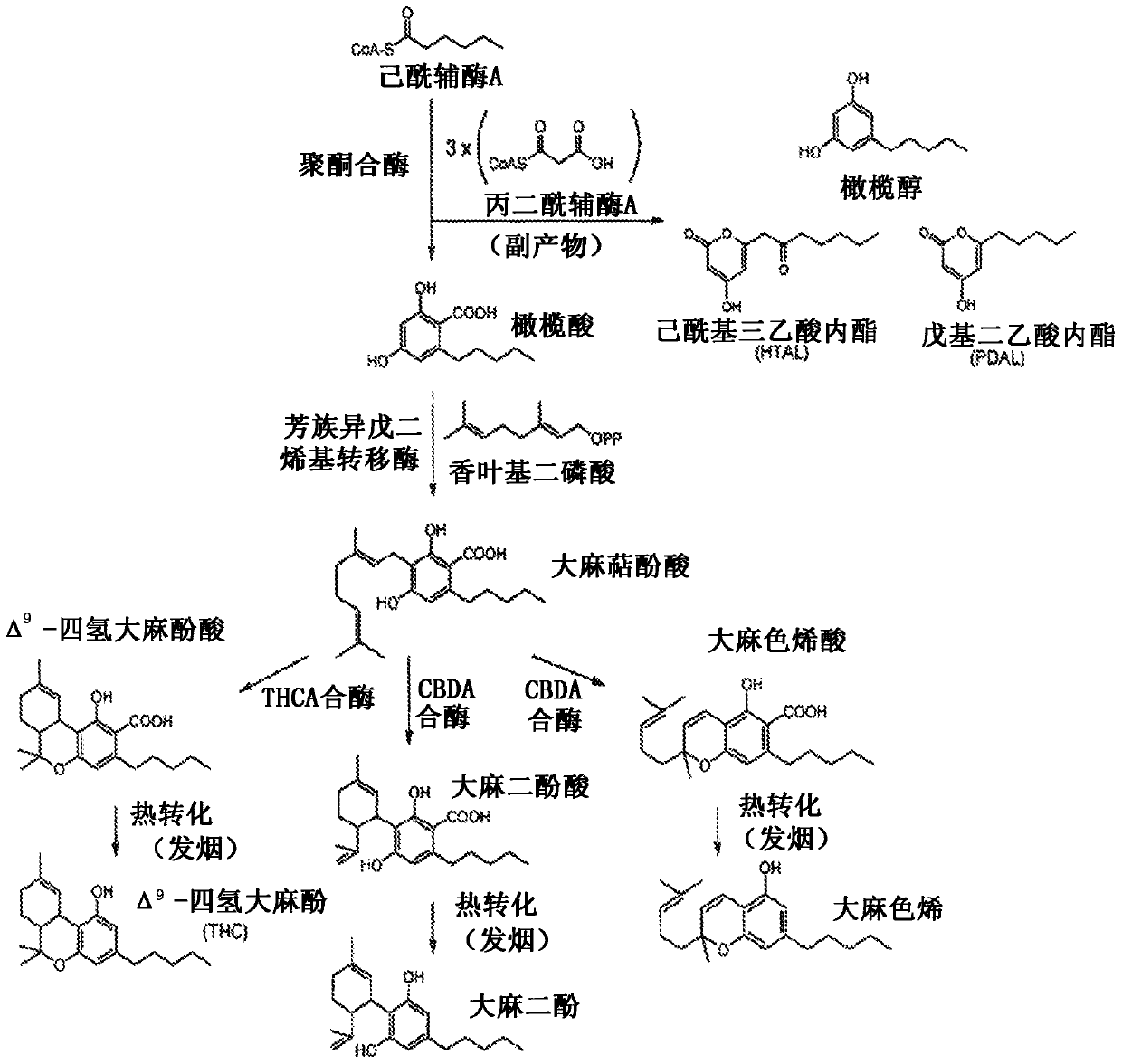
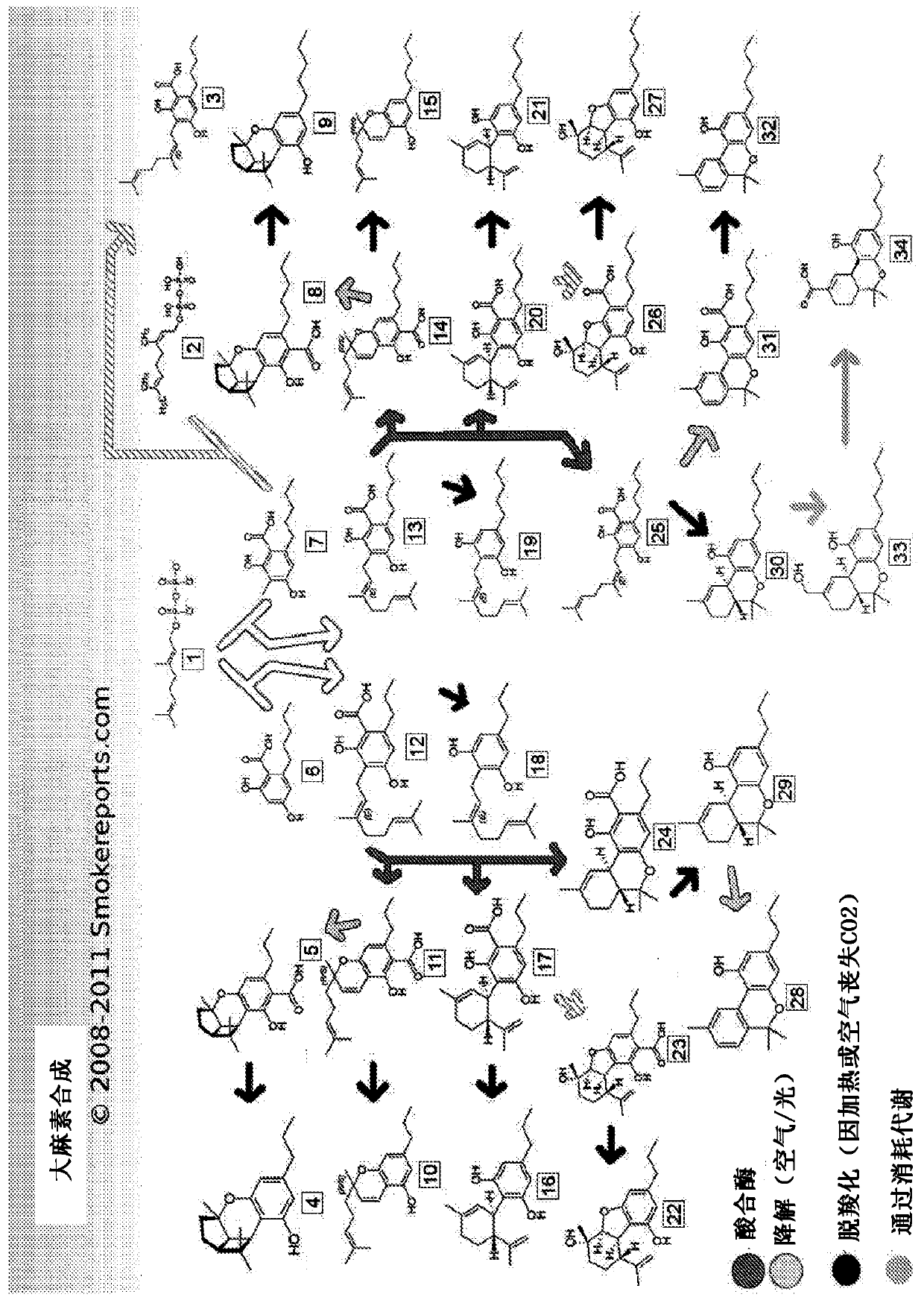
Production of cannabinoids in yeast
A technology of cannabinoids and yeast, applied in the direction of enzymes, fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of mixture purification, cannabinoid pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0261] Example 1: Vector Construction and Transformation
[0262] The Yarrowia lipolytica episomal plasmid contains a centromere, an origin, and a bacterial replicative backbone. Fragments of these regions were synthesized by TwistBioscience and cloned to make the episomal parental vector pBM-pa. Plasmids were constructed by Gibson assembly, Golden gate assembly, ligation or sequence and ligation independent cloning (SLIC). Genomic DNA was isolated from bacteria (E. coli) and yeast (Yarrowia lipolytica) using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit according to the manufacturer's protocol (Promega, USA). Synthetic genes were codon-optimized using GeneGenie or Genscript (USA) and assembled from gene fragments purchased from TwistBioscience. All engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strains were constructed by transformation of the corresponding plasmids. All gene expression cassettes were constructed using the TEF intronic promoter and a synthetic short terminator. Cloning of up t...
Embodiment 2
[0264] Embodiment 2: yeast culture condition
[0265] E. coli DH10B strain was used for cloning and plasmid propagation. DH10B were grown at 37°C with constant shaking in Luria-Bertani broth supplemented with 100 mg / L ampicillin for plasmid propagation. Yarrowia lipolytica strain W29 was used as the base strain for all experiments. Yarrowia lipolytica was cultured at 30°C under constant agitation. Yarrowia lipolytica cultures (2 ml) used in large-scale screens were grown in a shaking incubator at 250 rpm for 1 to 3 days, then larger culture volumes were shaken in 50 ml flasks or in bioreactors fermentation.
[0266] For colony selection and cell proliferation, Yarrowia lipolytica was grown on YPD liquid medium containing 10 g / L yeast extract, 20 g / L peptone and 20 g / L glucose or on YPD agar plates supplemented with 20 g / L agar. The medium is usually supplemented with 150 to 300 mg / L hygromycin B or 250 to 500 mg / L nourstacin as appropriate for selection. For cannabinoid-p...
Embodiment 3
[0267] Example 3: Cannabinoid Isolation
[0268] Yarrowia lipolytica cultures from shake flask experiments or bioreactors were pelleted and homogenized in acetonitrile followed by incubation on ice for 15 minutes. After centrifugation (13000 g, 4° C., 20 minutes), the supernatant was filtered (0.45 μm, Nylon) and analyzed by HPLC-DAD. The quantification of the product is based on the integrated peak area of the UV chromatogram at 225nm. Standard curves were generated for CBGA and THCA. The identity of all compounds can be confirmed by Brukercompact using positive ionization mode TM Mass spectra and tandem mass spectra of each sample analyzed by ESI-Q-TOF were compared with co-eluting standards.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com