High-toughness, high-temperature-resistant, impact-resistant road material and preparation method thereof
A high-temperature and impact-resistant technology, applied in the field of high-toughness, high-temperature-resistant and impact-resistant road materials and their preparation, and the field of road materials, can solve the problem that flexibility and impact resistance affect the road performance of the bridge deck pavement and reduce road traffic. Service level, poor impact resistance, etc., to achieve the effect of high fluidity, improved bonding effect, and high thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
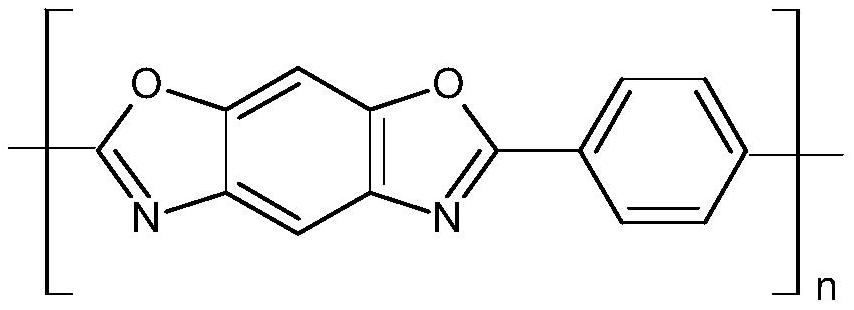
[0053] The preparation process of the poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fiber is as follows: 4,6-diaminoresorcinol and trimethylsilazane are used as raw materials and prepared by trimethylsilylation.
[0054] Poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fiber has a heat-resistant temperature of 600°C, has excellent thermal stability, and can be dissolved in solvents such as polyphosphoric acid and polyphosphoric acid methylsulfonic acid.
Embodiment 1
[0057] This example provides a preparation method of a road material with high toughness, high temperature resistance and impact resistance. The method includes the following steps:
[0058] Step 1, preparing ammoniated poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fiber:
[0059] soaking the pretreated poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fibers in ethylenediamine methanol solution to obtain ammoniated poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fibers;
[0060] In step 1, the pretreatment process is: soak the poly-p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole fiber in acetone for 12 hours to remove surface attachments, take it out, and place it in a blast drying oven for 4 hours at 100°C. The dried poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fibers were immersed in epichlorohydrin solution and irradiated with gamma rays, then washed with acetone repeatedly for 12 h, and dried at 100 °C for 1 h.
[0061] In step 1, soak the pretreated poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) fiber in an ethylenediamine methanol solution at 25° C. for 12 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0078] This example presents a method for preparing a high-toughness, high-temperature-resistant, and impact-resistant road material. The preparation steps of this method are basically the same as those in Example 1. The difference lies in the preparation of the high-toughness, high-temperature, and impact-resistant road material in this example. In the method, the proportioning of each main raw material is in parts by weight:
[0079] Add 10 parts of curing agent for every 100 parts of epoxy resin;
[0080] The fiber skeleton corresponding to every 100 parts of epoxy resin is made of 30 parts of poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole fiber raw materials;
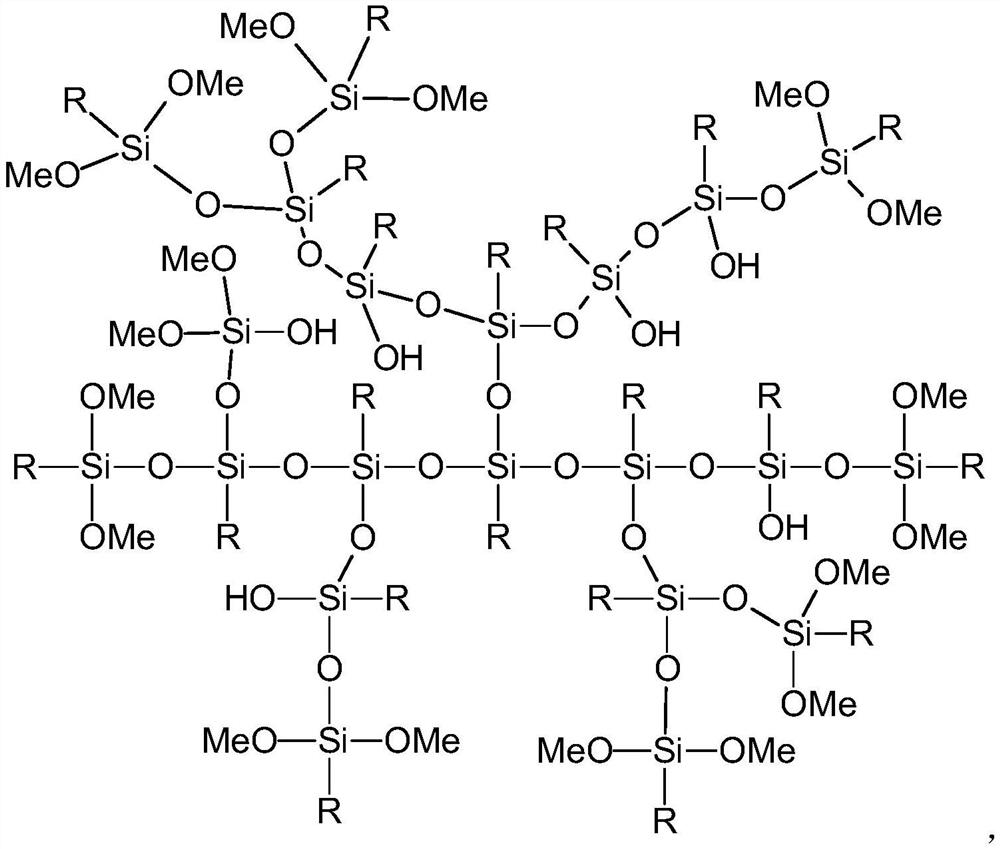
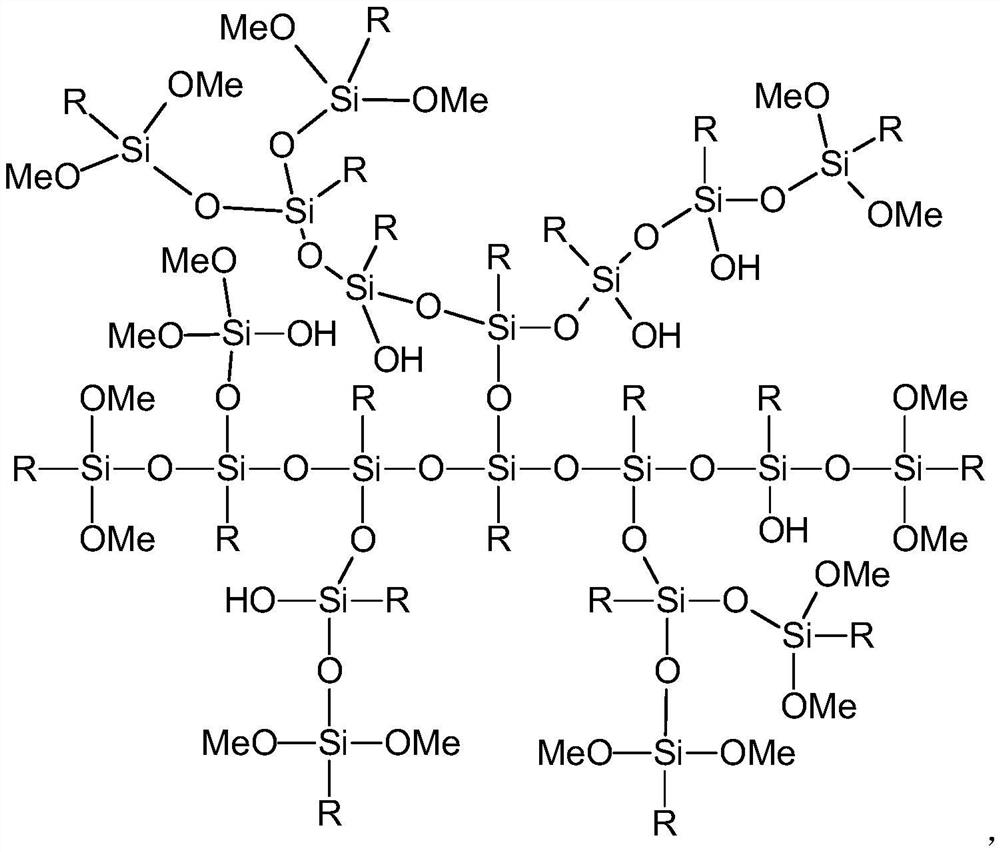
[0081] The fiber skeleton corresponding to every 100 parts of epoxy resin is hyperbranched polysiloxane made from the following raw materials: 8 parts of MPS, 10 parts of GPTMS, 16 parts of distilled water, and 40 parts of absolute ethanol.
[0082] The high-toughness, high-temperature, and impact-resistant road material is prep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com