Planting mode capable of reducing emission of soil greenhouse gas N2O
A greenhouse gas and soil technology, applied in grain cultivation, root crop cultivation, etc., to achieve the effect of taking into account crop yield and reducing emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: Single cropping corn
[0033] 1.1 Corn variety: Xundan 7
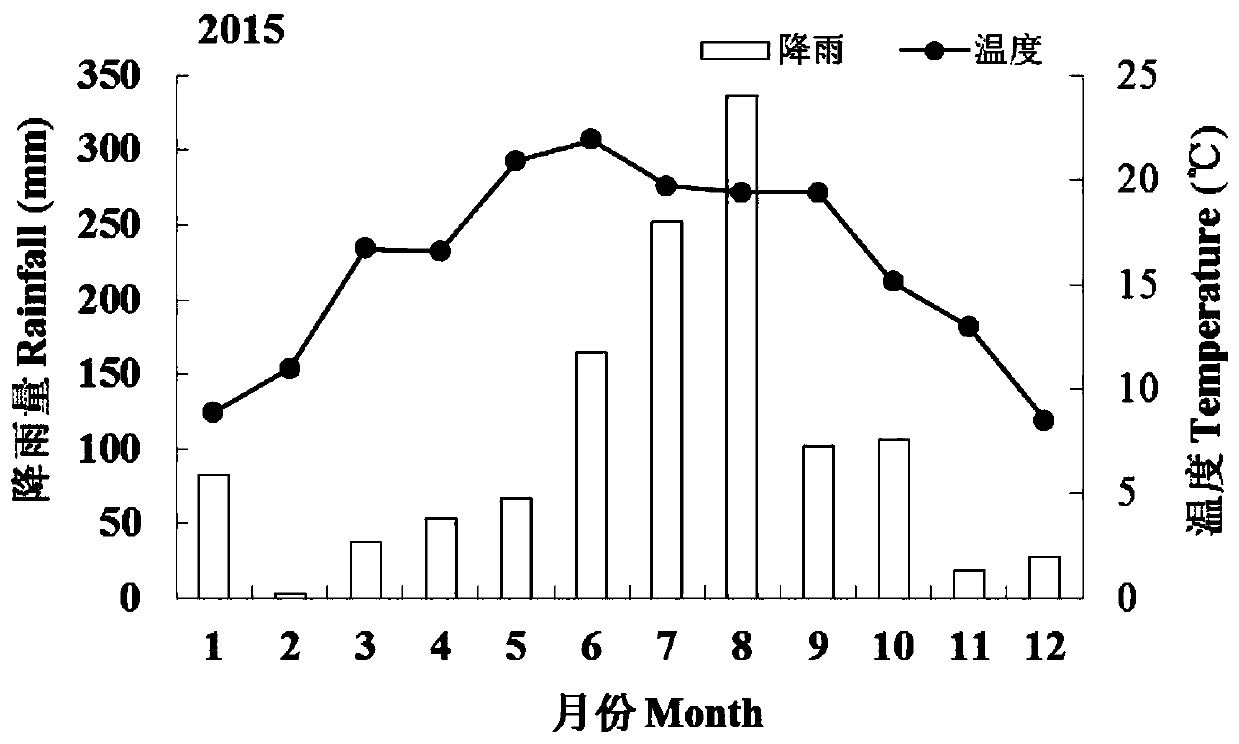
[0034] The field plot experiment adopted a random block design in which planting mode was the main treatment and nitrogen application rate was the secondary treatment.
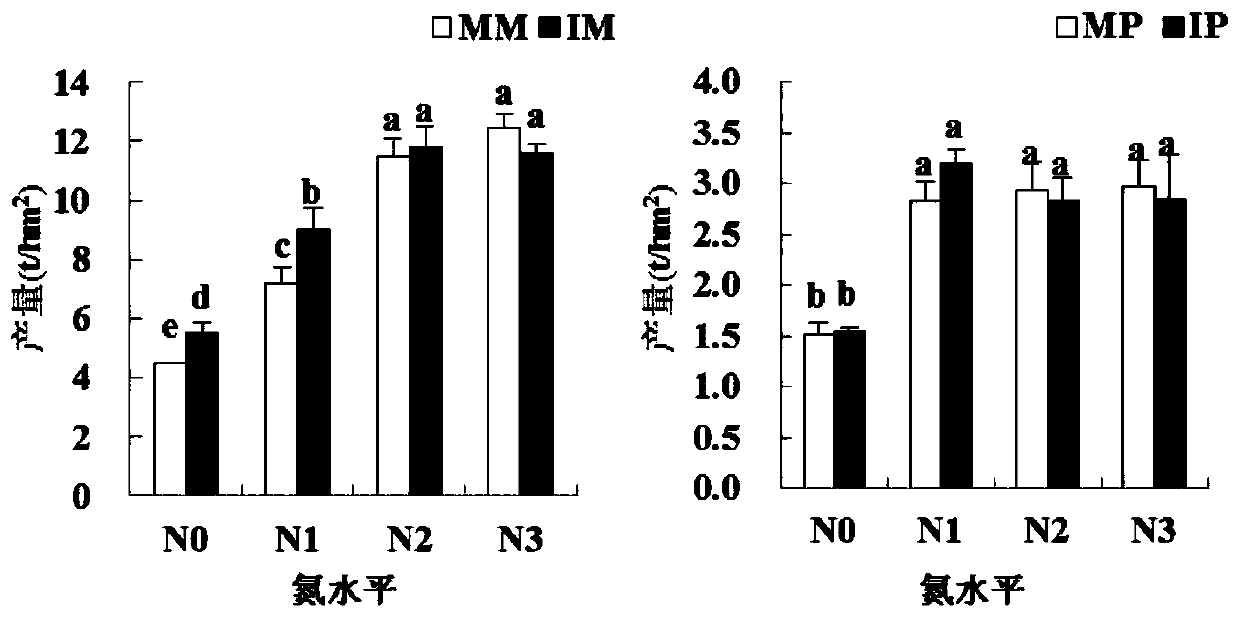
[0035] 1.2 Nitrogen application level: 4, no nitrogen application (N0), 1 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N1), conventional nitrogen application (N2), 3 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N3), conventional nitrogen application for corn is 250kg / hm 2 , divided into basal fertilizer, small trumpet-mouth topdressing and large trumpet-mouth topdressing for three times, accounting for 8 / 20, 5 / 20, and 7 / 20 of the total nitrogen application respectively. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers for corn were all applied as base fertilizer, respectively as phosphorus (P 2 o 5 )75kg / hm 2 , Potassium (K 2 O) 75kg / hm 2 , The nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers used in the test were 46% urea, 14% general calcium and 50% pot...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: Single cropping potatoes
[0050] 1.1 Potato variety: Huize No. 2
[0051] The field plot experiment adopted a random block design in which planting mode was the main treatment and nitrogen application rate was the secondary treatment.
[0052] 1.2 Nitrogen application level: 4, no nitrogen application (N0), 1 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N1), conventional nitrogen application (N2), 3 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N3), that is, the conventional nitrogen application of potatoes is 125kg / hm 2 , applied twice, basal fertilizer 60%, budding stage 40%. Phosphorus (P 2 o 5 )75kg / hm 2 , Potassium (K 2 O) 125kg / hm 2 , Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied in the form of base fertilizer. The nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers used in the experiment were 46% urea, 14% general calcium and 50% potassium sulfate. See Table 2 for details of conventional nitrogen fertilization methods.
[0053] Table 2 Potato field test ro...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment three: corn potato intercropping
[0067] 1.1 Potato variety: Huize No. 2, corn variety: Xundan No. 7
[0068] The field plot experiment adopted a random block design in which planting mode was the main treatment and nitrogen application rate was the secondary treatment.
[0069] 1.2 Nitrogen application level: 4, no nitrogen application (N0), 1 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N1), conventional nitrogen application (N2), 3 / 2 conventional nitrogen application (N3), conventional nitrogen application for potatoes is 125kg / hm 2 , applied twice, basal fertilizer 60%, budding stage 40%. Phosphorus (P 2 o 5 )75kg / hm 2 , Potassium (K 2 O) 125kg / hm 2 , Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied in the form of base fertilizer. The nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers used in the experiment were 46% urea, 14% general calcium and 50% potassium sulfate. The routine nitrogen application for corn is 250kg / hm 2 , divided into basal fertilizer, s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com