Ratio fluorescence analysis method for detecting mercury ions
An analytical method and a ratiometric fluorescence technique, applied in the field of fluorescence analysis, to achieve the effects of broad application prospects, high precision and sensitivity, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] This embodiment provides a ratiometric fluorescence analysis method for detecting mercury ions, which specifically includes the following steps:
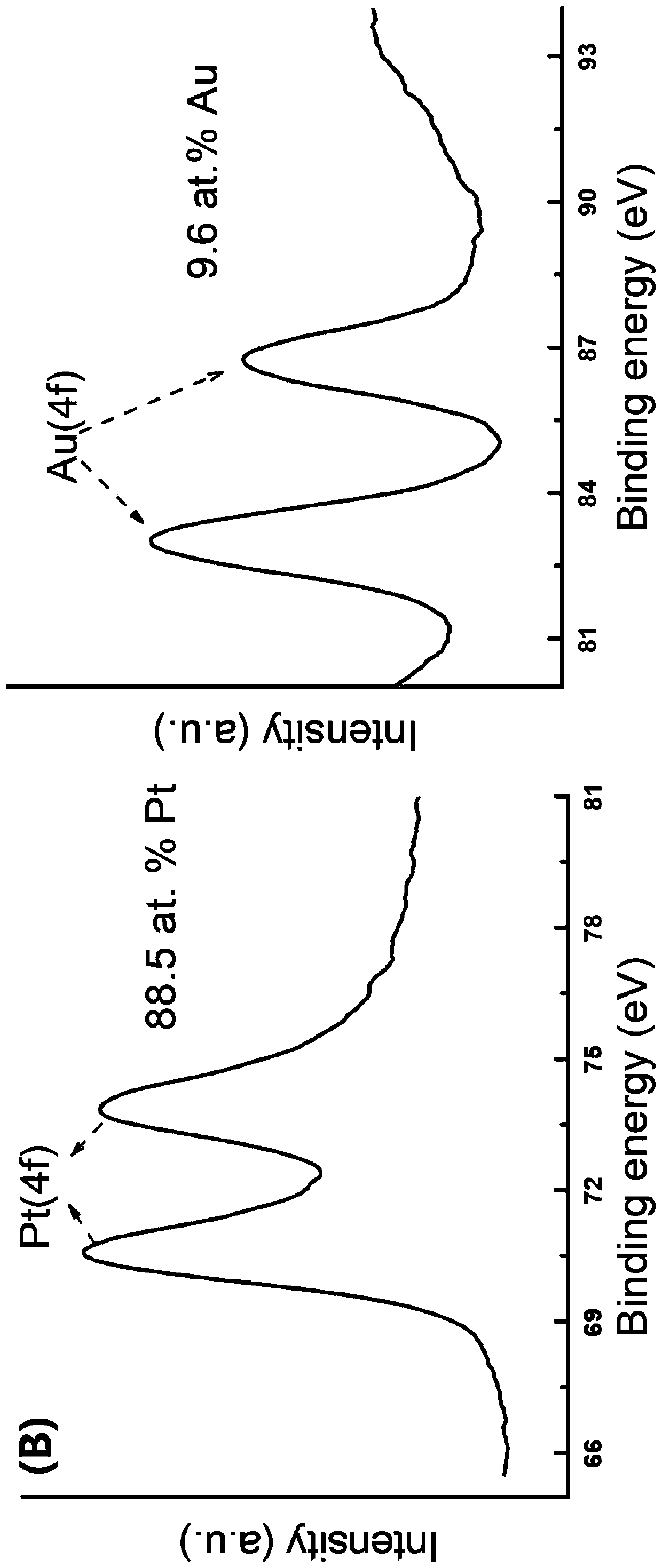
[0040] Step S11. Synthesis of platinum-gold nanoparticles: 0.9 mL K 2 PtCl 4 (20 mM), 0.1 mL HAuCl 4 (20mM) mixed, add 10 mg of poloxamer (Pluronic) F127, ultrasonic to dissolve it, then add 1.0 mL of ascorbic acid (100mM) as a reducing agent, the mixed solution was ultrasonically reacted in a water bath at 30ºC for 5 hours, and the product was subjected to 10000r / min Centrifuge for 20 min to separate, wash with ethanol and water repeatedly 5 times to remove residual PluronicF127, and reconstitute with 0.9 mL of water for later use.
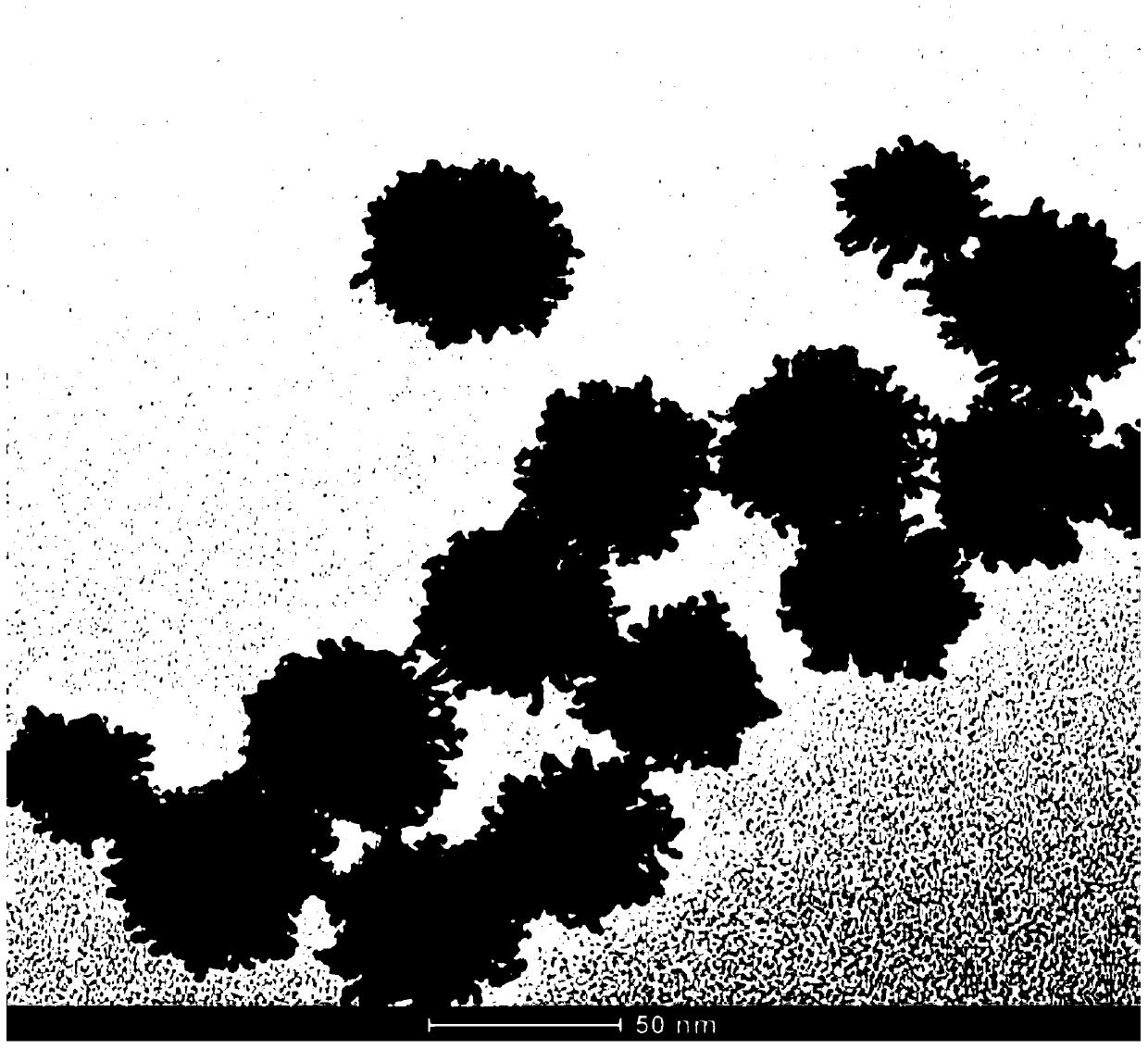
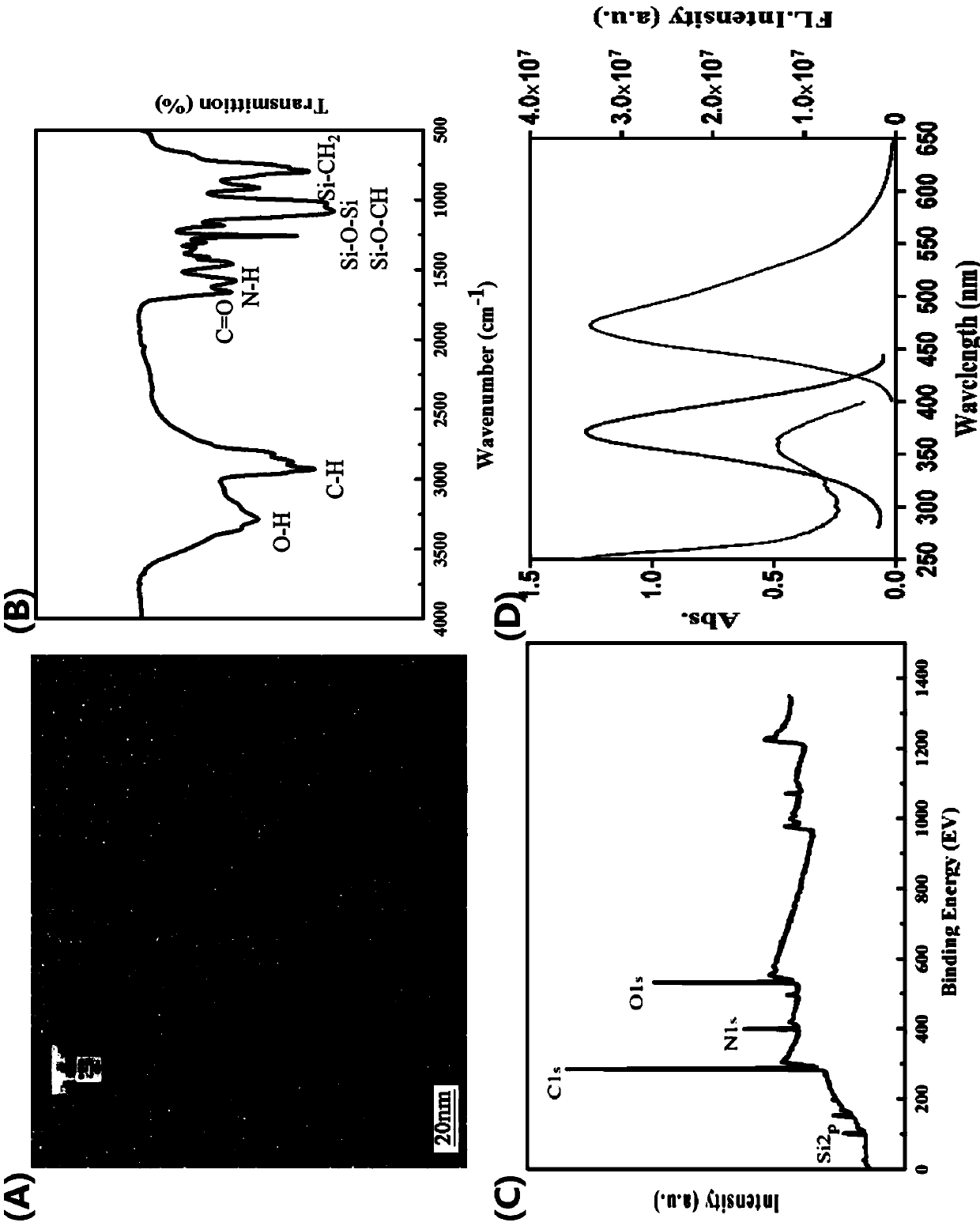
[0041] It can be seen from Figure 1 that the prepared platinum nanoparticles are porous nanostructures with a particle size of about 50 nm, and the surface is composed of uniformly distributed Pt nanoparticles of about 5 nm.
[0042] Step S12. Synthesis of silicon-doped carbon quantum dots: t...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment provides a ratiometric fluorescence analysis method for detecting mercury ions, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0051] Step S21. Synthesis of platinum-gold nanoparticles: 0.7 mL K 2 PtCl 4 (20 mM), 0.1 mL HAuCl 4 (20mM) mixed, add 10 mg of poloxamer (Pluronic) F127, ultrasonic to dissolve it, then add 1.0 mL of ascorbic acid (100mM) as a reducing agent, the mixed solution was ultrasonically reacted in a water bath at 30ºC for 8 hours, and the product was subjected to 10000r / min Centrifuge for 20 min to separate, wash with ethanol and water repeatedly 5 times to remove residual PluronicF127, and reconstitute with 0.9 mL of water for later use.
[0052] Step S22. Synthesis of silicon-doped carbon quantum dots: Take 0.2M N-β-(aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane in a 100 mL three-necked flask, degas with nitrogen for 5 min , heated to 240°C, quickly added 0.05M anhydrous citric acid under vigorous stirring, and kept heating at thi...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The present embodiment provides a ratiometric fluorescence analysis method for detecting mercury ions, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0057]Step S31. Synthesis of platinum-gold nanoparticles: 0.5 mL K 2 PtCl 4 (20 mM), 0.1 mL HAuCl 4 (20mM) mixed, add 10 mg of poloxamer (Pluronic) F127, ultrasonic to dissolve it, then add 1.0 mL of ascorbic acid (100mM) as a reducing agent, the mixed solution was ultrasonically reacted in a water bath at 30ºC for 10h, and the product was subjected to 10000r / min Centrifuge for 20 min to separate, wash with ethanol and water repeatedly 5 times to remove residual PluronicF127, and reconstitute with 0.9 mL of water for later use.
[0058] Step S32. Synthesis of silicon-doped carbon quantum dots: take 0.15M N-β-(aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane in a 100 mL three-necked flask, degas with nitrogen for 5 min , heated to 240°C, quickly added 0.05M anhydrous citric acid under vigorous stirring, and kept heating at ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com