Absolute quantitative transcriptome library construction method based on specific recognition sequence
A technology for sequence recognition and absolute quantification, which is applied in chemical libraries, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection. Achieve the effects of increasing the speed of library construction, reducing the initial amount of RNA library construction, and improving the efficiency of linker ligation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] [Example 1] Construction of Absolute Quantitative Transcriptome Library Based on Unique Recognition Sequence
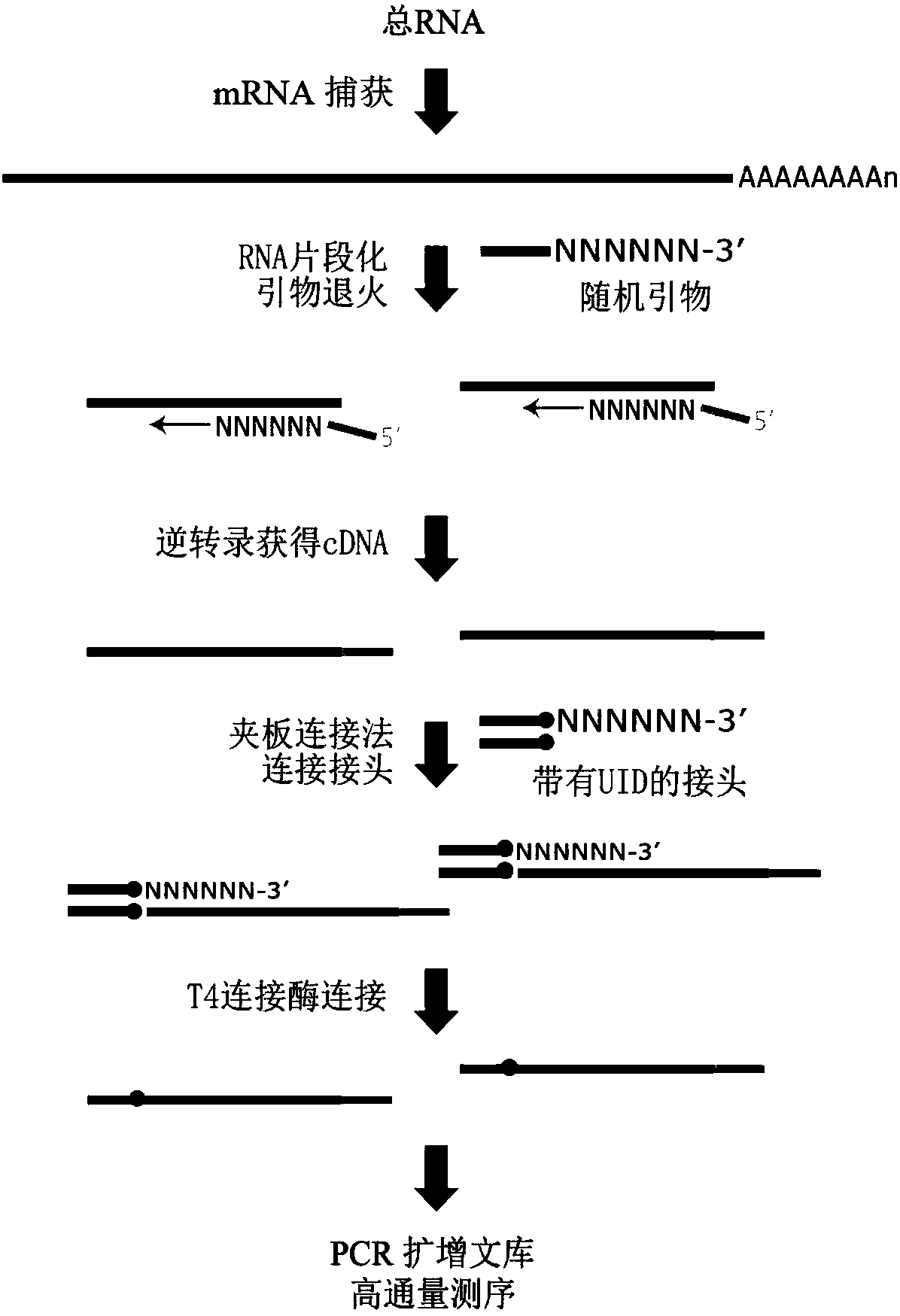
[0045] 1. mRNA capture
[0046] 1. Extract high-quality total RNA from control cells (NC) and GAS5 knockdown Hela cells (Si_GAS5) and capture mRNA from them. While adopting the technical scheme of the present invention to construct the transcriptome library, conventional transcription is performed to construct the library.
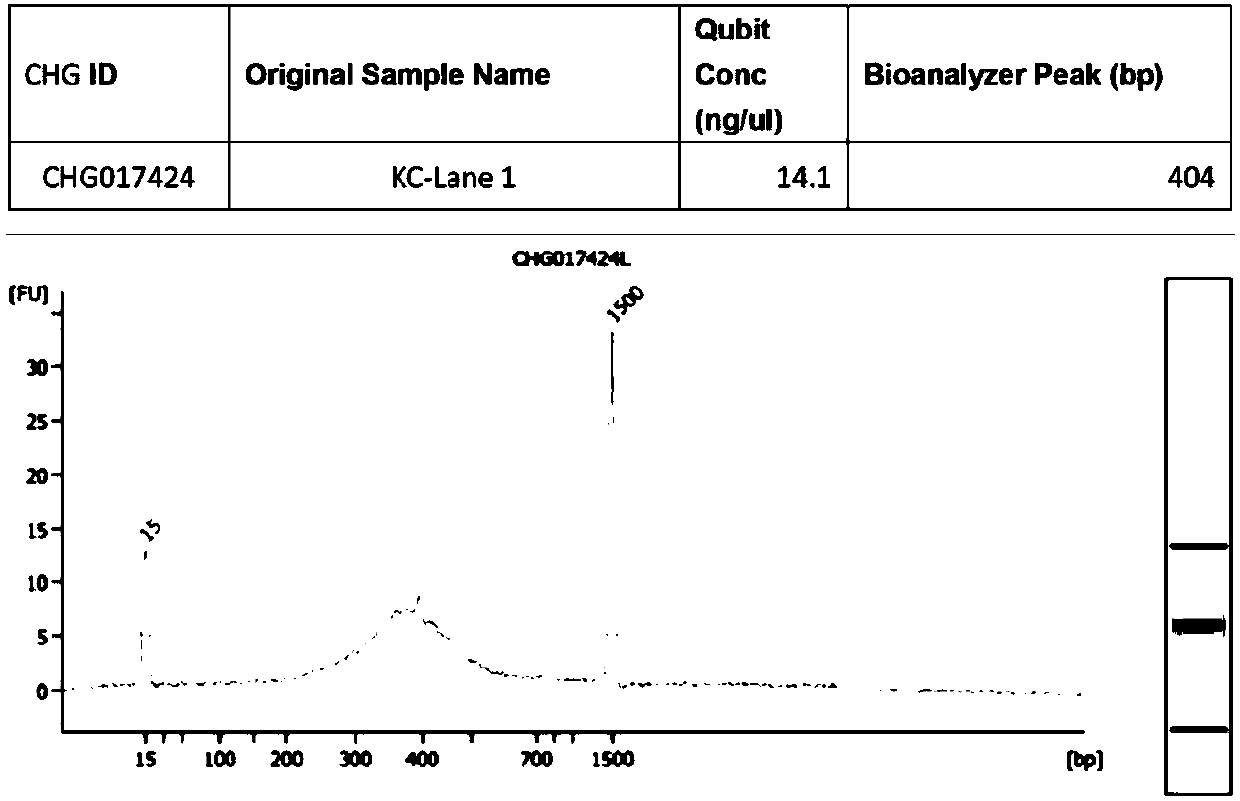
[0047] 2. In a Nuclease-free PCR tube, dissolve 0.1-4 μg of total RNA in Nuclease-free H 2 O, to a total volume of 50 μL, keep on ice for later use. Pipette 50 μL of washed magnetic beads (Roche, 11787896001) to mix with the RNA sample, pipette and mix well, then put it into a PCR machine and incubate at 65°C for 5min, then at 20°C for 5min. Place the sample on the magnetic stand for 5 minutes (until the solution is clarified), carefully remove the supernatant; take the sample out of the magnetic stand, add 200 μL Washing Buffer (Roche, ...
Embodiment 2
[0102] [Example 2] Sequencing data analysis process
[0103] S1: Perform quality control on raw data, remove low-quality bases and cut off corresponding adapters;
[0104] S2: Analyze the UID sequence on the reads, and regard the reads under the same UID sequence as a cluster (cluster);
[0105] S3: According to the above principles, since the reads under the same UID sequence come from the same molecule, the reads under each cluster are assembled consistently to form a consistent read. Such as Figure 4 As shown, in the process of assembly, the function of deduplication is actually realized, that is, molecules from the same source are finally merged into one sequence. At the same time, the purpose of error correction is also achieved, because the erroneous bases introduced by the reads under the same cluster during PCR amplification or sequencing on the machine will be corrected based on the consensus sequence of multiple reads. The resulting results are used as the final ...
Embodiment 3
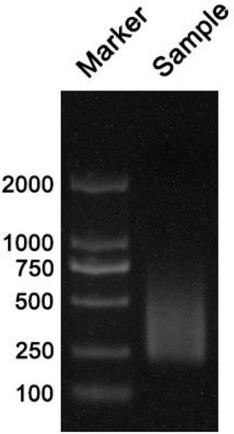
[0121] [Example 3] Library construction and sequencing with different starting quantities for library construction
[0122] Extract the total RNA of Hela cells, use 100ng, 500ng, and 1ug respectively as the initial amount of library construction, build the library according to the steps of [Example 1], and use 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the constructed library, as shown in Image 6 . Sequencing data analysis was performed according to the steps of [Example 2]. Correlation analysis was carried out on the sequencing results of different initial amounts of library construction, and the Pearson correlation coefficient R 2 The closer to 1, the higher the similarity of RNA expression patterns. The correlations of sequencing results with different starting amounts for library construction were all above 0.97. Such as Figure 7 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com