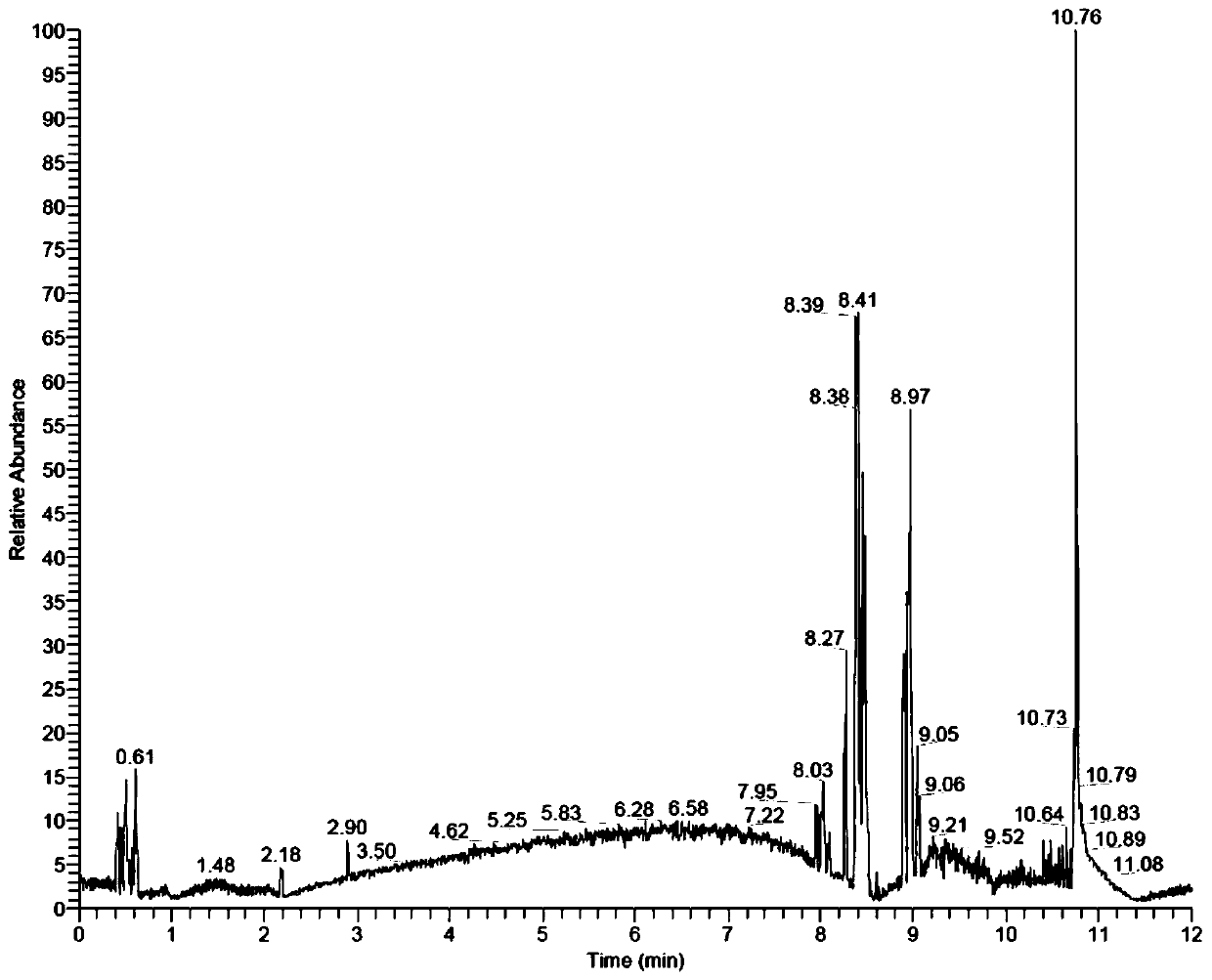
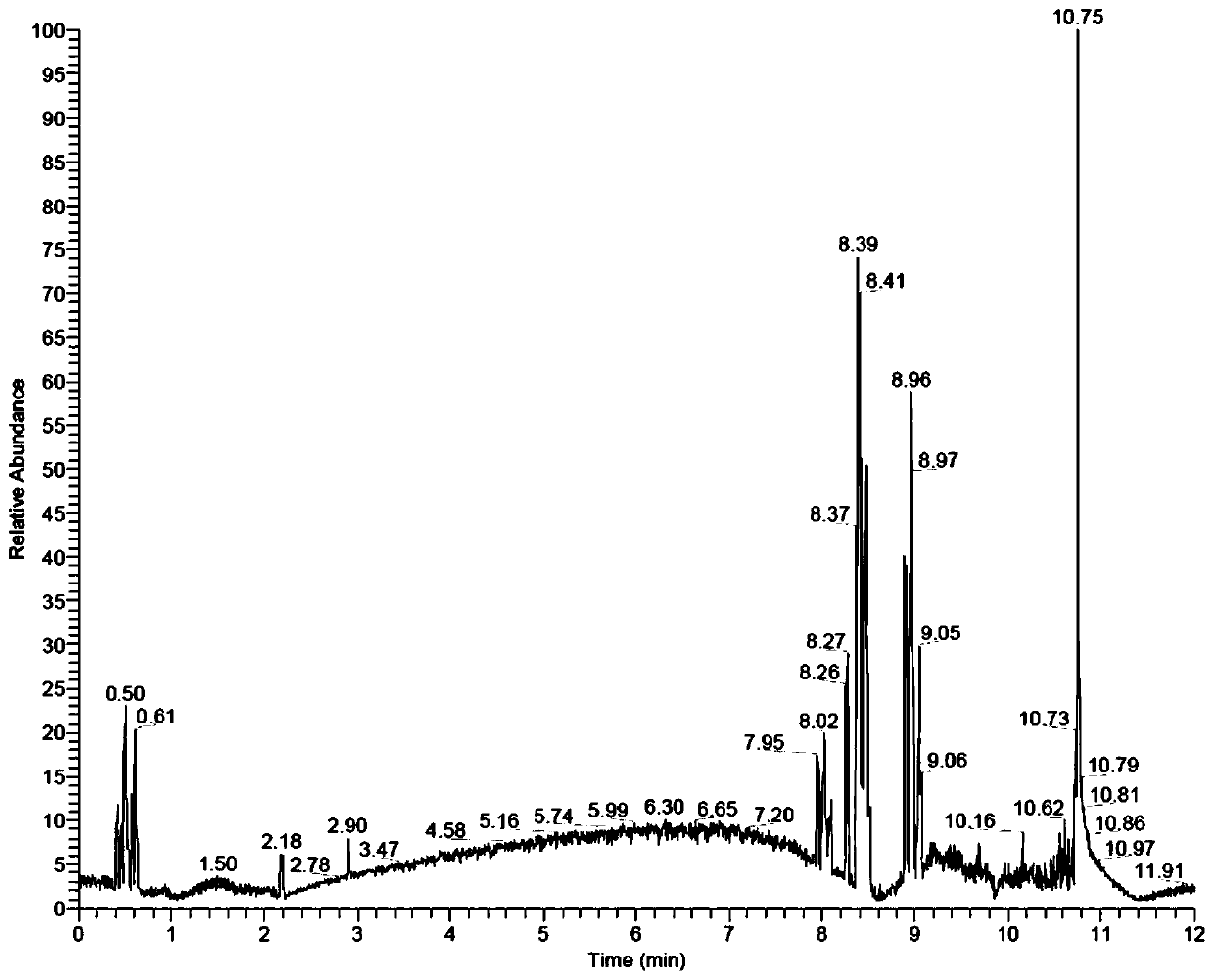
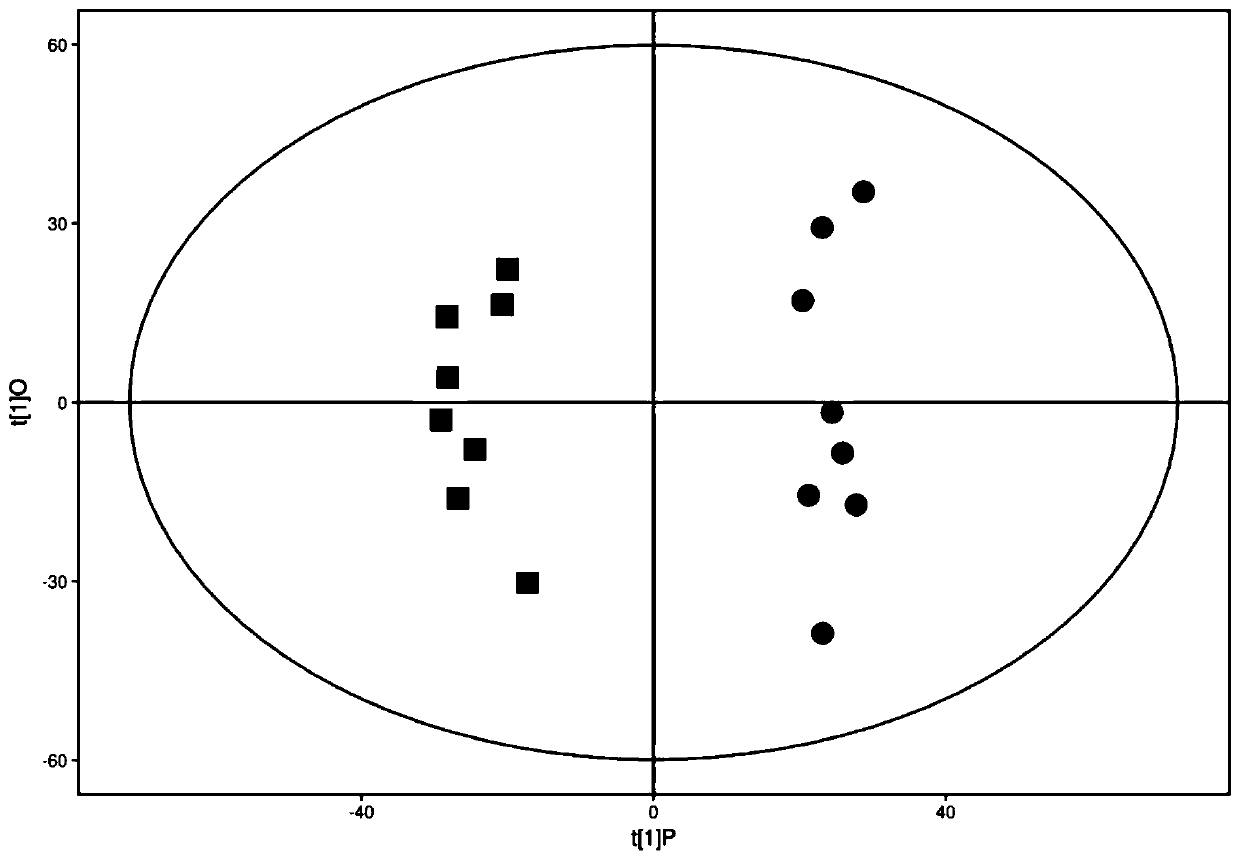
Method for obtaining metabolic difference between genetically modified and non-genetically modified maize based on UHPLC-MS (Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer)
A transgenic corn, non-transgenic technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of low accuracy of liquid mass analysis platform, less compound information, easy to introduce errors, etc., to achieve efficient and reliable metabolite information identification, high detection resolution, elimination of the effect of interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] This example provides a UHPLC-MS-based method for obtaining metabolic differences between transgenic and non-transgenic maize, specifically:
[0087] 1) Preparation of samples to be tested:
[0088] 1) The young leaves of the transgenic MhSnf7 corn (TJ806) and TJ806 non-transgenic corn that grew to the 5-6 leaf stage were collected, quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored in a -80°C refrigerator for later use;
[0089] 2) Quickly place the leaves taken out of the cryogenic refrigerator into a liquid nitrogen pre-cooled mortar; pour a little liquid nitrogen, and grind with a pre-cooled pestle until the leaves are in a powder state;
[0090] 3) Weigh 20 ± 1 mg of crushed sample, place it in a 2 mL centrifuge tube, place the centrifuge tube containing the sample on ice; add two grinding beads, one large and one small, into the sample centrifuge tube. The diameter of the large magnetic bead is 5mm, and the diameter of the small magnetic bead is 3mm;
[0091] 4) Add ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mobile phase | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com