Composite magnesium oxysulfate cementing material used for 3D printing as well as preparation method and application of composite magnesium oxysulfate cementing material
A 3D printing, magnesium oxysulfide glue technology, applied in additive processing and other directions, can solve the problem of unsuitable magnesium oxysulfide cementitious materials, achieve strong resistance to various soluble salt erosion, increase added value, cohesion good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
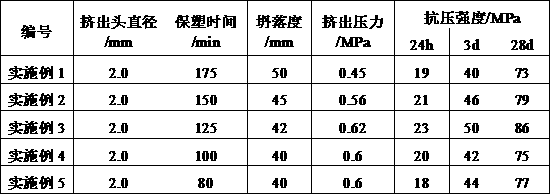
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this embodiment includes the following components by mass percentage: light-burned magnesium oxide 30wt%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 20wt%, water 20wt%, silica fume 1wt%, naphthalene-based reduced Water agent 1wt%, carboxymethyl cellulose 6wt%, sodium sulfate 3wt%, silicone hydrophobic powder 3wt%, sodium lignosulfonate 3wt%, tributyl phosphate 3wt%; fine aggregate (talc powder: dolomite powder = 7: 3) 10wt%.
[0048] The preparation method of the composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0049] (1) Dissolve selected amount of the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate in water and configure it as MgSO 4 Solution, stand for 24h, standby;
[0050] (2) The MgSO 4 The solution, the naphthalene-based water reducing agent, carboxymethyl cellulose, sodium sulfate, organic silicon water-repellent powder, sodium lignosulfonate and tribu...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this embodiment includes the following components in mass percentage: light-burned magnesium oxide 35wt%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 17wt%, water 17wt%, silica fume 1wt%, naphthalene-based reduced Water 1wt%, carboxymethyl cellulose 5.5wt%, sodium sulfate 2.5wt%, silicone hydrophobic powder 2wt%, sodium lignosulfonate 2wt%, tributyl phosphate 2wt%; fine aggregate (talc powder: Baiyun Stone powder = 7: 3) 15wt%.
[0054] The preparation method of the composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this example is the same as that of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this embodiment includes the following components in mass percentage: light-burned magnesium oxide 40wt%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 15wt%, water 15wt%, silica fume 0.5wt%, naphthalene series Water reducing agent 0.5wt%, carboxymethyl cellulose 5.5wt%, sodium sulfate 2.5wt%, silicone hydrophobic powder 2wt%, sodium lignosulfonate 2wt%, tributyl phosphate 2wt%; fine aggregate (talc : Dolomite powder = 7: 3) 15wt%.
[0057] The preparation method of the composite magnesium oxysulfide cementitious material for 3D printing in this example is the same as that of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com