Scattered field determining method of nonuniform medium target body
A technology of non-uniform medium and determination method, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of troublesome judgment process, non-uniform medium scattering, inability to save memory, etc., and achieve the effect of saving memory and reducing the number of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
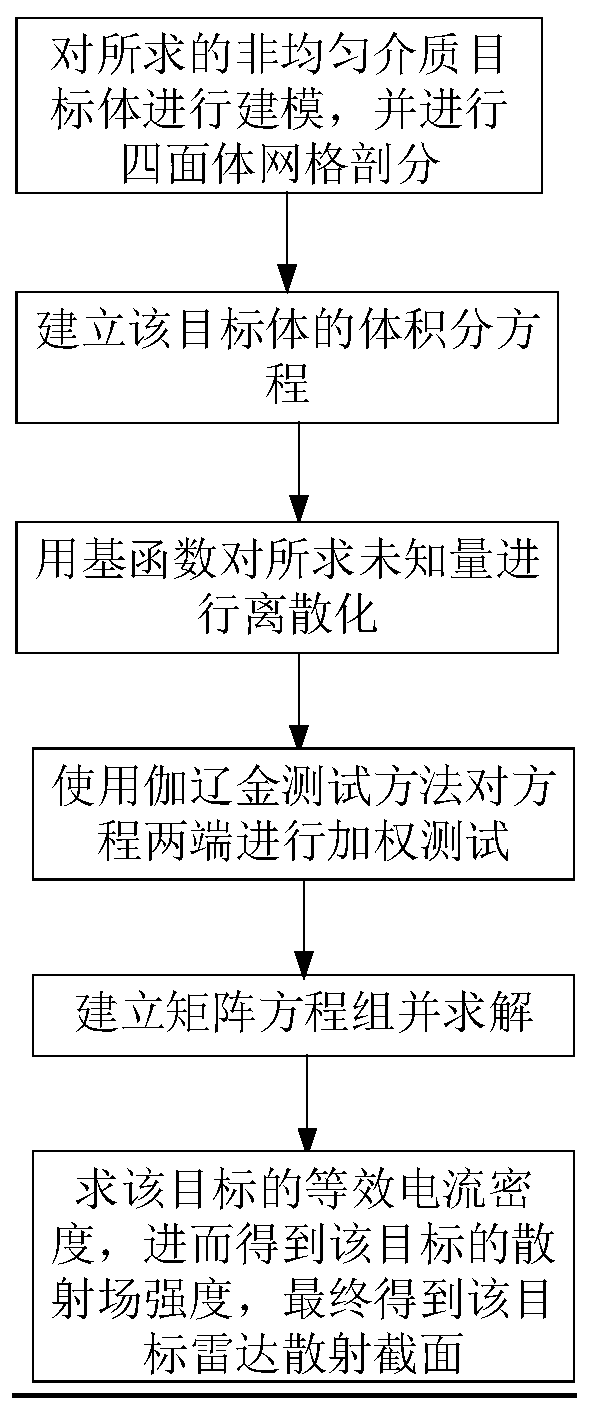
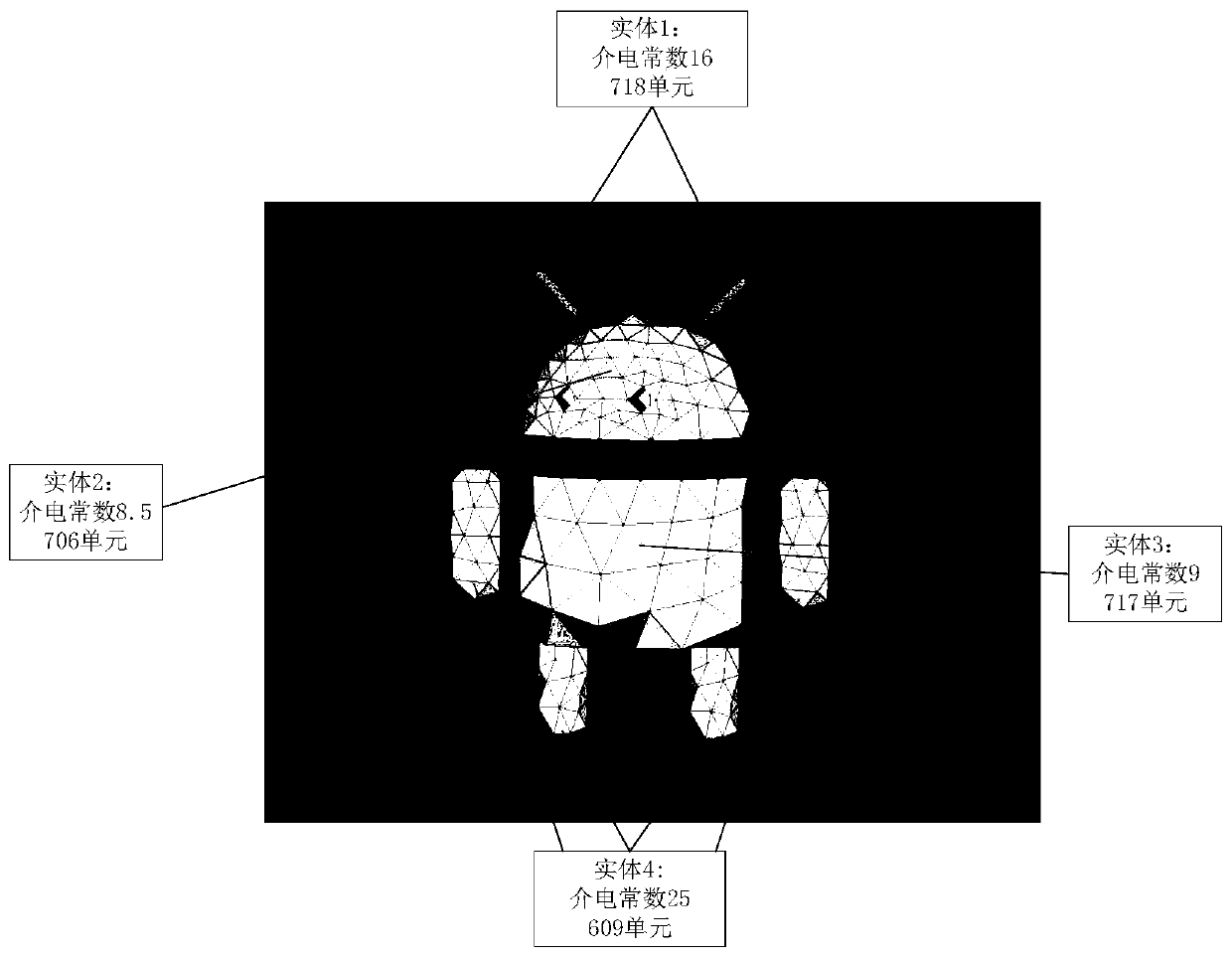
[0024] The research on the electromagnetic characteristics of medium targets is an important application research in the field of computational electromagnetics. It is used in radar system design, target recognition and classification, detection of space suspended medium objects, identification and stealth of military complex medium targets, and reduction of radar scattering cross section. Target stealth has become an important engineering application problem in military and communication. When solving the problem of medium body scattering, in order to better simulate the shape of medium targets, relatively fine subdivision rules are often used, and the requirements of non-uniform media for subdivision It is more strict, and conformal subdivision technology is required. In this way, the mesh must be divided according to the entity with the largest dielectric constant, resulting in a particularly small side length of the small tetrahedron, resulting in a huge unknown quantity, an...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The method for determining the electromagnetic scattering field of the heterogeneous medium target is the same as embodiment 1, and the establishment of the heterogeneous medium target volume integral equation described in step (3) includes the following steps:
[0047] E(r)-ZL(J)=E i (r)
[0048] in:
[0049]
[0050] J(r)=jω∈ 0 [∈ r (r)-1]E(r)
[0051]
[0052] In the formula:
[0053] E(r) represents the electric field strength inside the dielectric body.
[0054] Z represents the wave impedance of free space.
[0055] E. i (r) represents the incident field.
[0056] k represents the wave number in free space.
[0057] G represents the Green's function of free space.
[0058] ∈ 0 Indicates the permittivity of free space.
[0059] ∈ r Indicates the dielectric constant of the medium.
[0060] r represents the observation point and r' represents the source point.
Embodiment 3
[0062] The method for determining the electromagnetic scattering field of the heterogeneous medium object is the same as embodiment 1-2, the discretization process to the electric field intensity of each small tetrahedron described in step (4), see Figure 4 , including the following steps:
[0063] Expand the electric field strength E as:
[0064]
[0065] in:
[0066]
[0067] N represents the number of small tetrahedra after discretization.
[0068] i represents the four vertices of the small tetrahedron, see Figure 4 , Figure 4 The four vertices in are 1,2,3,4 respectively.
[0069] a mi Indicates the area of the face opposite to the i-th vertex of the small tetrahedron.
[0070] V m represents the volume of a small tetrahedron.
[0071] Represents the unit vector from the i-th vertex of the small tetrahedron to the i-th Gaussian integration point. When doing volume Gaussian integration, if the body center distance of two small tetrahedrons is d>0.1λ, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com