Heat-resistant reverse transcriptase mutant
A technology of reverse transcriptase and mutant, applied in the field of thermostable reverse transcriptase mutants, which can solve problems such as poor thermotolerance and inactivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0156] Example 1: Preparation of Reverse Transcriptase Mutants-1
[0157] (1) Preparation of MMLV reverse transcriptase mutants O1-O3 and P12, P13 (T55G, T55A, T55S, T55D, T55K)
[0158] According to Experimental Method 1-(1), an artificial gene encoding a mutant protein in which threonine at position 55 in the wild-type amino acid sequence of MMLV reverse transcriptase was replaced with glycine was prepared. Using the artificial gene thus obtained, protein expression and purification were performed according to Experimental Method 1-(1). The reverse transcriptase mutant with a threonine to glycine substitution mutation at position 55 was designated "01" as used herein. The reverse transcriptase mutant in which threonine at position 55 was replaced with alanine and the reverse transcriptase mutant in which threonine at position 55 was replaced with serine were named "O2" and "O3", respectively. The reverse transcriptase mutant in which the threonine at position 55 was replaced...
Embodiment 2
[0201] Example 2: Heat resistance evaluation test of reverse transcriptase mutants-1
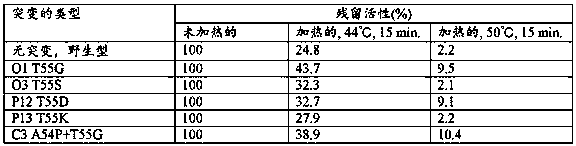
[0202] The heat resistance of the reverse transcriptase mutants and wild-type reverse transcriptase prepared in Example 1-(1) was tested according to the experimental method 1-(2). The results are shown in Table 1.
[0203] [Table 1]
[0204]
[0205] As shown in Table 1, after heat treatment at 44°C and 50°C for 15 minutes, mutants O1, P12 and C3 in particular had 1.3-4.7 times higher residual activity compared to reverse transcriptase with wild-type amino acid sequence. Mutants O3 and P13 had 1.1-1.3 times higher residual activity compared to wild-type reverse transcriptase after heat treatment at 44°C for 15 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0206] Example 3: Heat resistance evaluation test of reverse transcriptase mutants-2
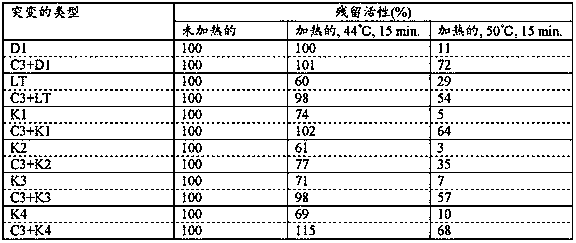
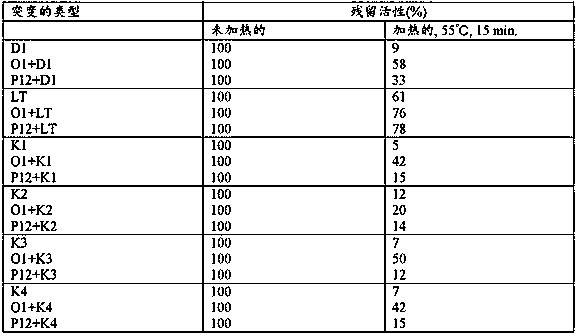
[0207] Amino acid substitutions of the present invention were examined in combination with known mutations that have been reported to be involved in thermotolerance or novel mutations that were first discovered by the present invention to be involved in thermotolerance. Specifically, Example 1-(3) and (5), Example 1-(6) and (8), Example 1-(9) and (11), were tested according to Experimental Method 1-(2). Prepared in embodiment 1-(12) and (14), embodiment 1-(15) and (17), embodiment 1-(18) and (20) and embodiment 1-(21) and (22) Thermotolerance of reverse transcriptase mutants. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0208] [Table 2]
[0209]
[0210] As shown in Table 2, it has been reported that any combination of the mutations D1, LT, K2, K3 and K4 involved in thermotolerance with the amino acid substitution C3 of the present invention increases the residual activity after heat treatment ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com