Method for adsorbing radioactive iodine
A technology of radioactive iodine and adsorbent, applied in the direction of radioactive purification, separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as explosion and fire, and achieve the effect of maintaining fire resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
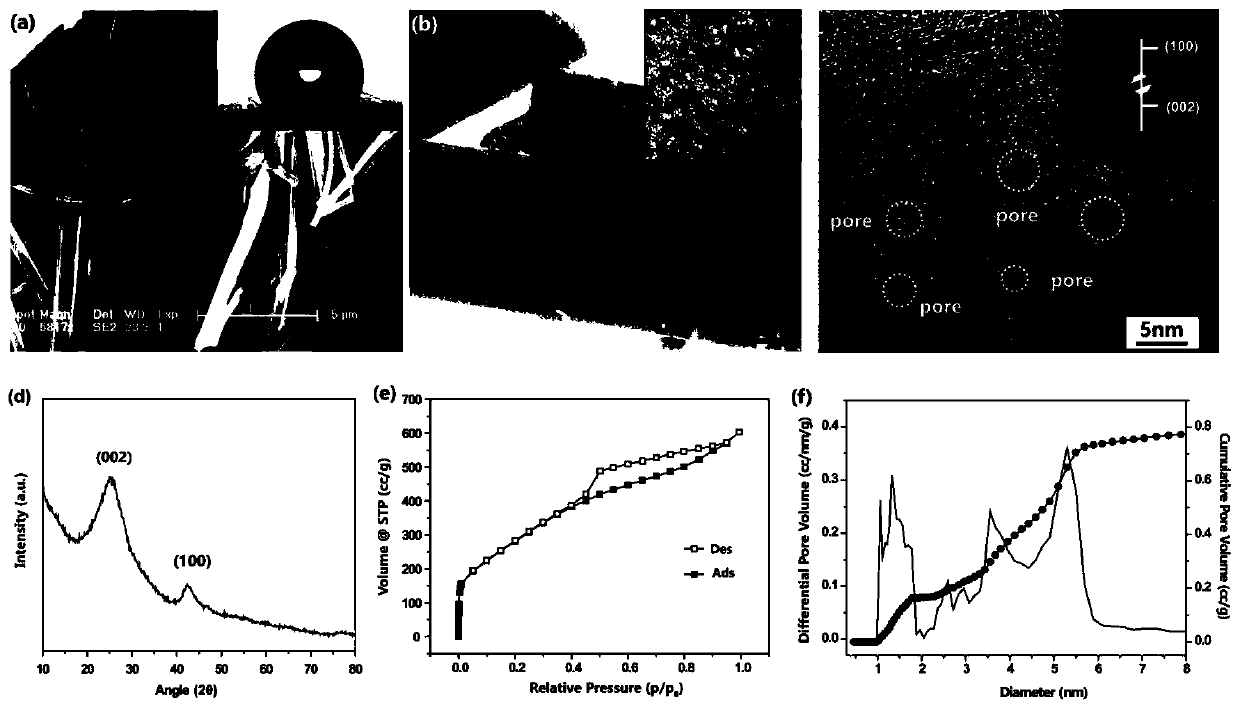
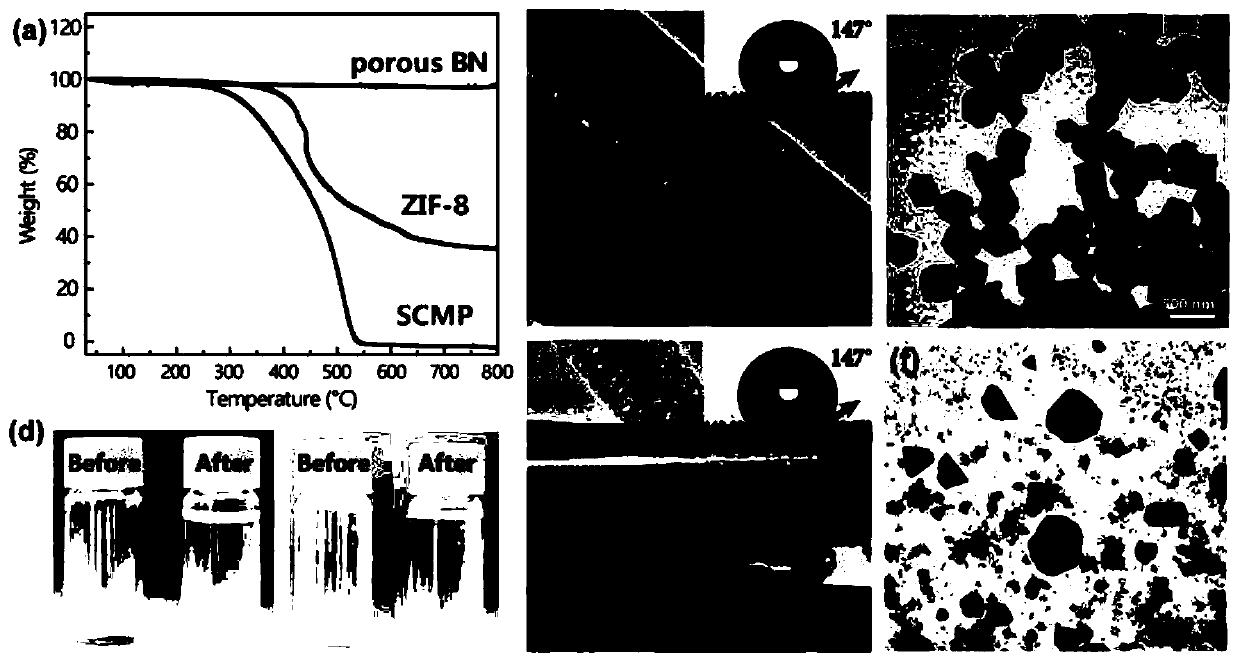
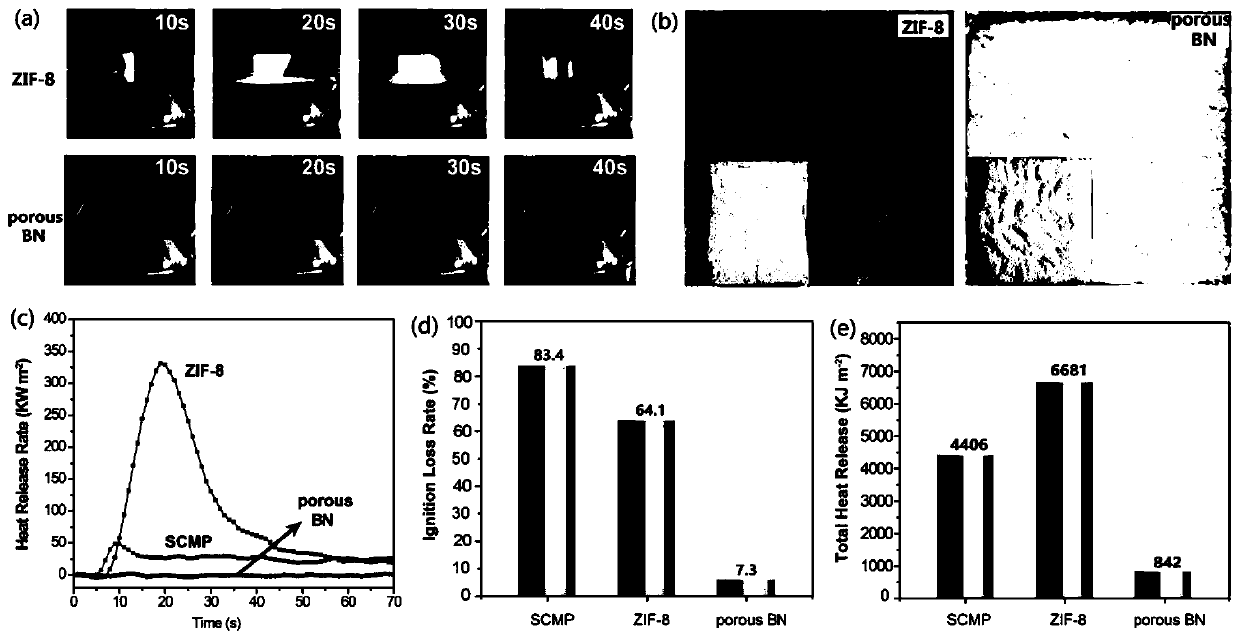
[0033] H 3 BO 3 (4g) and C 3 N 6 h 6 (4 g) was added to 200 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred to 85 °C for complete dissolution and stirring was continued for 6 hours, then cooled to ambient temperature to produce a white precipitate. After filtration, the precipitate was washed with cold deionized water and dried overnight to obtain the precursor. Transfer the precursor to a corundum tube. Porous boron nitride was subsequently produced by a multi-step pyrolysis process: the precursor was preheated at 550 °C for 2 h, then heated at 2 °C min -1 The rate was slowly heated to 1100°C and kept for 2 hours, and finally calcined at 1200°C for 4 hours. All reactions were carried out under the protection of argon.
Embodiment 2
[0035] H 3 BO 3 (4g) and C 3 N 6 h 6 (4 g) was added to 200 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred to 85 °C for complete dissolution and stirring was continued for 6 hours, then cooled to ambient temperature to produce a white precipitate. After filtration, the precipitate was washed with cold deionized water and dried overnight to obtain the precursor. Transfer the precursor to a corundum tube. Porous boron nitride was subsequently produced by a multi-step pyrolysis process: the precursor was preheated at 550 °C for 2 h, then heated at 2 °C min -1 The rate was slowly heated to 1100°C and kept for 2 hours, and finally calcined at 1250°C for 4 hours. All reactions were carried out under the protection of argon.
Embodiment 3
[0037] H 3 BO 3 (4g) and C 3 N 6 h 6 (4 g) was added to 200 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred to 85 °C for complete dissolution and stirring was continued for 6 hours, then cooled to ambient temperature to produce a white precipitate. After filtration, the precipitate was washed with cold deionized water and dried overnight to obtain the precursor. Transfer the precursor to a corundum tube. Porous boron nitride was subsequently produced by a multi-step pyrolysis process: the precursor was preheated at 550 °C for 2 h, then heated at 2 °C min -1 The rate was slowly heated to 1100°C and kept for 2 hours, and finally calcined at 1300°C for 4 hours. All reactions were carried out under the protection of argon.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com