Crosslinking agent of polyacrylamide plugging agent, and preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of polyacrylamide and cross-linking agent, applied in the field of cross-linking agent of polyacrylamide water blocking agent, can solve the problems of poor viscoelasticity, fast gel forming speed, easy precipitation, etc. Glue forming time, the effect of not easy to settling phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] A preparation method of a cross-linking agent of polyacrylamide water blocking agent, comprising the following steps:
[0025] S1, adding deionized water, chromium nicotinate complex, aluminum citrate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose and organic acid into the stirring reactor in sequence, and stirring and reacting at 80°C to 90°C for 6h to 9h; and
[0026] S2, adding an acidity regulator to the mixed solution after the stirring reaction in S1 to adjust to alkalinity to obtain a crosslinking agent product.
[0027] In S2, an acidity regulator is used to adjust the pH of the mixture to 7-8.
[0028] An application of the cross-linking agent in polyacrylamide water blocking agent, the mass ratio of the cross-linking agent to the polyacrylamide is 3-6:7-12.
Embodiment 1
[0030] Select raw materials by weight percentage
[0031] Cr 2 (C 6 h 4 NO 2 ) 3 Cl 3 : 20%
[0032] Aluminum citrate: 5%
[0033] Malonic acid: 15%
[0034] Sodium carboxymethylcellulose: 0.03%
[0035] Ammonia water (0.14×10 -2 mol / L): 15%
[0036] Deionized water: 44.97%
[0037] Concrete preparation steps are:
[0038] (1) Deionized water, Cr 2 (C 6 h 4 NO 2 ) 3 Cl 3 , aluminum citrate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and malonic acid were sequentially added into the stirred reactor, and stirred and reacted at 80°C for 6h.
[0039] (2) Add ammonia water to the mixed solution after the stirring reaction in step (1), and adjust to 7 to obtain a crosslinking agent product.
[0040] Preparation of water blocking agent: select polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 14 million (Japan Sanyo Chemical Company, industrial grade), take 4.5g of the above-mentioned polyacrylamide, add it to 1000mL water, stir to dissolve, and then add 1.6g of cross-linking agent to...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Select raw materials by weight percentage
[0044] Cr 2 (C 6 h4 NO 2 ) 3 Cl 3 : 25%
[0045] Aluminum citrate: 4%
[0046] Malonic acid: 30%
[0047] Sodium carboxymethylcellulose: 0.06%
[0048] Sodium carbonate aqueous solution (0.16×10 -2 mol / L): 15.94%
[0049] Deionized water: 25%
[0050] Concrete preparation steps are:
[0051] (1) Deionized water, Cr 2 (C 6 h 4 NO 2 ) 3 Cl 3 , aluminum citrate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and malonic acid were sequentially added into the stirred reactor, and stirred and reacted at 90°C for 9h.
[0052] (2) Add sodium carbonate aqueous solution to the mixed solution after the stirring reaction in step (1), and adjust to 8 to obtain a crosslinking agent product.
[0053] Preparation of water blocking agent: same as Example 1.
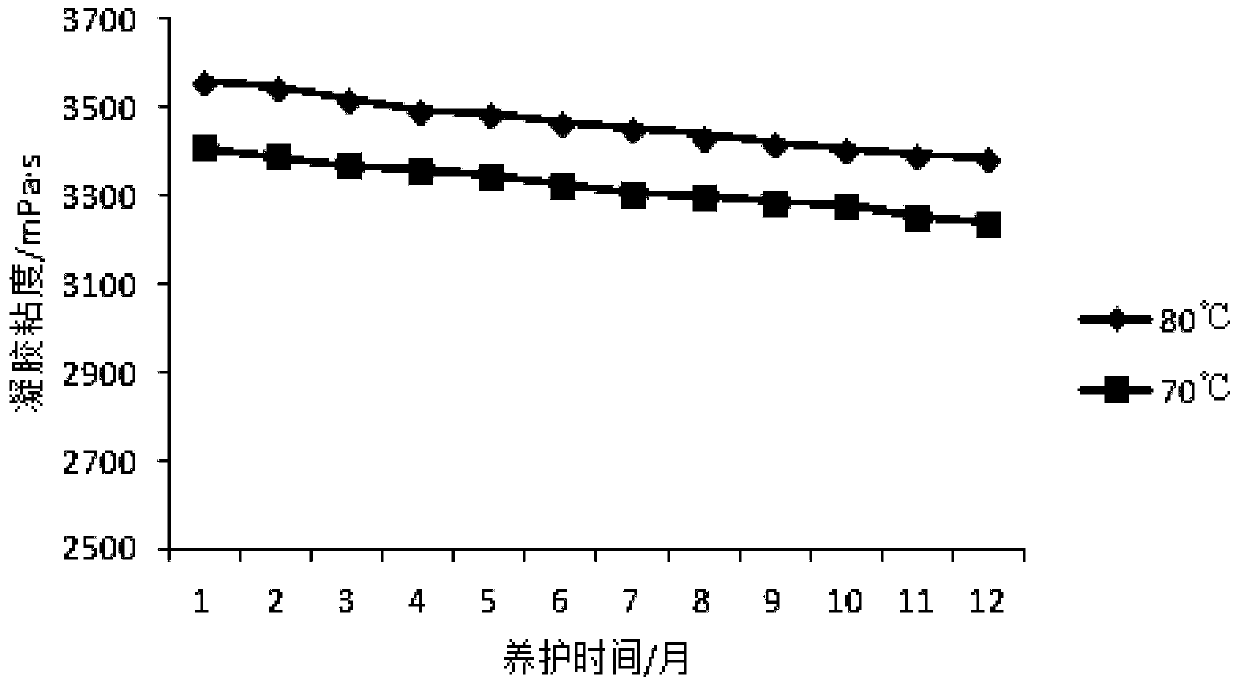
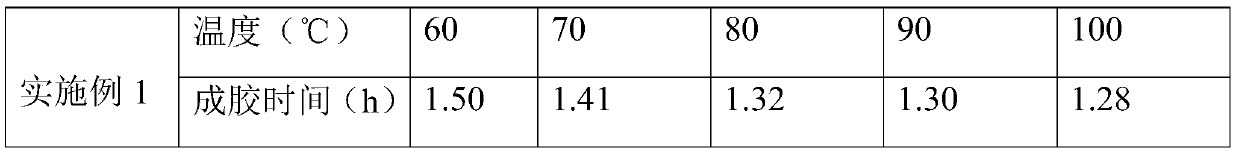
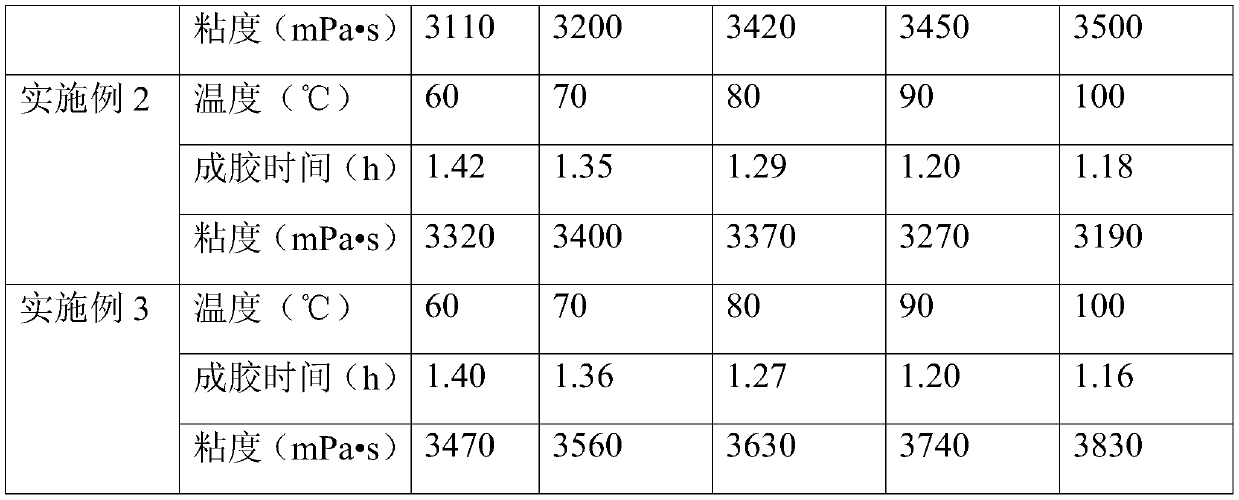
[0054] See Table 1 and Table 2 for the viscosity retention rate and gelation time of the weak gel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com