Method for predicting sensitivity of patients with NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer) to immunotherapies
A technology for non-small cell lung cancer and immunotherapy, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as restricting clinical application, long working cycle, and high technical platform requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] genome analysis
[0089] FFPE tumor samples from Chinese non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and paired peripheral whole blood control samples were studied. All patients provided written informed consent. Target-captured next-generation sequencing (NGS) at OrigiMed involves panels containing 450 cancer-related genes. DNA was extracted from all unstained FFPE sections and whole blood with no less than 20% tumor content by DNA FFPE Tissue Kit and DNA Mini Kit (QIAamp), and then quantified by dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Qubit). Using KAPA Hyper Prep Kit (KAPA Biosystems), the sonicated DNA of about 250 bp was fragmented to construct a library, followed by PCR amplification and quantification. Hybrid capture using a custom panel covering 2.6Mb of the human genome, targeting 450 cancer-associated genes and certain frequently rearranged introns. The captured libraries were pooled, denatured, and diluted to 1.5-1.8 pM, followed by paired-end sequencing on an Illumina NextSe...
Embodiment 2
[0106] A total of 637 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) participated in the study. The characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. Most patients were male (355 / 637, 55.7%), and the median age at diagnosis was 60 years (IQR, 53-67 years). The most common histological type was non-squamous cell carcinoma (N=553, 86.8%), including adenocarcinoma (N=537) and other non-squamous cell carcinoma (N=16). Among them, there were 211 cases (33.1%) in stage I, 64 cases (10%) in stage II, 138 cases (21.7%) in stage III, and 224 cases (35.2%) in stage IV. 637 patients were tested for PD-L1 and TMB. The distribution of PD-L1 expression and TMB according to demographic characteristics is shown in Table 1. Weak positive (PD-L1 TPS score = 1-49%) and strong positive PD-L1 expression (PD-L1 TPS score ≥ 50%) were 16.5% and 10%, respectively. We performed a univariate analysis of the association between PD-L1 expression (assessed as a categorical variable with cutoffs o...
Embodiment 3
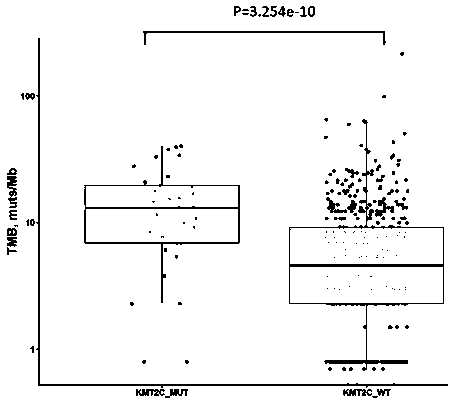
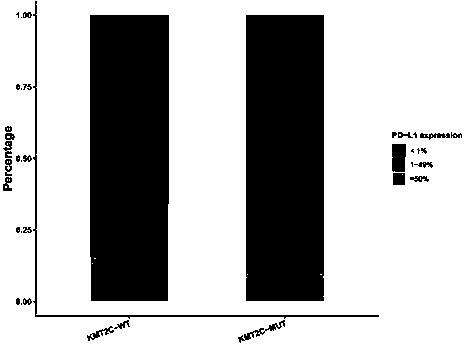
[0109] The top three mutated genes in the cohort of 637 NSCLC patients were TP53 (55.9%), EGFR (51.3%) and KRAS (12.6%). Among 637 NSCLC patients, 32 patients carried KMT2C gene mutation, accounting for 5%. Among the 32 patients with KMT2C mutation, 24 patients also carried TP53 gene mutation, accounting for 75%. The TMB of KMT2C mutant patients was significantly higher than that of KMT2C wild-type patients (median TMB: 13.1 vs. 4.6, pfigure 1 ). The positive expression rate of PD-L1 in patients with KMT2C mutation (PD-L1TPS≥1%) was higher than that in KMT2C wild-type patients (34.4% vs. 26.1%, p>0.05) ( figure 2 ).
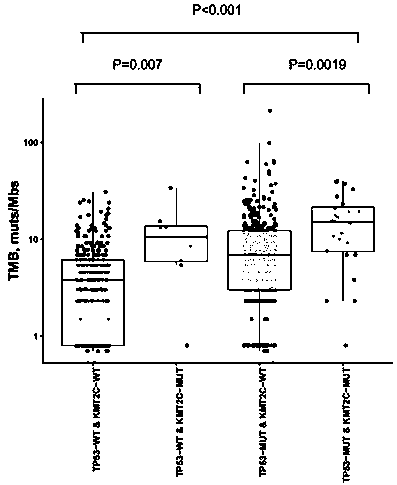
[0110] In the cohort of 637 NSCLC patients, 42.9% (273 / 637) were TP53-WT / KMT2C-WT patients, 1.3% (8 / 637) were TP53-WT / KMT2C-MUT patients, and 52.1% (332 / 637) were TP53 -MUT / KMT2C-WT patients, 3.7% (24 / 637) were TP53-MUT / KMT2C-MUT patients. The tumor TMB of TP53-WT / KMT2C-MUT patients was significantly higher than that of TP53-WT / KMT2C-WT patients (median TMB:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com