A base cloth processing technology for superfine fiber synthetic leather
A technology of ultra-fine fiber and processing technology, which is applied in fiber processing, textiles and papermaking, etc. It can solve the problems of non-woven fabric dyeing difficulties, non-woven fabrics with increased difficulty, and different foaming states.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
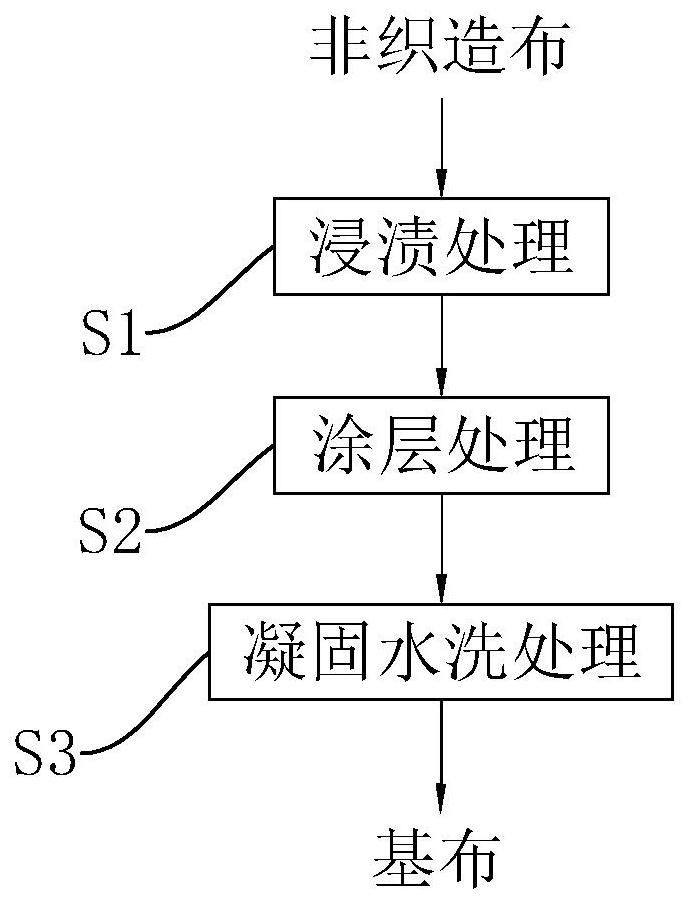
[0044] refer to figure 1 , the following substances are in parts by weight.
[0045] A base cloth processing technology for superfine fiber synthetic leather, the commercially available non-woven fabric is processed through the following steps:
[0046] S1: Dipping treatment. Dipping treatment includes the following steps:
[0047] A1: Put 75 parts of DMF into the stirred tank first, and make the stirred tank start to stir, stir for 17 minutes, and control the temperature in the stirred tank to 53°C.
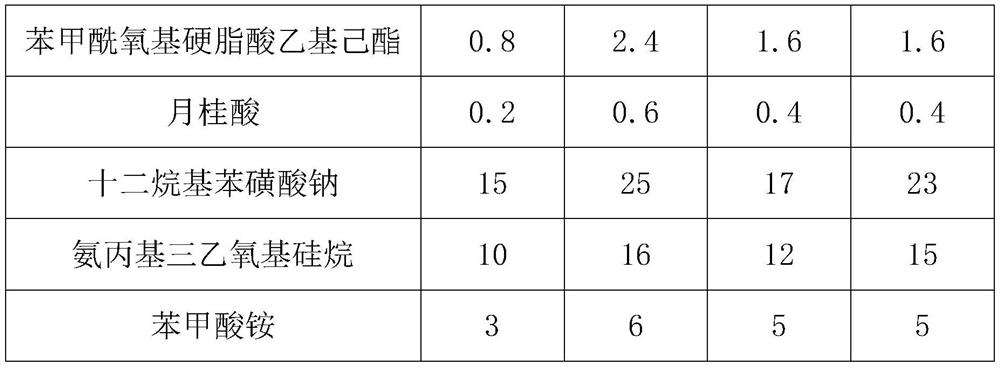
[0048] A2: Add 1.6 parts of benzoyloxy ethylhexyl stearate, 0.4 parts of lauric acid, 20 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and 13 parts of aminopropyltriethoxysilane to the In the stirred tank after A1 treatment, first stir for 10 min, then raise the temperature in the stirred tank to 65° C., and then stir for 10 min.
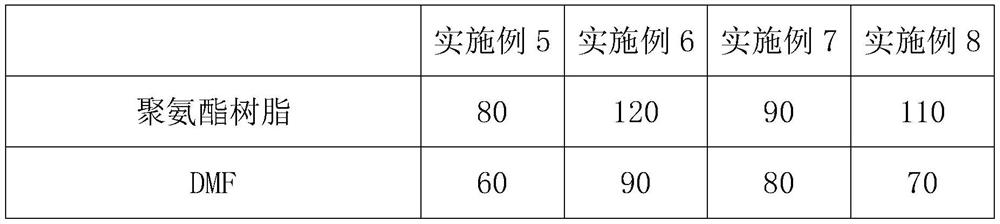
[0049] A3: Add 100 parts of polyurethane resin into the stirred tank treated in A2, lower the temperature in the stirred tank to 40° C., and stir for ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The following substances are all in parts by weight.
[0063] A base cloth processing technology for superfine fiber synthetic leather, the commercially available non-woven fabric is processed through the following steps:
[0064] S1: Dipping treatment. Dipping treatment includes the following steps:
[0065] A1: Put 75 parts of DMF into the stirred tank first, and make the stirred tank start to stir, stir for 17 minutes, and control the temperature in the stirred tank to 53°C.
[0066] A2: Add 1.6 parts of benzoyloxy ethylhexyl stearate, 0.4 parts of lauric acid, 20 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and 13 parts of aminopropyltriethoxysilane to the In the stirred tank after A1 treatment, first stir for 10 min, then raise the temperature in the stirred tank to 65° C., and then stir for 10 min.
[0067] A3: Add 100 parts of polyurethane resin into the stirred tank treated in A2, lower the temperature in the stirred tank to 40° C., and stir for 60 minutes.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The following substances are all in parts by weight.
[0081] A base cloth processing technology for superfine fiber synthetic leather, the commercially available non-woven fabric is processed through the following steps:
[0082] S1: Dipping treatment. Dipping treatment includes the following steps:
[0083] A1: Put 75 parts of DMF into the stirred tank first, and make the stirred tank start to stir, stir for 17 minutes, and control the temperature in the stirred tank to 53°C.
[0084] A2: Mix 1.6 parts of ethylhexyl benzoyl oxystearate, 0.4 parts of lauric acid, 20 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, 13 parts of aminopropyltriethoxysilane, 4 parts of ammonium benzoate Add them into the stirred tank treated with A1 in no sequence, stir for 10 minutes first, then raise the temperature in the stirred tank to 65°C, and stir for another 10 minutes.
[0085] A3: Add 100 parts of polyurethane resin into the stirred tank treated in A2, lower the temperature in the sti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com