High-spatial resolution photofilament fluorescence spectrum imaging and positioning method and system
A technology of fluorescence spectrum and positioning method, which is applied in spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, fluorescence/phosphorescence, radiation pyrometry, etc., which can solve the problem of monochromatic filament information and limited spatial resolution of filament imaging high-speed, high-spatial-resolution full-color filamentary spectral imaging and positioning, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
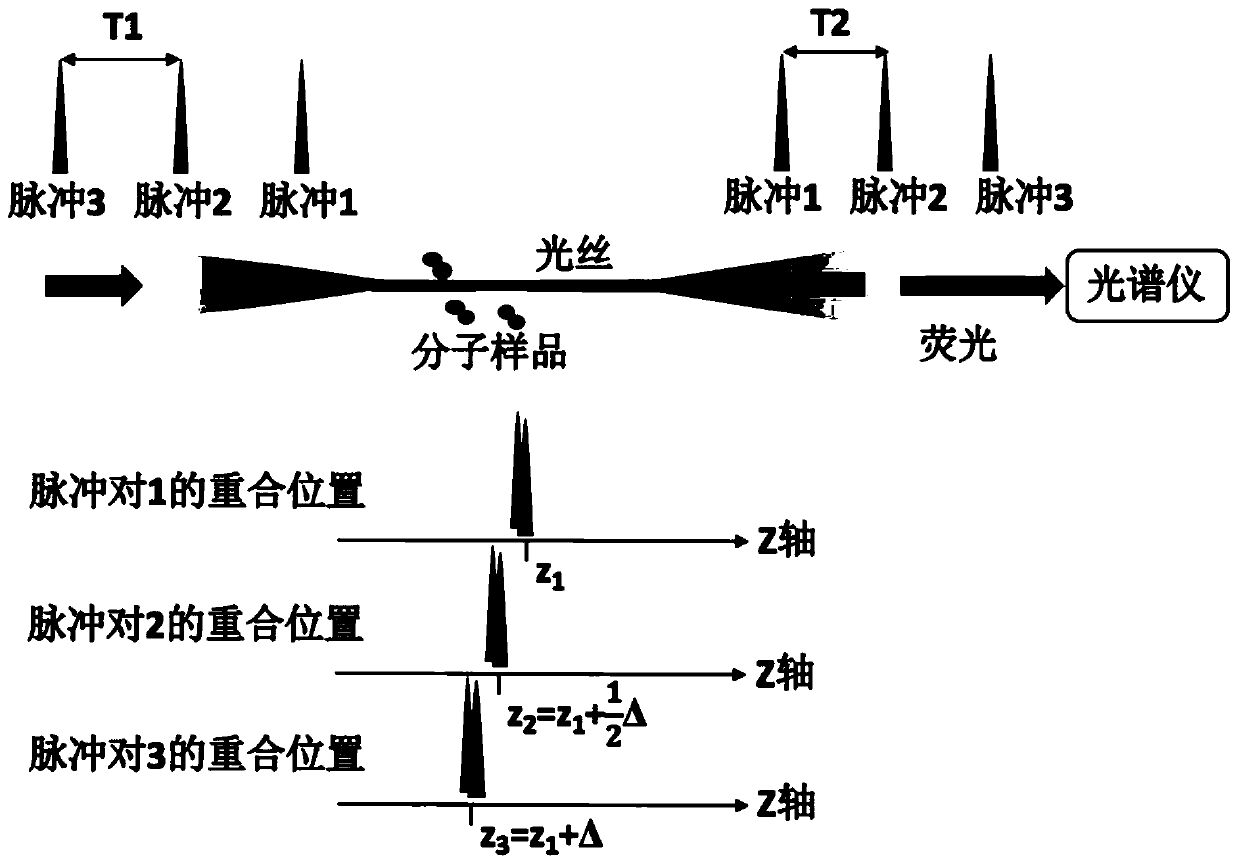
[0041] see figure 1 , using the above technology, the filament fluorescence spectrum imaging and positioning method of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0042]The method utilizes a group of two-color field asynchronous femtosecond pulses, which propagate collinearly and oppositely, and form a light filament in the medium (sample) after being focused by a lens. The two-color field pulses in the light filament interact nonlinearly at the coincident positions of time and space, and jointly excite the multiphoton absorption process of molecules, resulting in molecular fluorescence that can be measured by a spectrometer. Fluorescence is collected along the direction of propagation of one femtosecond light (i.e., the opposite direction of the other) and measured by a spectrometer. Since the femtosecond pulses propagating in opposite directions will meet at different positions of the light filament, the generated fluorescence has the position information of the light propagat...
Embodiment 2
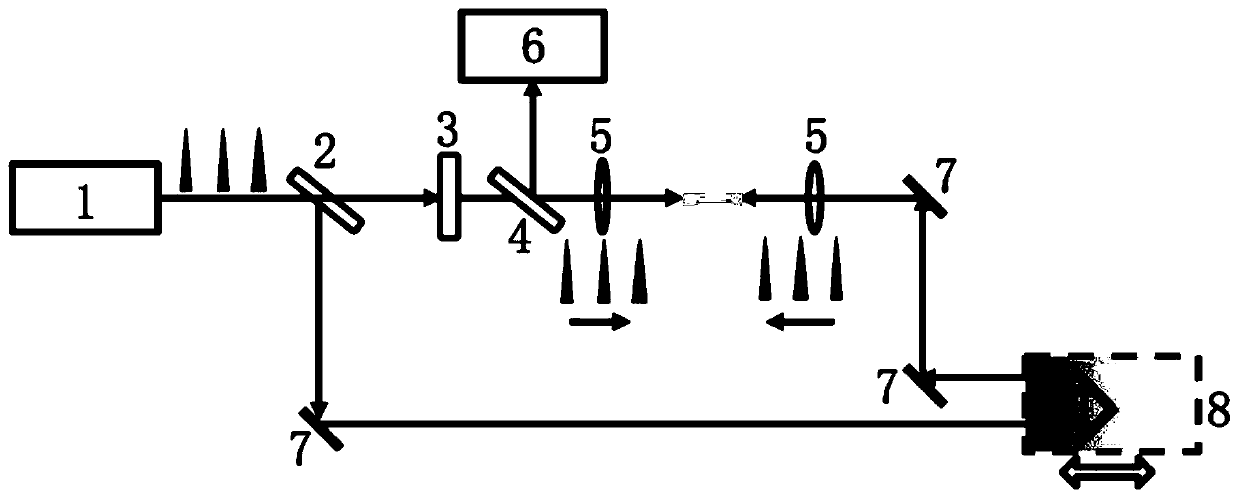
[0044] The above method can be implemented by using figure 2 In the system shown, a femtosecond pulsed laser 1 is used, and its laser parameters are as follows: output repetition frequency 1 kHz, pulse width 60 fs, center wavelength 800 nm, and single pulse energy 10 mJ. The near-infrared pulsed light is frequency-multiplied to generate ultraviolet (400nm) femtosecond pulses through a type I phase-matched frequency-doubling crystal. Femtosecond pulsed laser 1 outputs laser light through beam splitter 2 for beam splitting, in which the transmitted light passes through frequency doubling crystal 3 to obtain a beam in the 400nm band, and the reflected light part passes through mirror 7 and one-dimensional motor delay platform 8, and is then combined with frequency doubling Light travels collinearly. The two paths of light respectively pass through an ultraviolet fused silica plano-convex lens 5 with a focal length of f (=1000mm) to focus the light beams, and form light filament...
Embodiment 3
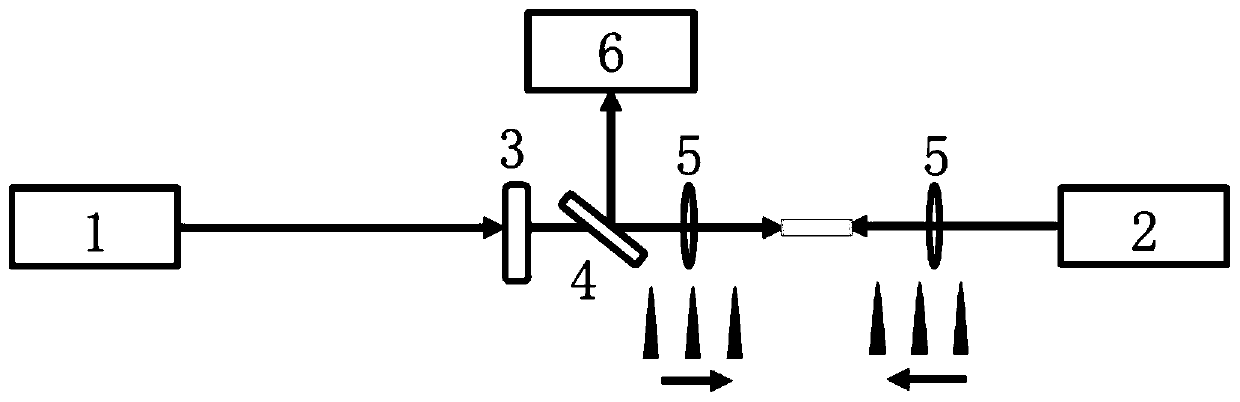
[0046] The above method can also be implemented by using image 3 In the system shown, the 800nm fundamental frequency light passing through the one-dimensional motor delay platform is replaced by another femtosecond pulsed laser 1'. This laser has the same spectral parameters as the first one, but a different repetition rate or repetition period. Using the same optical path design as in Example 2 for the rest, the spatial and spectral information of the light filament can be obtained by means of non-mechanical scanning, thereby realizing fluorescence positioning and spectral measurement.
[0047] Specifically, a femtosecond laser 1 outputs laser light through a frequency doubling crystal 3 to obtain ultraviolet femtosecond pulses; another femtosecond laser 1' outputs laser light, which propagates oppositely and collinearly with the frequency doubling light; the two paths of light respectively pass through a focal length of The ultraviolet fused silica plano-convex lens 5 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com