Biodegradable foamed material and method for utilizing biodegradable foamed material to manufacture heat-resistant foamed lunch box
A biodegradable and foaming material technology, applied in the field of foaming materials, can solve problems such as poor fluidity, poor processing performance, rotation and translation restrictions, etc., to improve heat resistance, increase melt strength, and improve foaming performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1) The formula of the biodegradable foaming material is (by mass parts):
[0034] Polylactic acid (8052D, NatureWorks, USA): 100;
[0035] Chain extender (S-MA-GMA, ADR 4370, BASF, Germany): 0.8
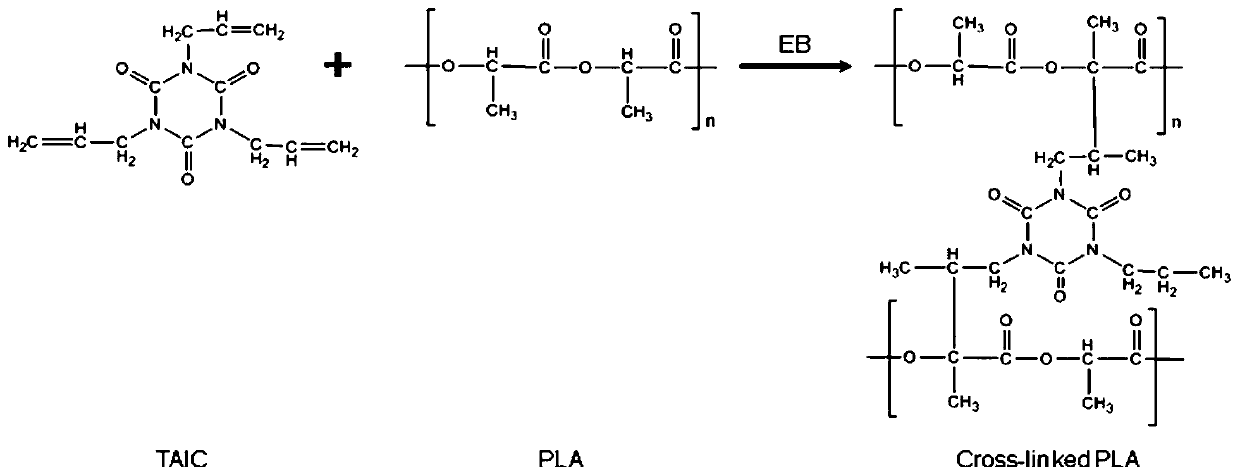
[0036] Triallyl isocyanurate: 0.6;
[0037] Tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate] pentaerythritol ester: 0.2;
[0038] Other additives: 0.5.
[0039] 2) Preparation process of biodegradable foam sheet
[0040] First dry polylactic acid in a dryer at 80°C for 10 hours, then dry polylactic acid, ADR 4370, triallyl isocyanurate, tetrakis[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzene base) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester and other additives are added to the high-speed mixer according to the above-mentioned mass fraction and mixed evenly, and supercritical carbon dioxide is used as a foaming agent to continuously extrude and foam the described The mixture is obtained from the biodegradable foam sheet.
[0041] 3) thermoforming the biodegradable foamed sheet in...
Embodiment 2
[0044] 1) The formula of the biodegradable foaming material is (by mass parts):
[0045] Polylactic acid (8052D, NatureWorks, USA): 100;
[0046] Chain extender (S-MA-GMA, ADR 4370, BASF, Germany): 0.8
[0047] Triallyl isocyanurate: 0.1;
[0048] Tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate] pentaerythritol ester: 0.2;
[0049] Other additives: 0.5.
[0050] 2) Preparation process of biodegradable foam sheet
[0051] First dry polylactic acid in a dryer at 80°C for 10 hours, then dry polylactic acid, ADR 4370, triallyl isocyanurate, tetrakis[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzene base) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester and other additives are added to the high-speed mixer according to the above-mentioned mass fraction and mixed evenly, and supercritical carbon dioxide is used as a foaming agent to continuously extrude and foam the described The mixture is obtained from the biodegradable foam sheet.
[0052] 3) thermoforming the biodegradable foamed sheet in...
Embodiment 3
[0055] 1) The formula of the biodegradable foaming material is (by mass parts):
[0056] Polylactic acid (8052D, NatureWorks, USA): 100;
[0057] Chain extender (S-MA-GMA, ADR 4370, BASF, Germany): 0.8
[0058] Triallyl isocyanurate: 5;
[0059] Tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate] pentaerythritol ester: 0.2;
[0060] Other additives: 0.5.
[0061]2) Preparation process of biodegradable foam sheet
[0062] First dry polylactic acid in a dryer at 80°C for 10 hours, then dry polylactic acid, ADR 4370, triallyl isocyanurate, tetrakis[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzene base) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester and other additives are added to the high-speed mixer according to the above-mentioned mass fraction and mixed evenly, and supercritical carbon dioxide is used as a foaming agent to continuously extrude and foam the described The mixture is obtained from the biodegradable foam sheet.
[0063] 3) thermoforming the biodegradable foamed sheet into ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com