Low-power-consumption waveguide optical detector of optical isolation between photosensitive table board and N contact table board
A technology of optical waveguide and optical isolation, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., to achieve the effect of alleviating the mutual constraints of bandwidth and quantum efficiency, high responsivity, and high RF output power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described clearly and in detail below with reference to the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. The described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the invention.
[0018] The technical scheme of the present invention to solve the above-mentioned technical problems is: a monolithic integrated low-power waveguide photodetector structure is proposed, which solves the mutual restriction problem between the quantum efficiency and frequency response bandwidth of traditional semiconductor photodetectors, and can be widely used In optical fiber communication, satellite communication and optical signal processing and other fields.
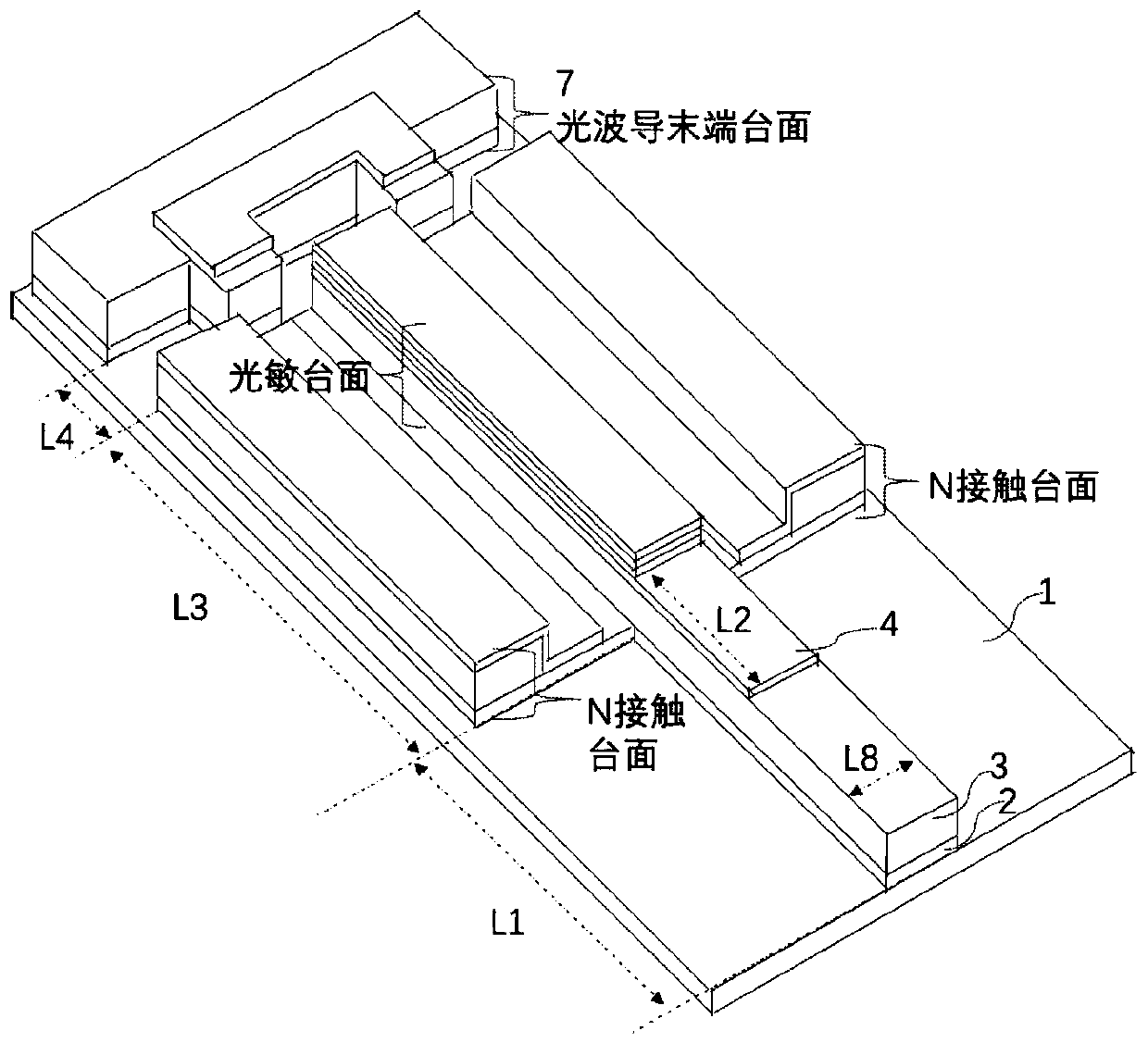
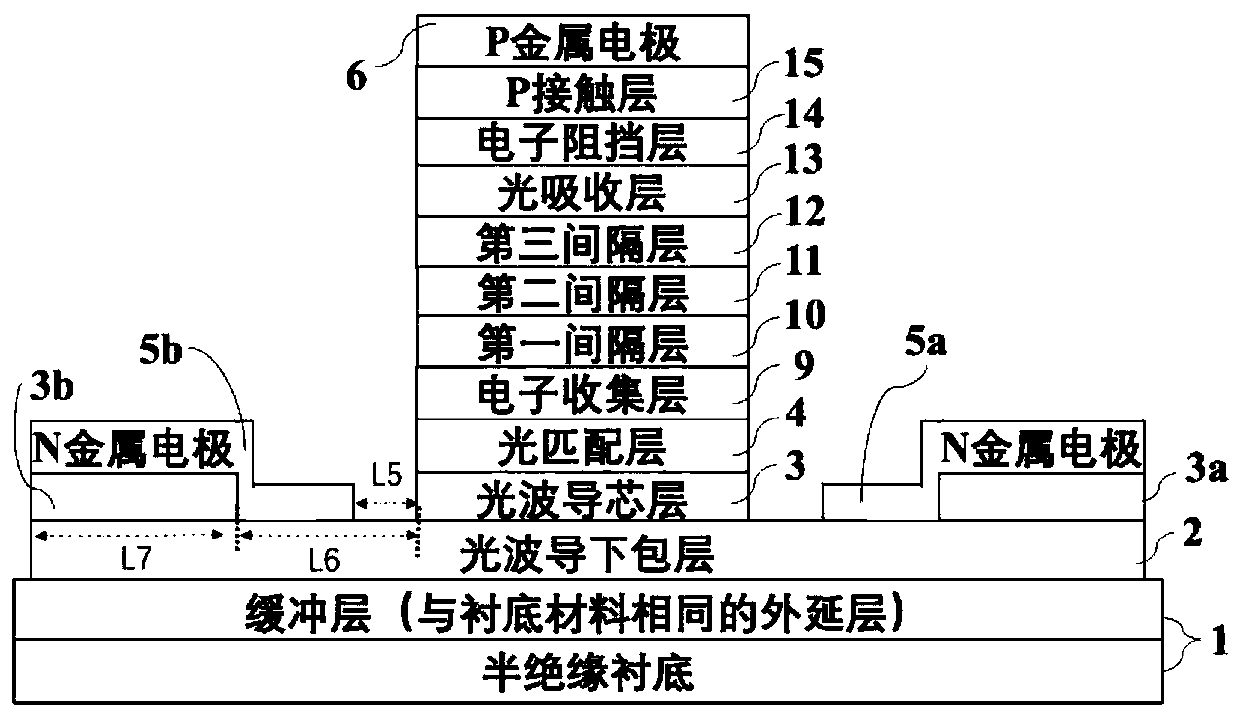
[0019] see figure 1 The three-dimensional schematic diagram of the device and figure 2The schematic diagram of the cross-section of the active region perpendicular to the light incident direction is shown. As a specific embodiment, the low-powe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com