Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitors
An alkyl and compound technology, applied in the field of influenza treatment, can solve the problems of inability to act as an influenza treatment agent, poor pharmacological properties, and poor efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
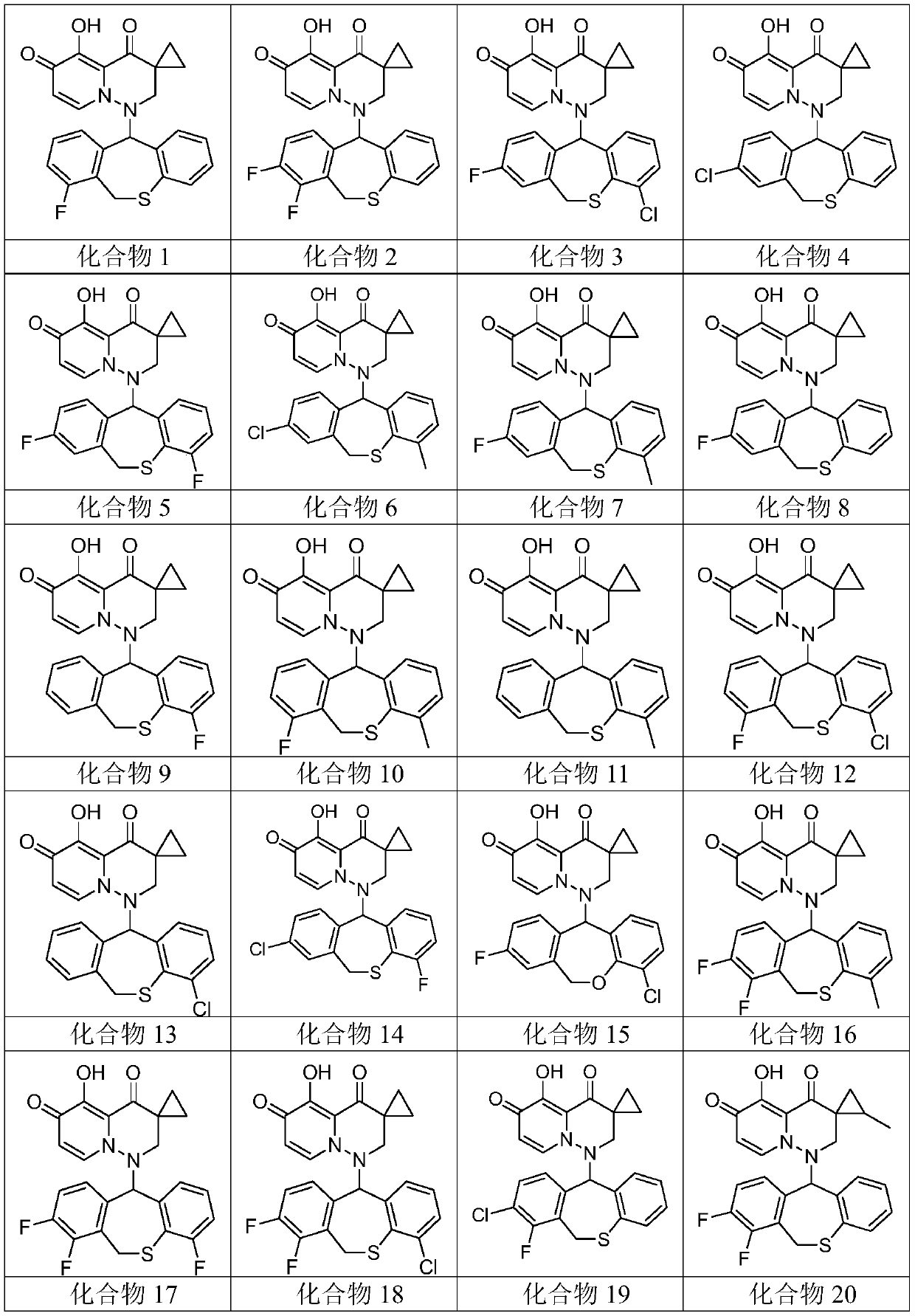
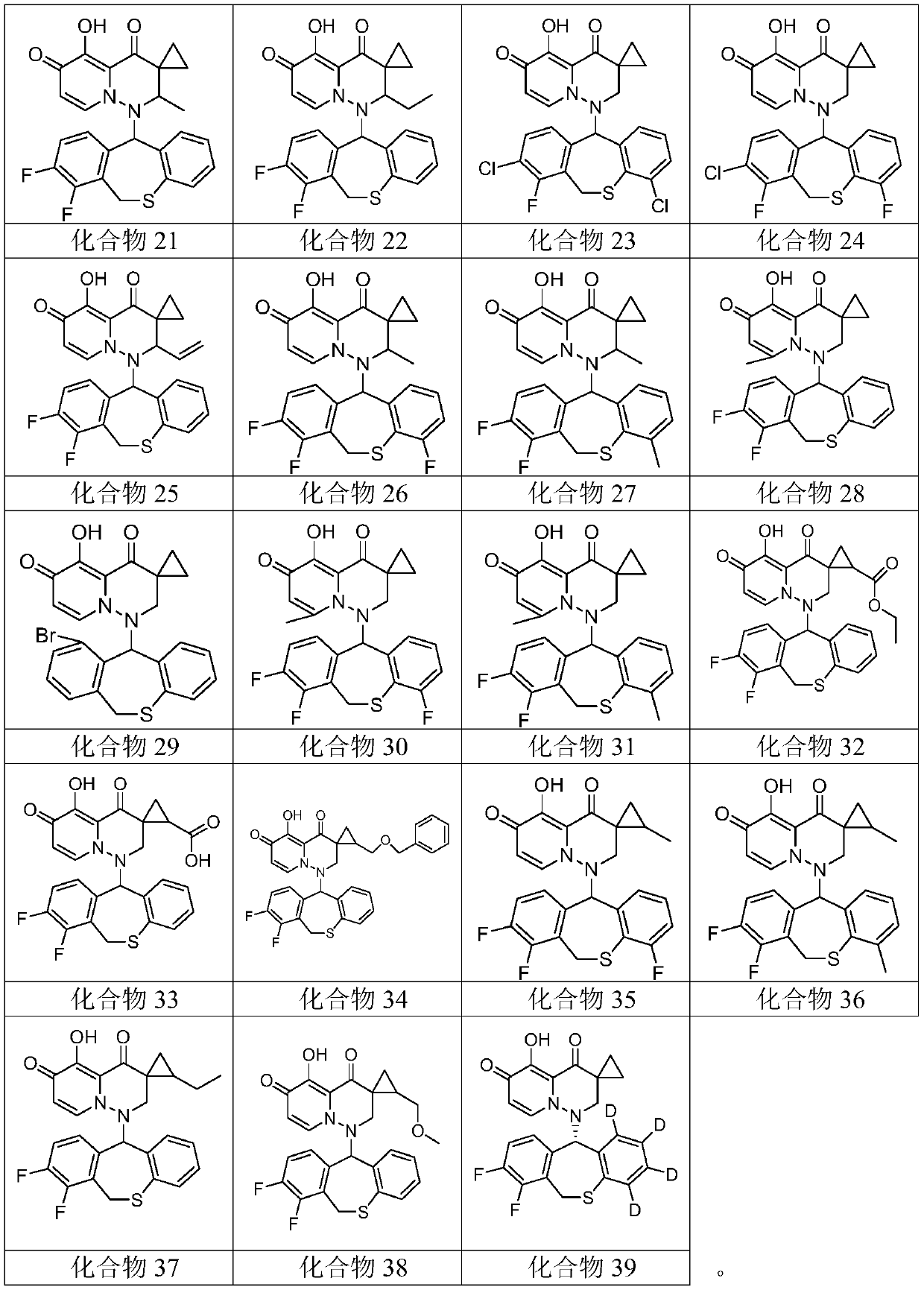
[0077] Embodiment 1: Preparation and characteristics of compound 1 to compound 39
[0078] Synthesis and Characterization of Compound 1
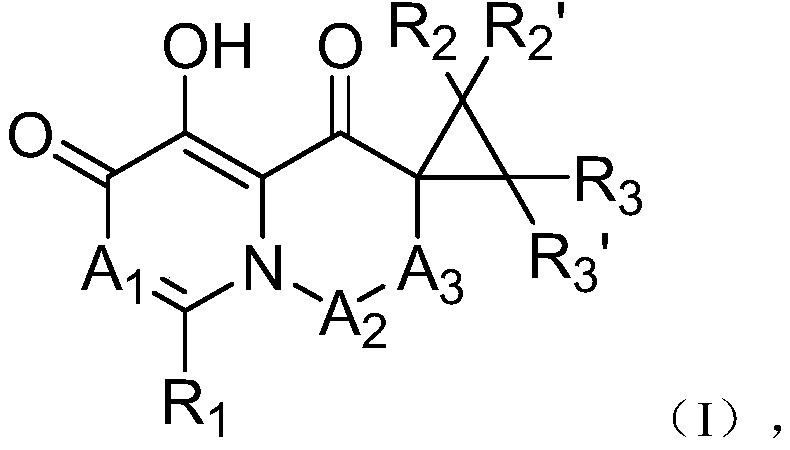
[0079] 1-(1-fluoro-5,11-dihydro-10-thia-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)-5-hydroxy-3,3-cyclopropyl-2, 3-Dihydro-1H-pyrido[1,2-b]pyridazine-4,6-dione (Compound 1)
[0080] Compound I-3 was first prepared from commercially available 3-benzyloxy-4-oxyl-4H-pyran-2-carbaldehyde and intermediates I-1 and I-2 in the manner shown below .
[0081]
[0082] Pyrrolidine (30.9g, 434mmole) was added to 3-(benzyloxy)-4-oxyl-4H-pyran-2-carbaldehyde (100g, 434mmole) and cyclopropanaldehyde (91.3g, 1.30mmole) in solvent DMSO (1 L), and the mixture was stirred at 50°C for 23 to 24 hours, then cooled to room temperature. The resulting mixture was dissolved in CH 2 Cl 2 (1 L) with 1N HCl (aq) (1 L) and saturated NaHCO 3 (1 L) aqueous solution, followed by washing with saturated brine (1 L). The organic phase was separated and dried over anhydrous magne...
Embodiment 2
[0160] Example 2: Cytopathic Effect (CPE) Inhibition Test)
[0161] CPE inhibition assays were performed as follows to assess the potency of test compounds to inhibit cap-dependent endonuclease activity.
[0162] MDCK cells in 96-well tissue culture plates were incubated with test compounds and influenza A or influenza B virus at low infection rates at 37°C for 72 hours. Plates were fixed by adding 0.5% formaldehyde and then stained with 0.5% crystal violet. Subsequently, the absorbance at a wavelength of 570 nm was measured with a microdisk analyzer (Multiskan Ascent, Thermo). Relative to the virus control group, the concentration required for the test compound to reduce the virus-induced CPE by 50%, expressed as the 50% effective dose (EC 50 ).
[0163] Compounds 1 to 39 were evaluated using the CPE inhibition assay, where, for influenza A virus infection, 30 test compounds (i.e. compounds 1 to 10, 13, 16 to 22, 25, 27 to 30, 32 to 33, 35 to 38 and 39) Unexpectedly exhib...
Embodiment 3
[0170] Embodiment 3: Survival rate test after infecting influenza virus 24 hours
[0171] The following experiment was performed to evaluate the effect of the compound of formula (I) on the survival rate at 24 hours after infection in a mouse model of influenza A virus.
[0172] First, mice were infected with 100 or 500 pfu using mouse influenza A virus, and then the compound of formula (I) was administered 24 hours after infection. Dosing was twice daily for 5 days. Each compound was orally administered to mice at doses of 5, 10 or 20 mg / kg. Mice infected with 100 or 500 pfu of virus showed extremely high mortality. Unexpectedly, it was observed that the mice treated with oseltamivir showed a survival rate of 16.7% and the mice treated with Comparative Example Compound B1 showed a survival rate of 14.3%. Compound (eg Compound 1 and Compound 2) treated mice exhibited 80 to 100% survival. Oseltamivir is a commercial drug used to treat influenza, and Compound B1 of Comparati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com