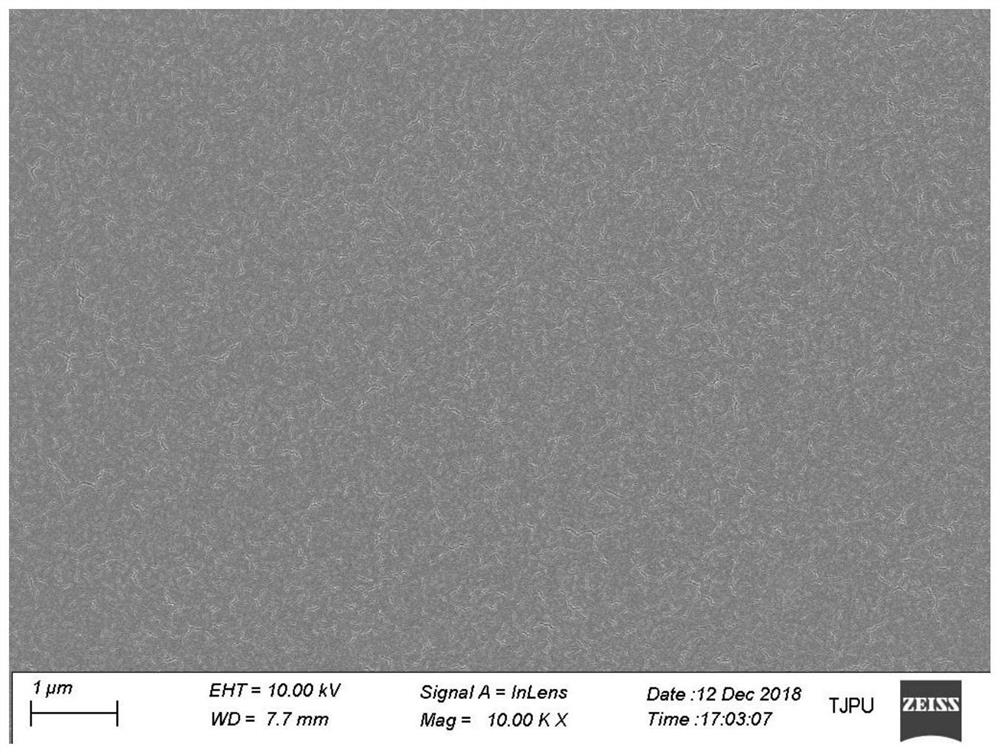
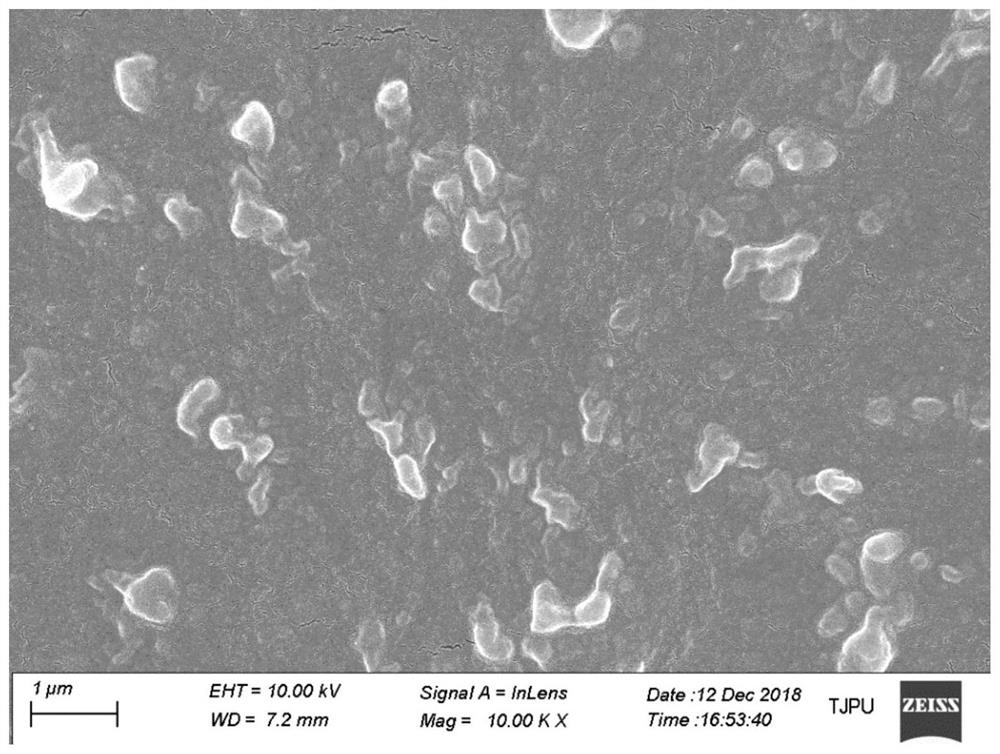
A preparation method based on ionic bond-covalent bond cooperative surface heparinized anticoagulant medical device
A medical device, ionic bond technology, applied in the coating and other directions, to achieve the effect of improving the fixed amount of heparin, no solvent toxicity, and controllable process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 A method for preparing an anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond synergistic surface heparinization
[0035] An anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond cooperative surface heparinization, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0036] (1) Based on the hydrophilic polymer with a large amount of double bonds in the side chain, prepare the hydrophilic polymer with low molecular weight hyperbranched PEI in the side chain: 5g ethylene oxide and 2g allyl glycidyl ether are separated by anion Cyclocopolymerization reaction to obtain a hydrophilic polyethylene oxide (PEO) polymer containing a large number of double bonds; add 2g mercaptoethanol and 1g AIBN, and carry out addition reaction at 80°C for 48h, so that all the double bonds in the side chain are converted into hydroxyl groups ; Use 2g 4-NC to activate the hydroxyl group in the hydrophilic polymer to obtain a hydrophilic PEO polymer with a side chain mod...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 A method for preparing an anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond synergistic surface heparinization
[0042] An anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond cooperative surface heparinization, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0043] (1) Based on the hydrophilic polymer with a large number of double bonds in the side chain, prepare a hydrophilic polymer with a low molecular weight hyperbranched PEI in the side chain: 2g ethylene glycol and 0.5g allyl glycidyl ether are opened by anion Copolymerization reaction to obtain a hydrophilic polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymer with a large number of double bonds in the side chain; add 0.5g mercaptoethanol and 1g AIBN, and carry out addition reaction at 50°C for 24h, so that all the double bonds in the side chain are converted into Hydroxyl; use 0.2g 4-NC to activate the hydroxyl group in the hydrophilic polymer to obtain a hydrophilic PEG polymer with NC-modified ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 A method for preparing an anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond synergistic surface heparinization
[0049] An anticoagulant medical device based on ionic bond-covalent bond cooperative surface heparinization, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0050] (1) Based on the hydrophilic polymer with a large number of double bonds in the side chain, prepare a hydrophilic polymer with a low molecular weight hyperbranched PEI side chain: 10g α, ω-aminopropyl-ethylene glycol and 5g allyl shrink Glyceryl ether was obtained by anionic ring-opening copolymerization reaction to obtain a hydrophilic α, ω-aminopropyl-polyethylene glycol polymer modified with double bonds; adding 10 g mercaptoethanol and 5 g AIBN, and carried out the addition reaction at 100 ° C for 48 h, so that The double bonds of the side chains are all converted into hydroxyl groups; 5g of 4-NC is used to activate the hydroxyl groups in the hydrophilic polymer to obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com