Monopole antenna array source for semiconductor process equipment
A monopole antenna and antenna array technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, resonant antenna, and slender active unit end feeding, etc., can solve the problem that the microwave source cannot meet strict uniformity, and achieve good temperature Effects of controlling, improving processing speed, and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
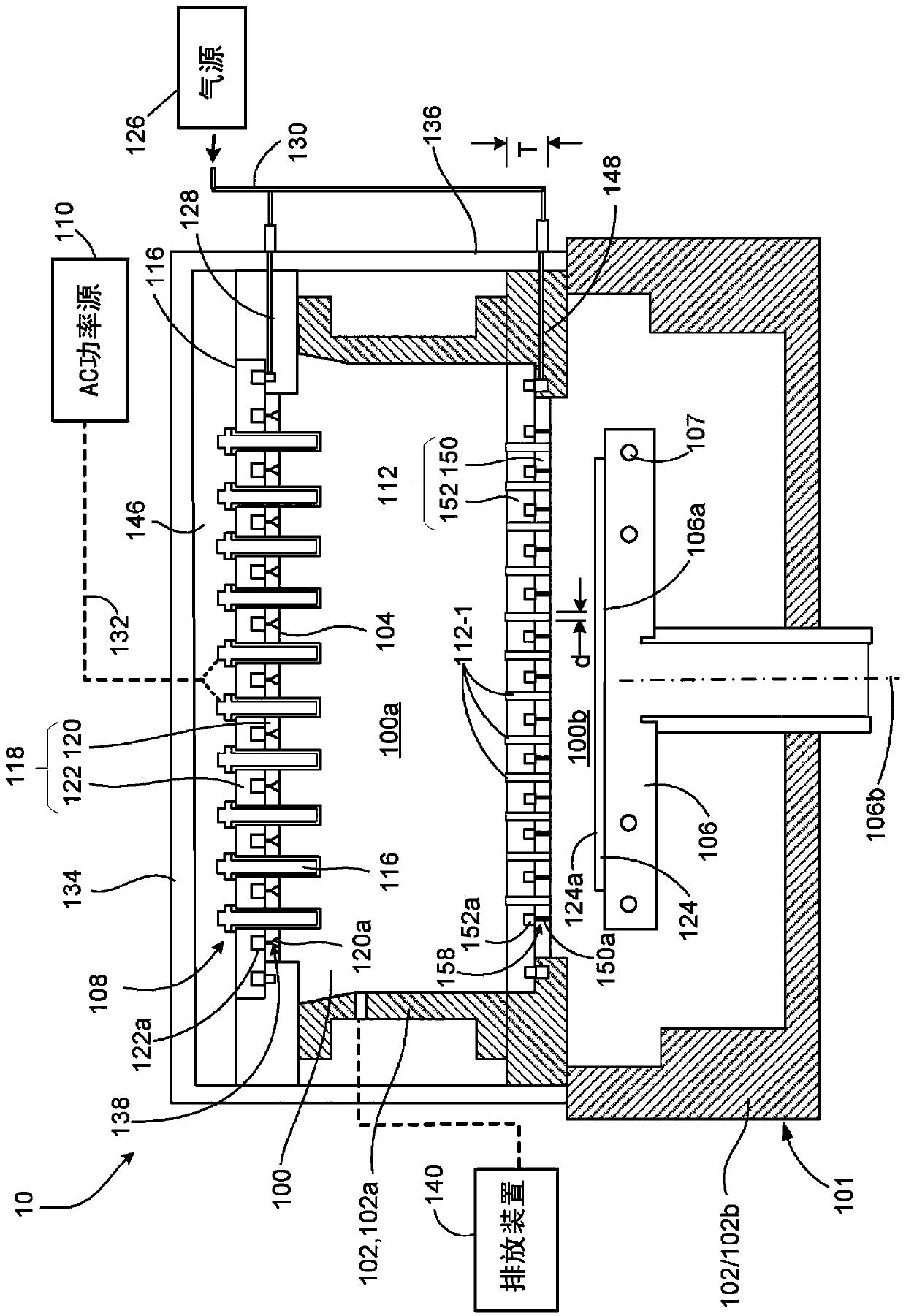
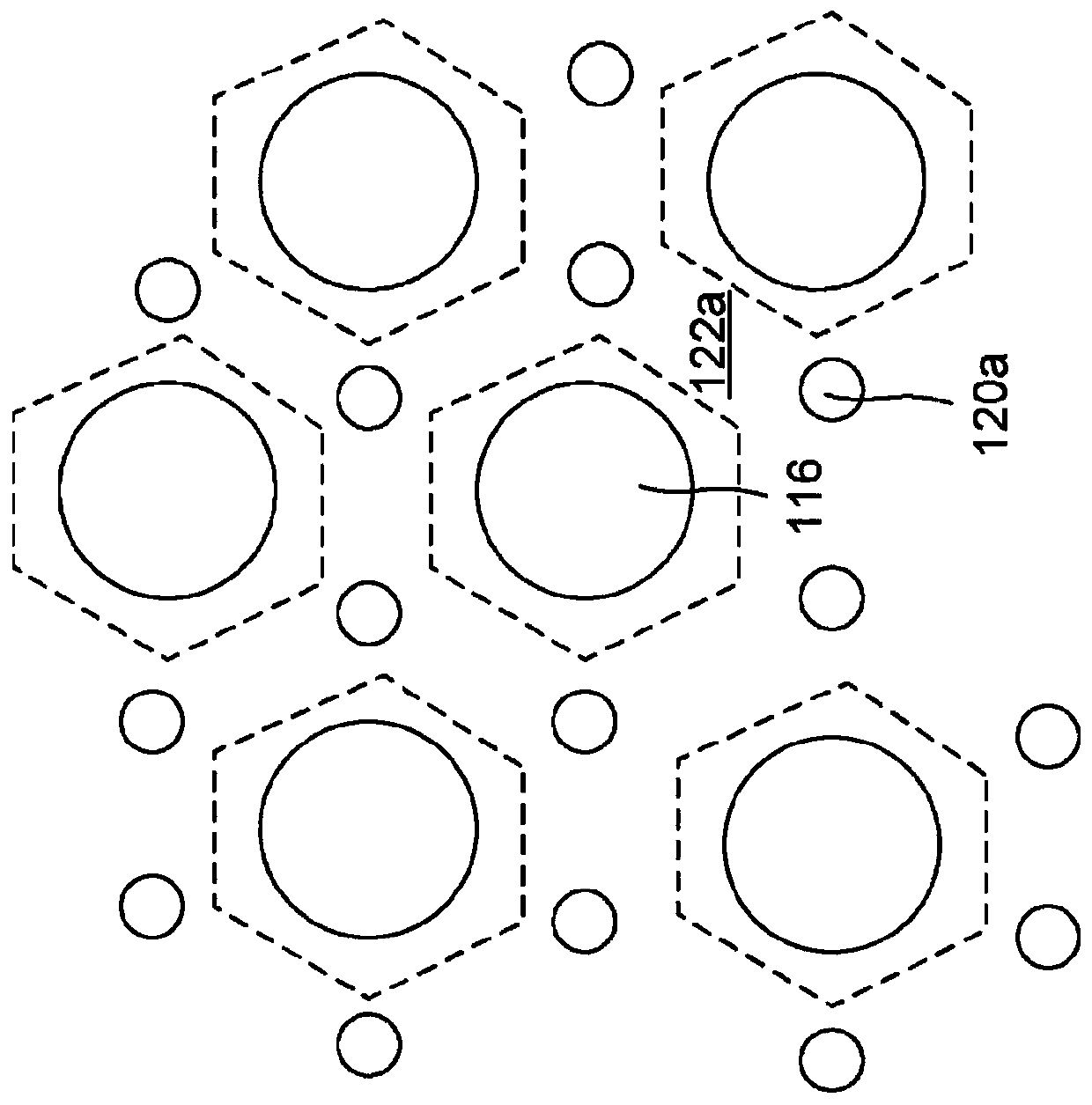
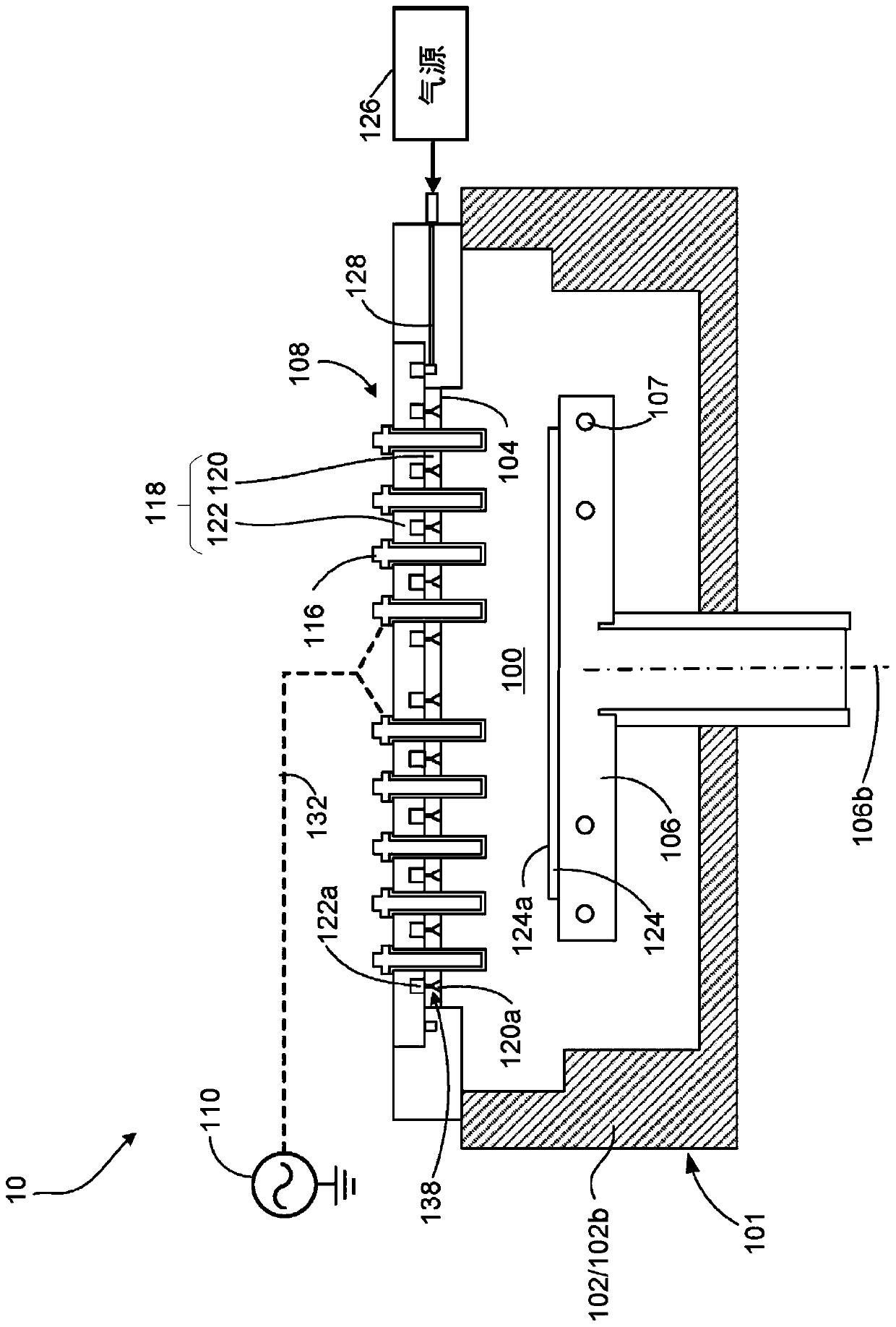
[0042] Processing of workpieces, such as semiconductor wafers, may be performed in plasma reactors. For example, electromagnetic energy such as RF power or microwave (MW) power can be employed to generate a plasma in a chamber to perform plasma-based processing such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) or plasma Volume Enhanced Reactive Ion Etching (PERIE)). Some processes, such as the deposition of diamond-like carbon (DLC) films, require high plasma ion densities and low plasma ion energies. Higher plasma densities require higher source powers and generally result in shorter deposition times.
[0043] The advantage of microwave sources is that they can produce very high plasma ion densities with less plasma ion energy than other sources (e.g., inductively coupled RF plasma sources or capacitively coupled RF plasma sources). plasma source). Another advantage of microwave plasma sources is the ability to generate plasma over a wide range of chamber pressures...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com