g / mL phospholipase C solution (diluted with pH 6.7 phosphate buffer) was added. In a water-bath shaker, react at 30°C and 150r / min for 7.9h. Subsequently, the immobilized phospholipase C was separated with a permanent magnet, and washed repeatedly with phosphate buffer (pH=7.0) until no free enzyme was detected in the supernatant. The immobilized phospholipase C was prepared.
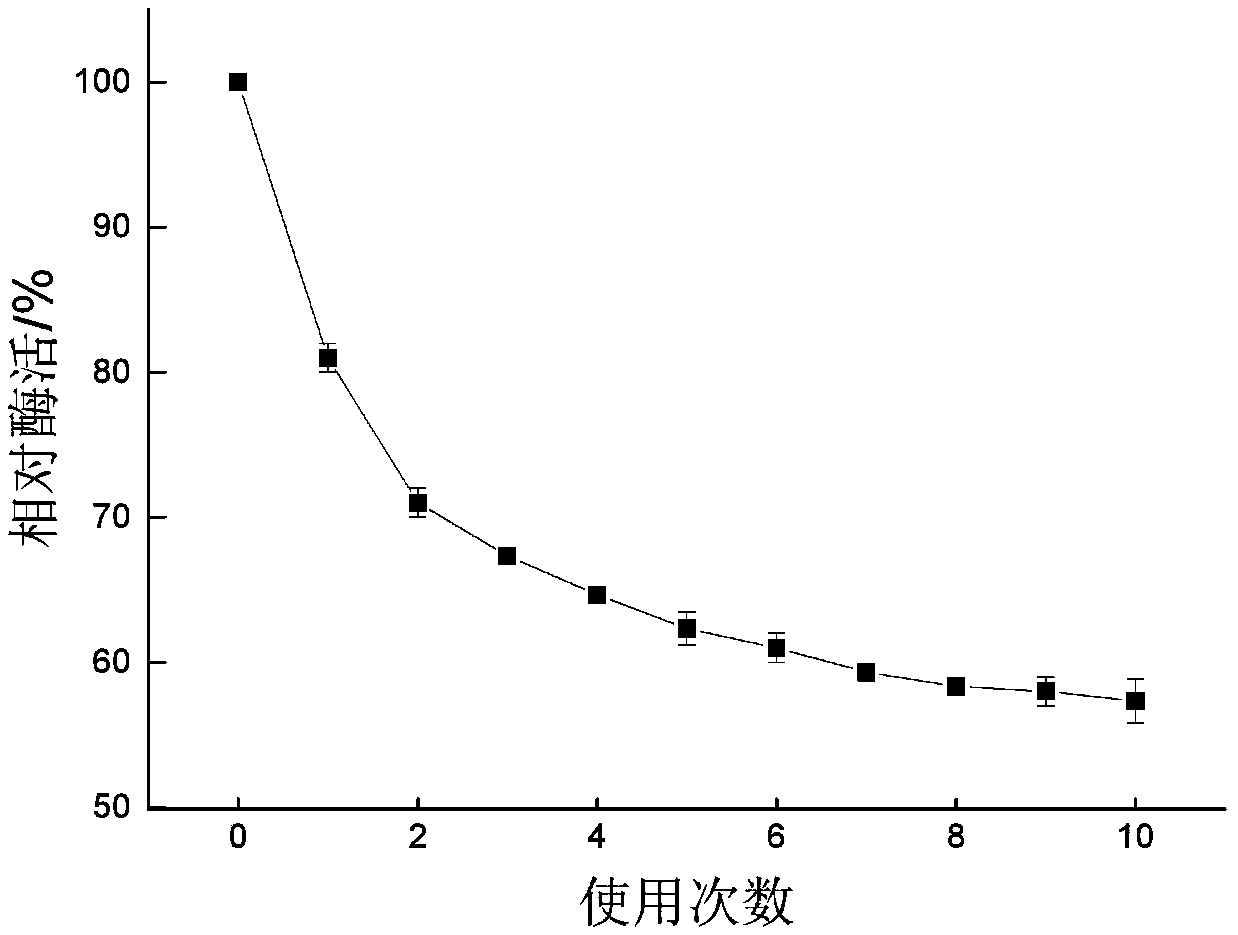
[0044] immobilized phospholipase A 1 Preparation: Take 0.2 g of the pretreated macroporous resin, place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 6.0 mL of phospholipase A diluted with 0.1 mol / L, pH 7.0 phosphate buffer 1 The enzyme solution was immobilized in a water-bath shaker at 25°C for 6.0 hours, then added a certain amount of glutaraldehyde solution to cross-link for 8.0 hours, and finally washed several times with phosphate buffer u...
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for degumming rapeseed oil, comprising the following steps:
[0058] S1: phospholipase immobilization;
[0059] Phospholipase A 1 The immobilization of and the immobilization of phospholipase C;
[0060] Preparation of immobilized phospholipase C: Weigh the cross-linked Fe 3 o 4 50 mg of the composite carrier was put into an Erlenmeyer flask, and 6.0 mL of 0.02 g / mL phospholipase C solution (diluted with pH 6.7 phosphate buffer) was added. In a water-bath shaker, react for 7.0 h at 35° C. and 160 r / min. Subsequently, the immobilized phospholipase C was separated with a permanent magnet, and washed repeatedly with phosphate buffer (pH=7.0) until no free enzyme was detected in the supernatant. The immobilized phospholipase C was prepared.
[0061] immobilized phospholipase A 1 Preparation: Take 0.2 g of the pretreated macroporous resin, place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 6.0 mL of phospholipase A diluted...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of method of soybean oil degumming, comprises the following steps:
[0071] S1: phospholipase immobilization;
[0072] Phospholipase A 1 The immobilization of and the immobilization of phospholipase C;
[0073] Preparation of immobilized phospholipase C: Weigh the cross-linked Fe 3 o 4 50 mg of the composite carrier was put into an Erlenmeyer flask, and 8.0 mL of 0.02 g / mL phospholipase C solution (diluted with pH 6.7 phosphate buffer) was added. In a water-bath shaker, react for 8.0 hours at 25°C and 150r / min. Subsequently, the immobilized phospholipase C was separated with a permanent magnet, and washed repeatedly with phosphate buffer (pH=7.0) until no free enzyme was detected in the supernatant. The immobilized phospholipase C was prepared.
[0074] immobilized phospholipase A 1 Preparation: Take 0.2 g of the pretreated macroporous resin, place it in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 6.0 mL of phospholipase...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com