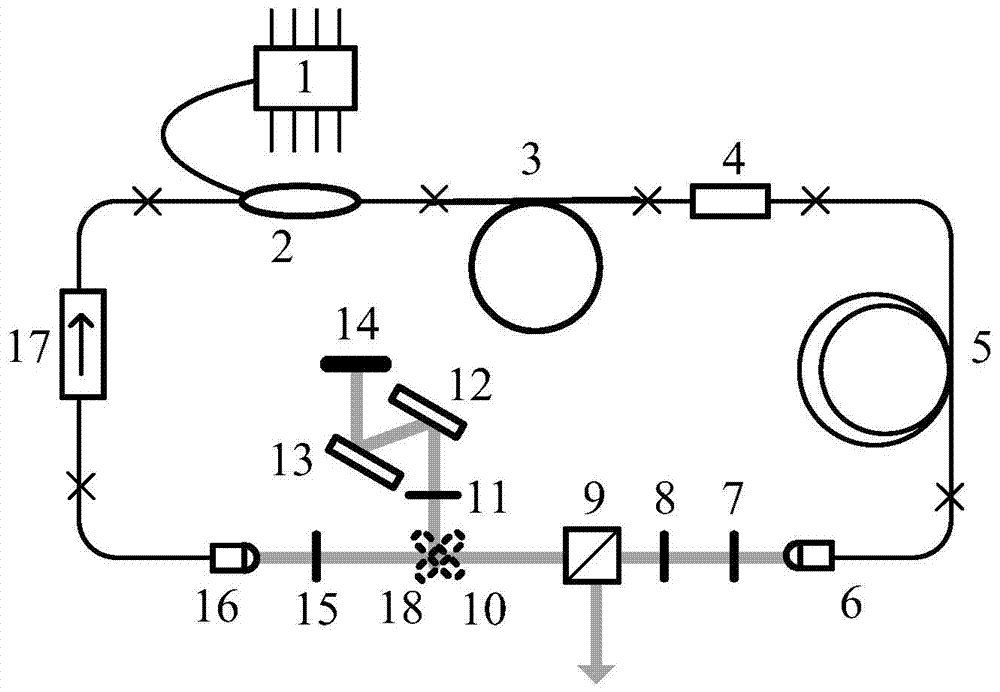
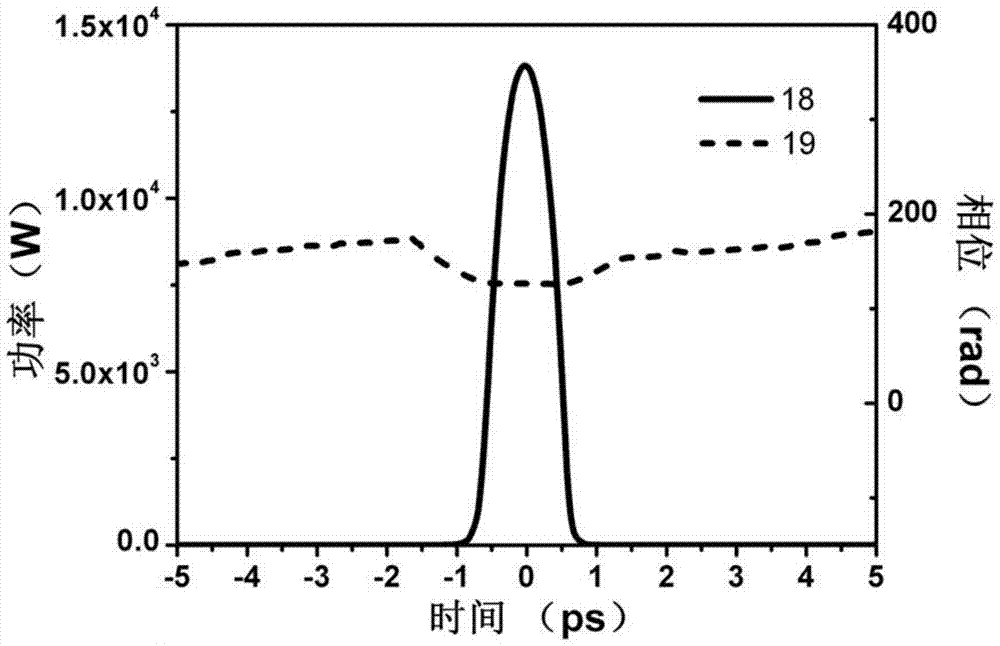
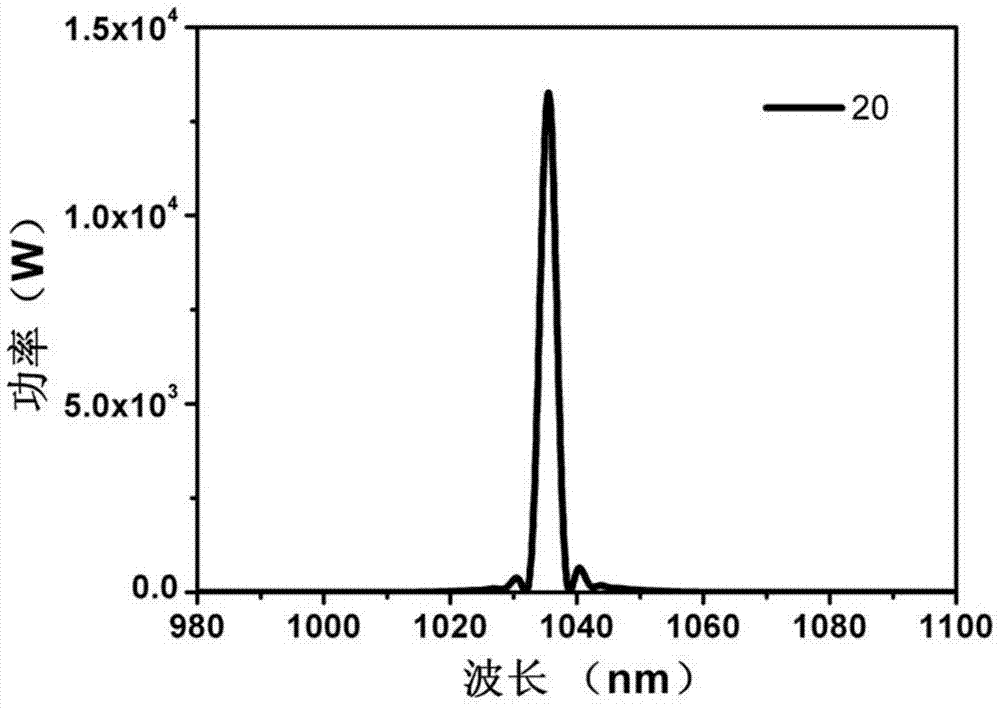
A self-similar mode-locked fiber femtosecond laser based on spectral compression and amplification
A femtosecond laser, self-similar technology, applied in the direction of lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the loss of fiber laser compactness and easy operation advantages, is not conducive to high-energy femtosecond laser pulse output, loss of cavity Internal pulse energy and other issues to achieve the effect of increasing spectral energy density, realizing nonlinear phase balance, and increasing pulse spectral broadening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0029]The femtosecond laser of the present invention utilizes the self-phase modulation effect induced positive frequency chirp during the amplification process of the negative chirped pulse in the positive dispersion gain fiber to balance the initial negative chirp, so that the pulse energy of the long and short wave parts of the negative chirped pulse is redistributed , continuously concentrated near the central wavelength, while amplifying the energy of the negatively chirped pulse, realize spectral nonlinear compression, form a narrow-band high peak power chirp-free picosecond pulse and then inject it into the single-mode fiber, using the self-phase of the single-mode fiber Modulation and positive group velocity dispersion complete self-similar evolution and spectral broadening, and directly output broadband linearly chirped parabol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com