Radix astragali-penicillium cicada fermentation bacterium and application thereof
A technology of Paecilomyces cicadae and fermenting bacteria, applied in the field of traditional Chinese medicine fermentation mycoplasma, can solve problems such as no reports on the pharmacological activity of Astragalus-Paecilomyces cicadae fermentative mycoplasma, etc., and achieves the treatment of hyperuricemia and/or hyperuricemia. Triglyceridemia, the effect of increasing polysaccharide content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035]The medicinal materials of Astragalus are pulverized and passed through an 8-mesh sieve to obtain the medicinal powder of Astragalus. The medicinal powder of astragalus and distilled water are uniformly mixed in a weight ratio of 2.5:1, placed in a 90° C. steam sterilizer for sterilization for 60 minutes, and cooled to room temperature to obtain an astragalus solid medium. Paecilomyces cicadae was evenly inoculated into the solid medium of Astragalus, and the inoculation amount was 10wt% of the medicinal materials of Astragalus, and cultured at constant temperature and humidity for 24 days under the conditions of a culture temperature of 26°C and a relative humidity of 80% to obtain Astragalus-Paecilomyces cicadae fermentation. Mycoplasma A (hereinafter referred to as "mycoplasma A").
Embodiment 2
[0037] The medicinal materials of Astragalus are pulverized and passed through an 8-mesh sieve to obtain the medicinal powder of Astragalus. The medicinal powder of astragalus and distilled water are uniformly mixed in a weight ratio of 2.5:1, placed in a 90° C. steam sterilizer for sterilization for 60 minutes, and cooled to room temperature to obtain an astragalus solid medium. Paecilomyces cicadae was evenly inoculated into the solid medium of Astragalus, and the inoculation amount was 10 wt% of the medicinal material of Astragalus; the seed liquid of Paecilomyces cicadae was evenly inoculated into the solid medium of Astragalus, and the inoculation amount was 4 wt% of the medicinal material of Astragalus, Under the conditions of a culture temperature of 26° C. and a relative humidity of 80%, cultured at constant temperature and humidity for 24 days to obtain Astragalus-Paecilomyces cicadae fermentation mycoplasma B (hereinafter referred to as “mycoplasma B”).
experiment example 1
[0046] Experimental example 1 Determination of bacterial growth consumption rate
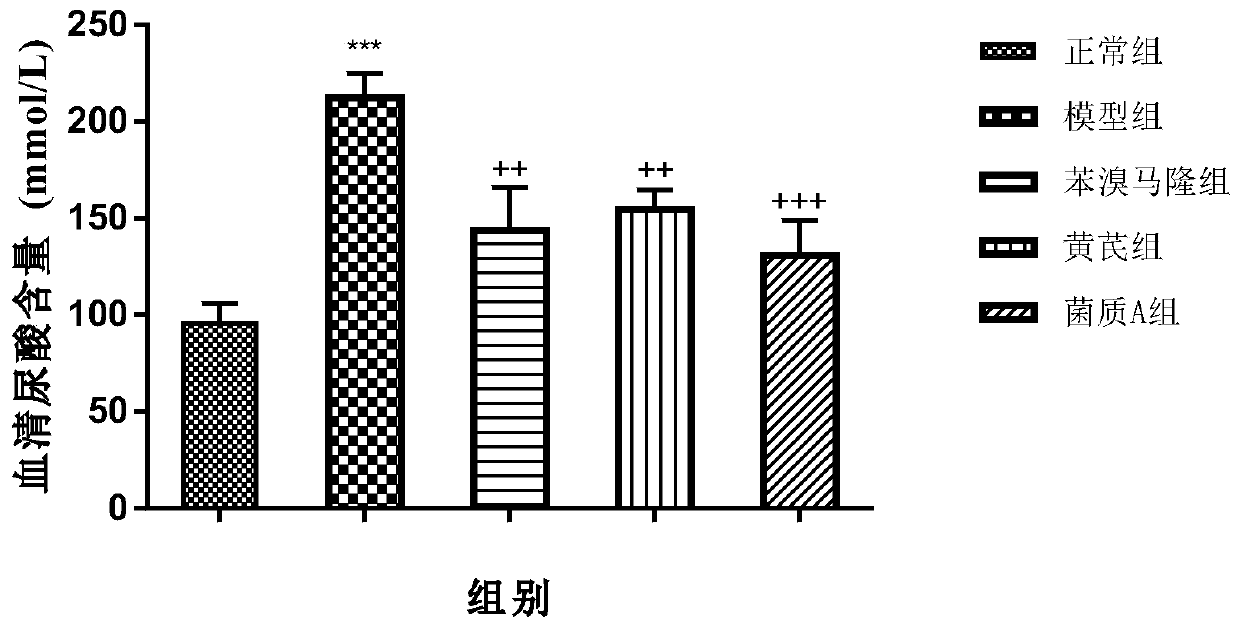
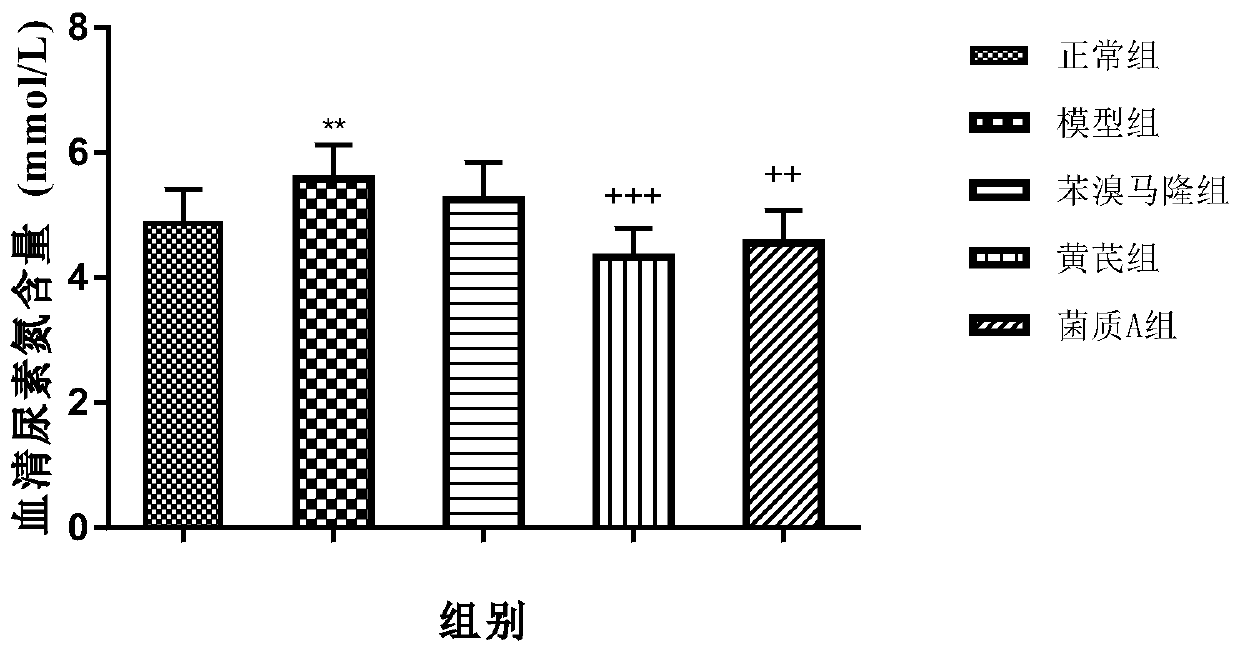
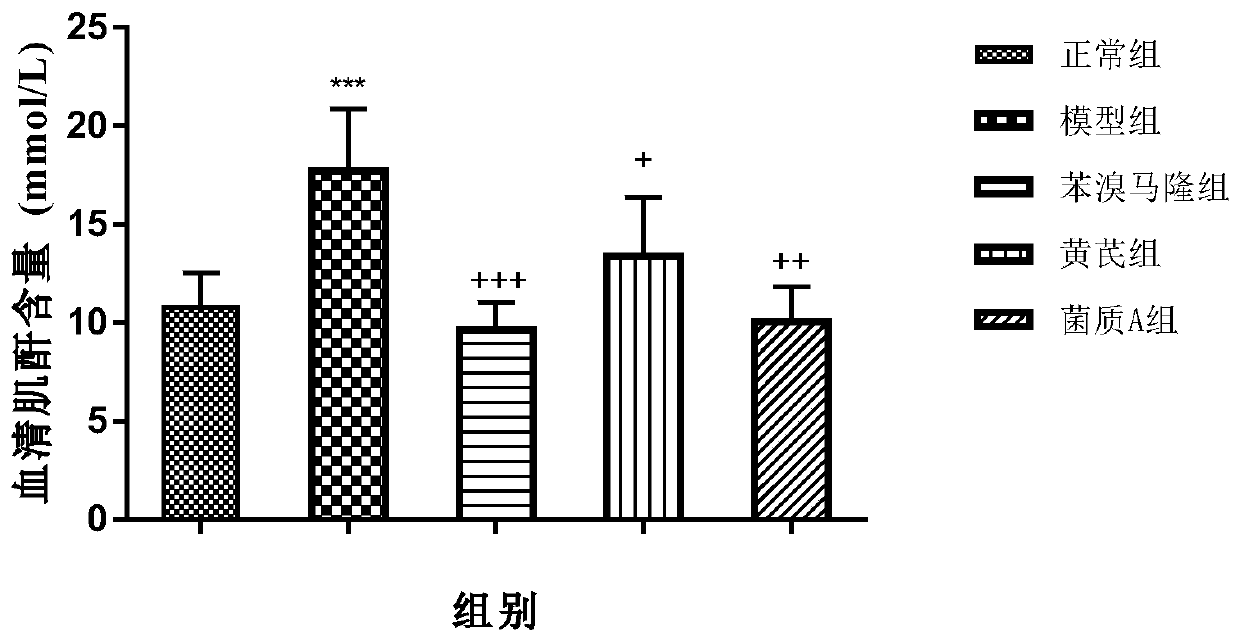
[0047] Astragalus - Paecilomyces cicadae fermentation mycelium A to E were all sampled on the 24th day of fermentation, the bottom and surface of the fermentation substrate were covered with dense mycelium, the wet weight of the mycelium was measured, and the mycelium was washed three times with distilled water, and then placed Dry in a 60°C oven to constant weight, weigh, calculate the weight change before and after fermentation, and calculate the consumption rate. The higher the consumption rate, the better the culture conditions are for mycelial growth.
[0048] Consumption rate = (the weight of the original medicinal material - the weight of the fungus after drying and fermentation) / the weight of the original medicinal material × 100%.
[0049] The results are shown in Table 1.
[0050] Table 1
[0051]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com