Preparation method of in vivo targeted ovarian cancer cell imaging nano material composed of multifunctional macromolecule and metal-organic frames (MOFs)
A technology of metal-organic framework and ovarian cancer cells, which is applied in the field of nano-biomedical materials, can solve the problems of poor targeting, and achieve the effect of satisfying production and application, good physical and chemical stability, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
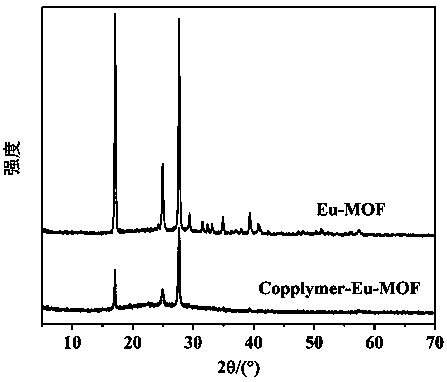
[0028]A multifunctional polymer and metal-organic framework in vivo targeting ovarian cancer cell imaging nanomaterials, synthesized by RAFT reaction with polymers targeting ovarian cancer cell peptides, and then coordinated with Eu-MOF synthesized by solvothermal method , to obtain multifunctional nanomaterials with targeting ovarian cancer cells and in vivo fluorescence imaging, the steps are as follows:
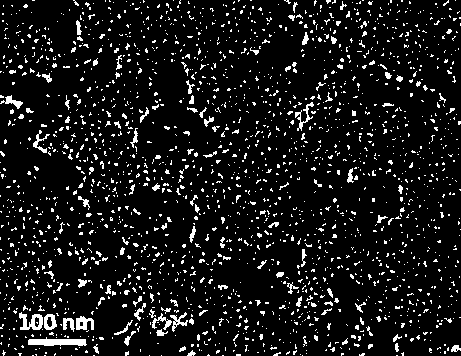
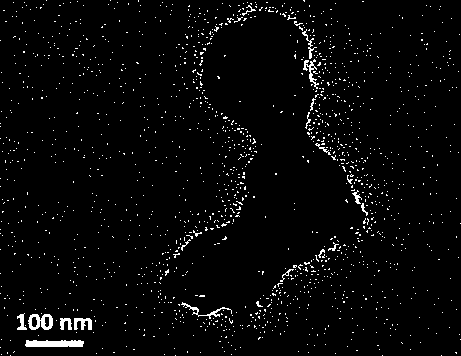
[0029] (1) Preparation of rare earth metal europium-organic framework (Eu-MOF) nanoparticles: the same amount of 0.001 mol of H 2 IPA and Eu(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in a mixed solution of 6 mL of dimethylformamide (DMF) and 24 mL of water, and 0.6 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone-K30 (PVP, K30) was added as a surfactant. Stir and heat in the bath for 10 min, filter and dry under vacuum at room temperature to obtain the product Eu-MOF nanoparticles;
[0030] (2) Synthesis of high-molecular polymers grafted with targeting peptides: 0.01 mol NIPAM, 0.1 mmol trithiocarbona...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A nanomaterial for in vivo targeting ovarian cancer cell imaging composed of multifunctional polymers and metal-organic frameworks, according to the following steps:
[0038] (1) Preparation of rare earth metal europium organic framework (Eu-MOF) nanoparticles: 0.001 mol of H 2 IPA and 0.002 molEu(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in a mixed solution of 6 mL of dimethylformamide (DMF) and 24 mL of water, and 0.6 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone-K30 (PVP, K30) was added as a surfactant. Stir and heat in the bath for 10 min, filter and dry under vacuum at room temperature to obtain the product Eu-MOF nanoparticles.
[0039] (2) Synthesis of polymers grafted with targeted peptides: 0.01 mol NIPAM, 0.1 mmol trithiocarbonate (DATC), 0.4 mmol azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) were dissolved in 4 In mL of anhydrous dioxane, in which DATC is used as a chain transfer agent and AIBN is used as an initiator, the reactant is stirred and heated in an oil bath at 65°C for 24 h, and the product...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A nanomaterial for in vivo targeting ovarian cancer cell imaging composed of multifunctional polymers and metal-organic frameworks, according to the following steps:
[0044] (1) Preparation of rare earth metal europium organic framework (Eu-MOF) nanoparticles: 0.001 mol of H 2 IPA and 0.005 molEu(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in a mixed solution of 6 mL dimethylformamide (DMF) and 24 mL water, and 0.6 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone-K30 (PVP, K30) was added as a surfactant. The reactants were stirred and heated in an oil bath at 100 °C for 10 min, filtered and then vacuum-dried at room temperature to obtain the product Eu-MOF nanoparticles.
[0045] (2) Synthesis of polymers grafted with targeted peptides: 0.01 mol NIPAM, 0.1 mmol trithiocarbonate (DATC), 0.4 mmol azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) were dissolved in 4 mL of anhydrous dioxane with DATC as chain transfer agent and AIBN as initiator. The reactant was stirred and heated in an oil bath at 65°C for 24 h, the prod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com