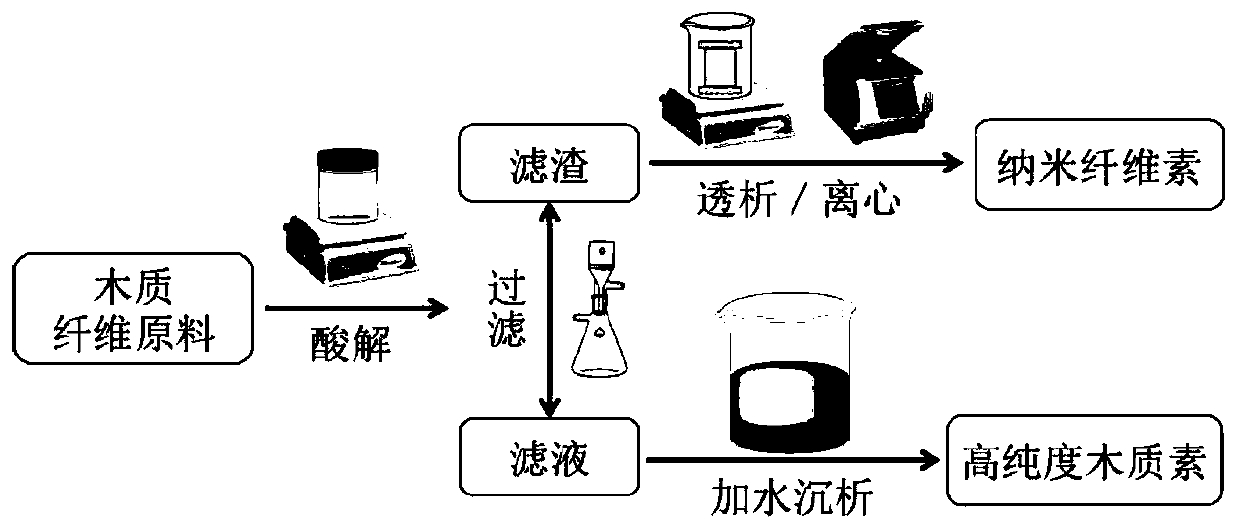
Method for extracting nanocellulose and lignin from wood fiber raw material
A lignocellulosic raw material and nano-cellulose technology, which is applied in fiber raw material processing, natural cellulose pulp/paper, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of high equipment requirements, poor β-1,4-glucosidic bond and hydrogen bond capacity , low yield of hydrolyzed nanocellulose, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing yield, reducing pulping and bleaching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Extraction of nanocellulose and lignin by oxalic acid compounded with toluenesulfonic acid to hydrolyze poplar wood powder.
[0023] The concentrations of p-toluenesulfonic acid compounded oxalic acid are O20P55, O30P45, O40P35, O50P25, O60P15, where O refers to oxalic acid, P refers to p-toluenesulfonic acid, OxPy refers to the mass concentration of oxalic acid is x, and the mass concentration of p-toluenesulfonic acid Be y, wherein x takes 20wt%, 30wt%, 40wt%, 50wt%, 60wt%; y takes 55wt%, 45wt%, 35wt%, 25wt%, 15wt%;
[0024] Acid hydrolysis temperature Ti, wherein, Ti refers to i°C, and i is 90, 100, 110;
[0025] Acid hydrolysis time th, wherein, th refers to h min, and h is 30, 60, 120, 240.
[0026] Add oxalic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid and water into a 100mL blue cap bottle in proportion, seal it and place it in an oil bath to dissolve, add 20-80 mesh poplar wood powder after the solid acid is completely dissolved, and magnetically Stir for 30-240 m...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Extraction of nano-cellulose and lignin by compounding oxalic acid with toluenesulfonic acid to hydrolyze wheatgrass wood powder.
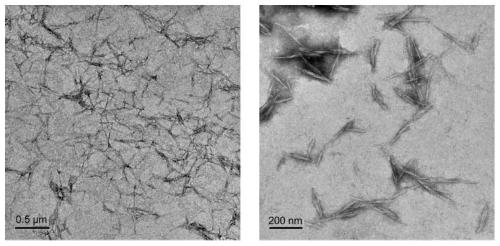
[0040] Add oxalic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid and water in proportion (O50P25) to a 100mL blue cap bottle, seal and place in an oil bath to dissolve, add 20-80 mesh wheatgrass powder after the solid acid is completely dissolved, and set temperature (100 °C) at a speed of 500 rpm for 120 min with magnetic stirring. After acidolysis, filter and separate the filter residue and filtrate, and wash with hot water several times, transfer the washed filter residue to a dialysis bag, dialyze to neutrality, and extract nanocellulose by centrifugation. Adding water to the filtrate part of acid hydrolysis and filtration can precipitate lignin as precipitate.
[0041] The experimental results show that when the concentration of oxalic acid is 50%, the concentration of p-toluenesulfonic acid is 25%, the temperature is 100°C, and the acid hyd...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com